Embed presentation
Download to read offline

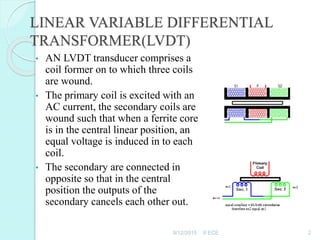

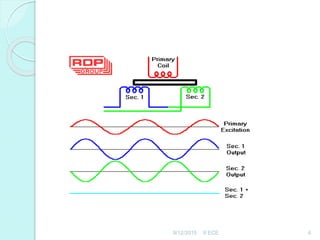


An LVDT transducer comprises three coils wound onto a coil former, with a ferrite core positioned in the center. When the core is centered, it induces equal voltages in the secondary coils which cancel each other out, resulting in a null output voltage. If the core moves from the center position towards one secondary coil, it increases the flux in that coil and decreases the other, producing a positive or negative output voltage depending on the direction of displacement. The LVDT output voltage is thus proportional to the displacement of the ferrite core from its centered null position.





