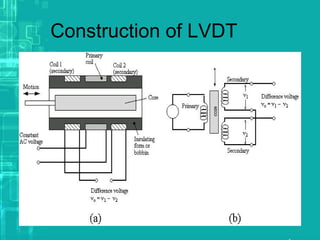
The document discusses the Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT). It describes the principle of operation, construction, working, advantages, disadvantages and applications. Specifically:
- LVDT works on the principle of mutual induction to convert linear displacement into an electrical signal. It consists of a primary coil surrounded by two secondary coils, with an iron core that can move within.
- As the core moves, it induces different voltages in the secondary coils, with the output being the difference between these voltages. This allows precise measurement of the core's position.
- LVDTs provide high resolution, output, sensitivity and linearity. However, they require shielding and can be affected by vibration and temperature changes.

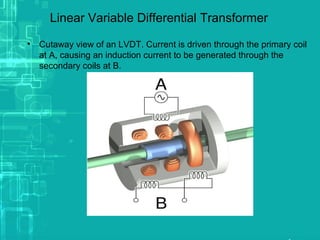
![Principle of LVDT
• The linear variable differential transformer(LVDT) (also
called linear variable displacement transformer,[1] linear
variable displacement transducer, [2] or
simply differential transformer[3]) is a type of
electrical transformer used for measuring linear
displacement (position).
• LVDT works under the principle of mutual induction, and
the displacement which is a non-electrical energy is
converted into an electrical energy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lvdtppt-171126055757/85/LVDT-3-320.jpg)