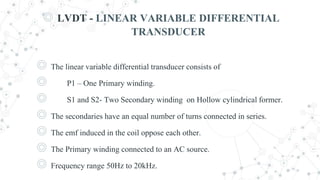
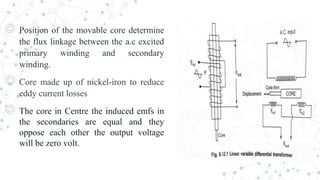
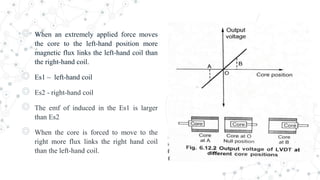
An LVDT consists of a primary winding, two secondary windings on a hollow cylindrical former, and a movable core. The secondary windings have an equal number of turns connected in series to oppose each other's induced EMFs. The position of the core determines the flux linkage between the AC-excited primary and secondary windings. When the core moves from the center, more flux links one secondary coil than the other, producing an output voltage proportional to the direction and amount of core movement. The LVDT's output voltage varies linearly with core position within its range of motion.