Embed presentation
Downloaded 38 times


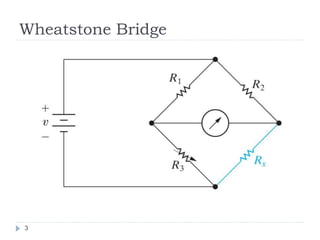
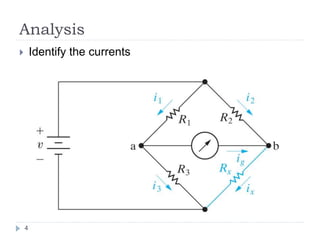

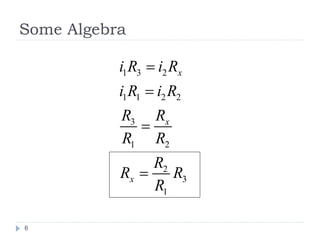
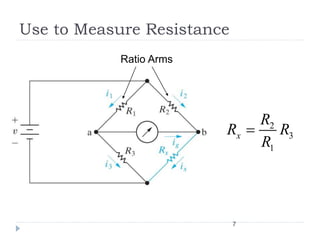




The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit invented in 1833 by Samuel Hunter Christie to measure an unknown electrical resistance. It uses a galvanometer to monitor a balanced state where no current flows through the galvanometer (ig=0). By adjusting variable resistors to reach this balanced state, the mathematical ratio of the arms can be used to calculate the fourth unknown resistance. The Wheatstone bridge found many applications in measuring strain, locating breaks in power lines, and indirectly measuring other variables that impact electrical resistance, such as temperature, force, and pressure.










