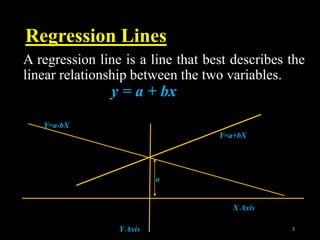
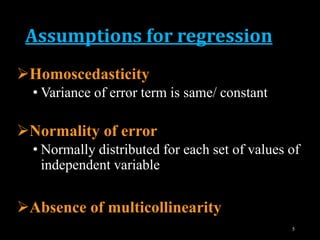
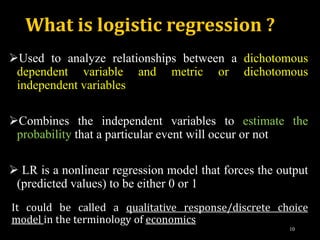
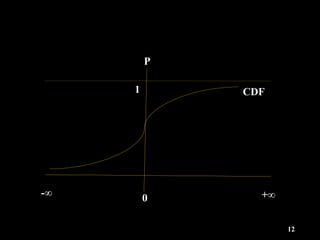
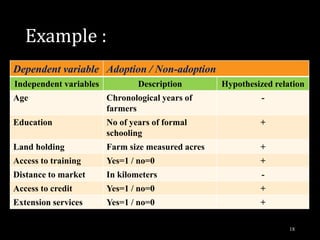
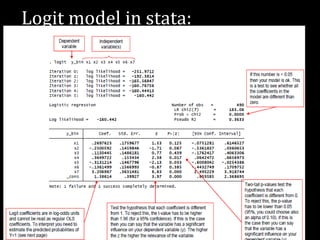
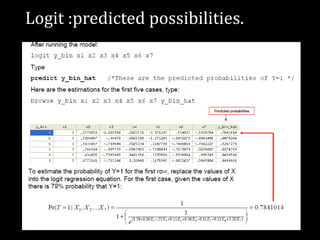
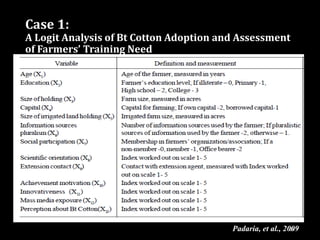
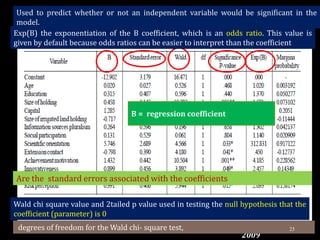
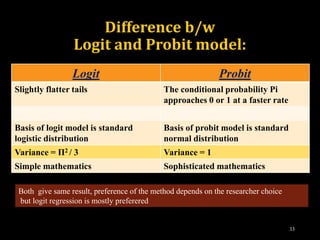
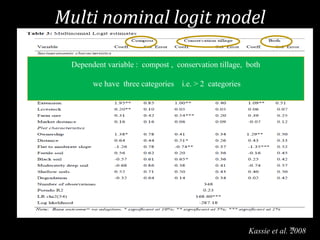
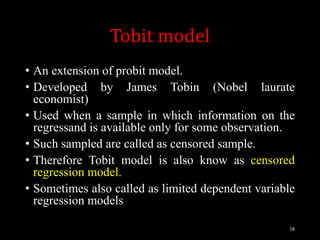
This document provides an overview of regression analysis and different types of regression models used when the dependent variable is dichotomous (can only take two values, such as 0 and 1). It defines regression analysis and discusses linear regression assumptions. It then introduces logistic regression, probit regression, and tobit regression as alternatives to linear regression when the dependent variable is dichotomous. The key differences between these models and their applications are summarized.