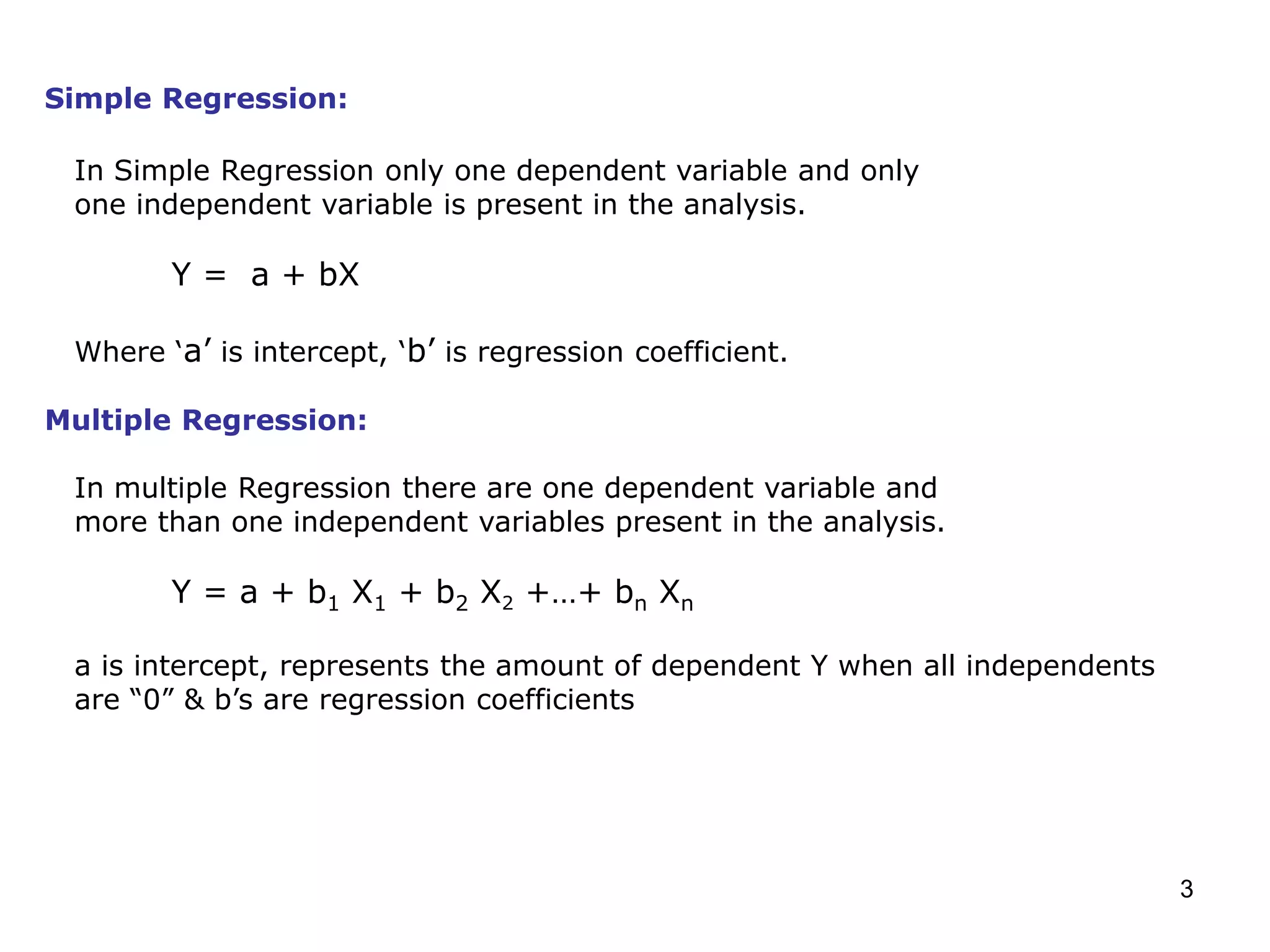
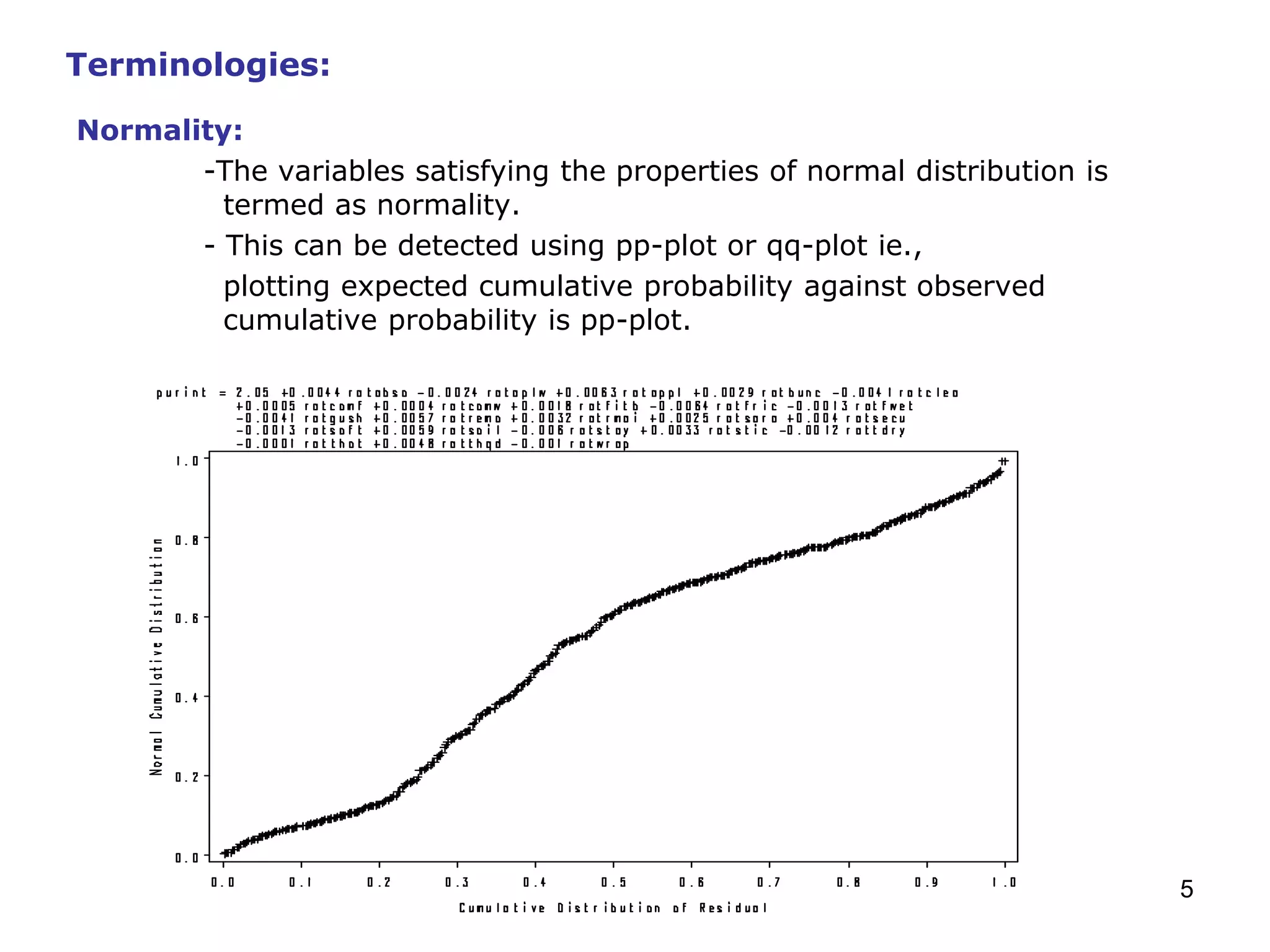
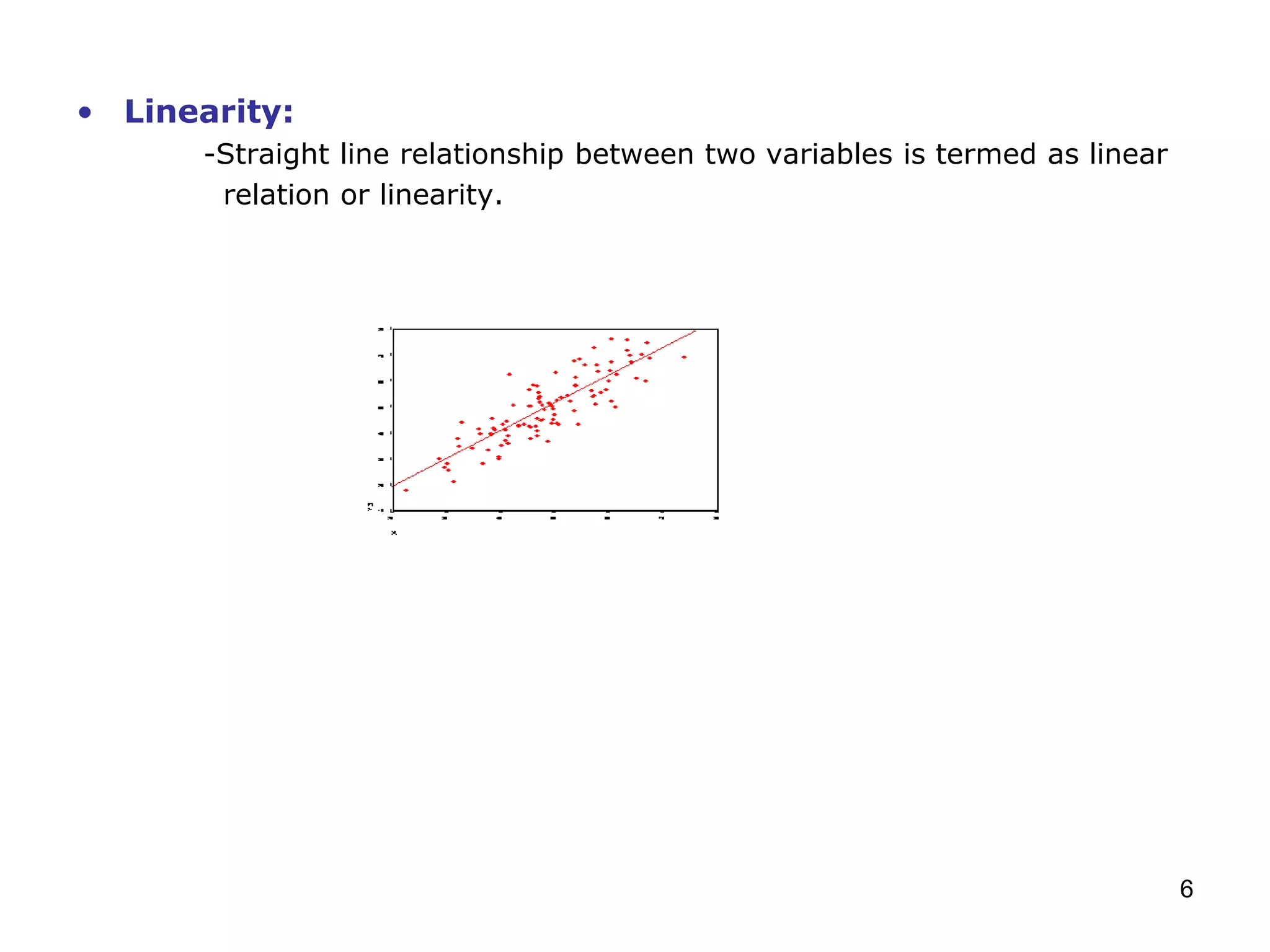
This document provides an overview of regression analysis, including simple and multiple regression models. Simple regression involves one dependent and one independent variable, while multiple regression has one dependent variable and more than one independent variable. Regression is used to identify factors that influence metrics like brand preference, demand, and sales. Key aspects discussed include assumptions of linearity, normality, absence of outliers and multicollinearity. Metrics like R-square, adjusted R-square, residuals, and variance inflation factor (VIF) are defined.