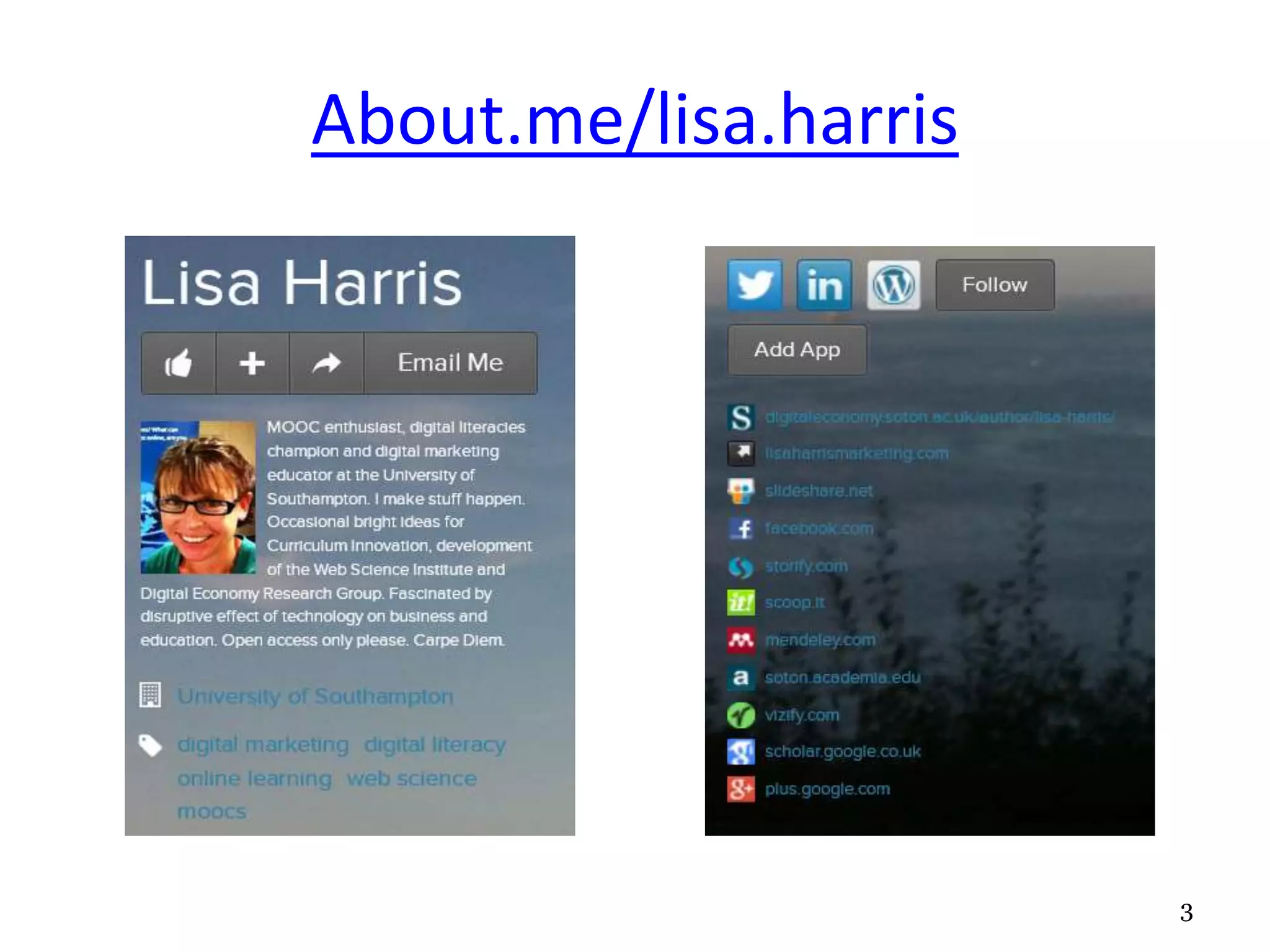
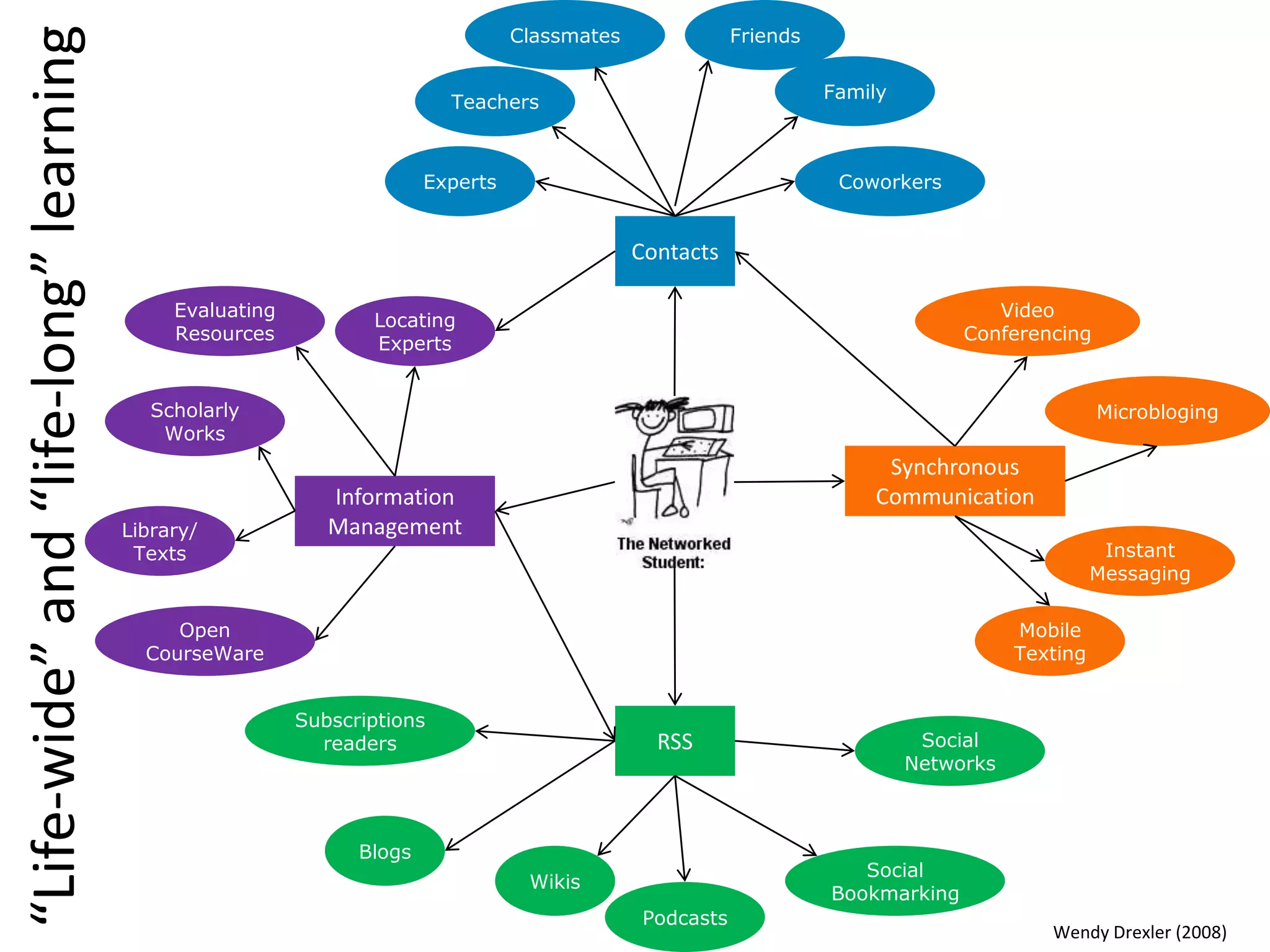
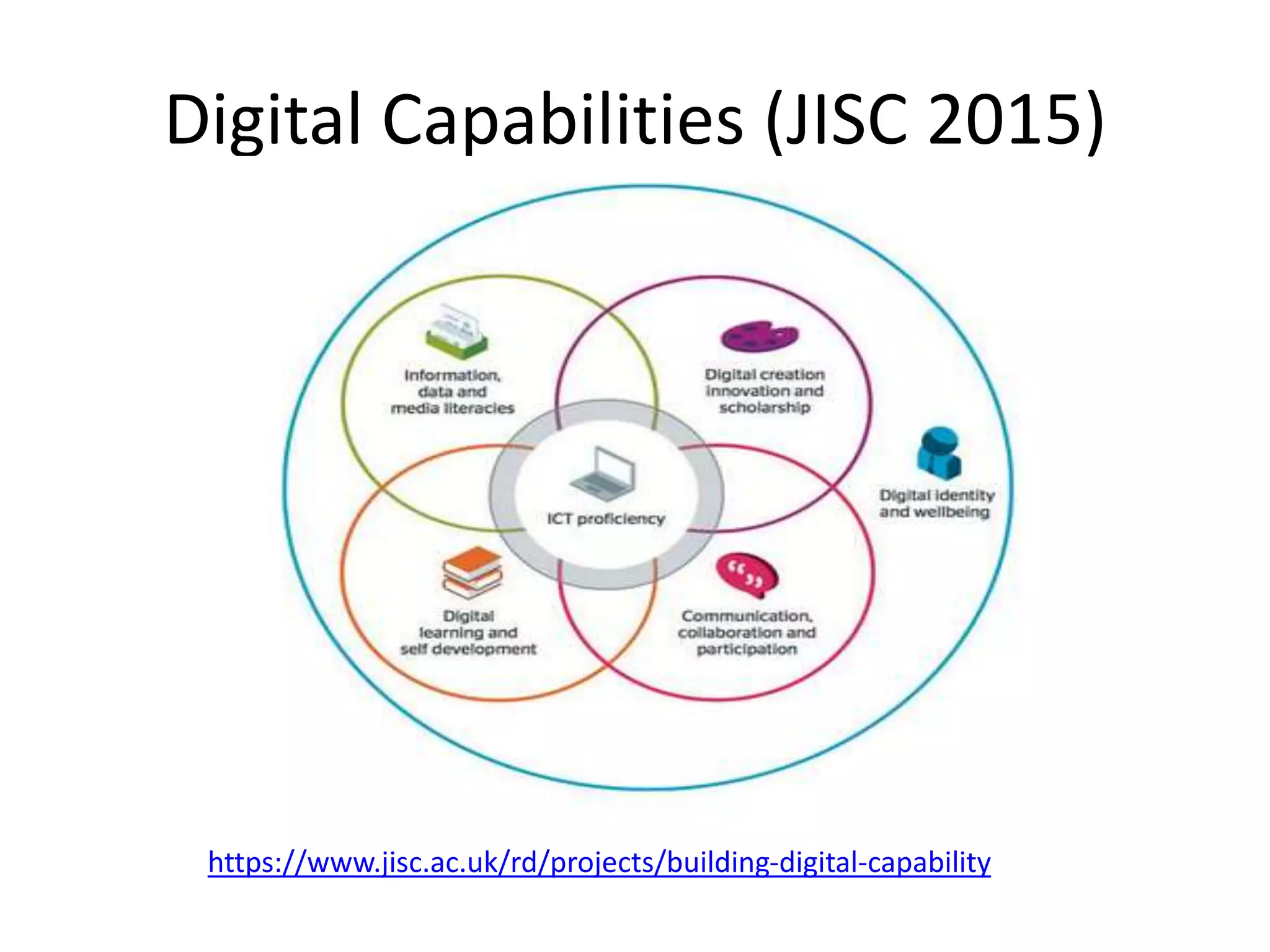
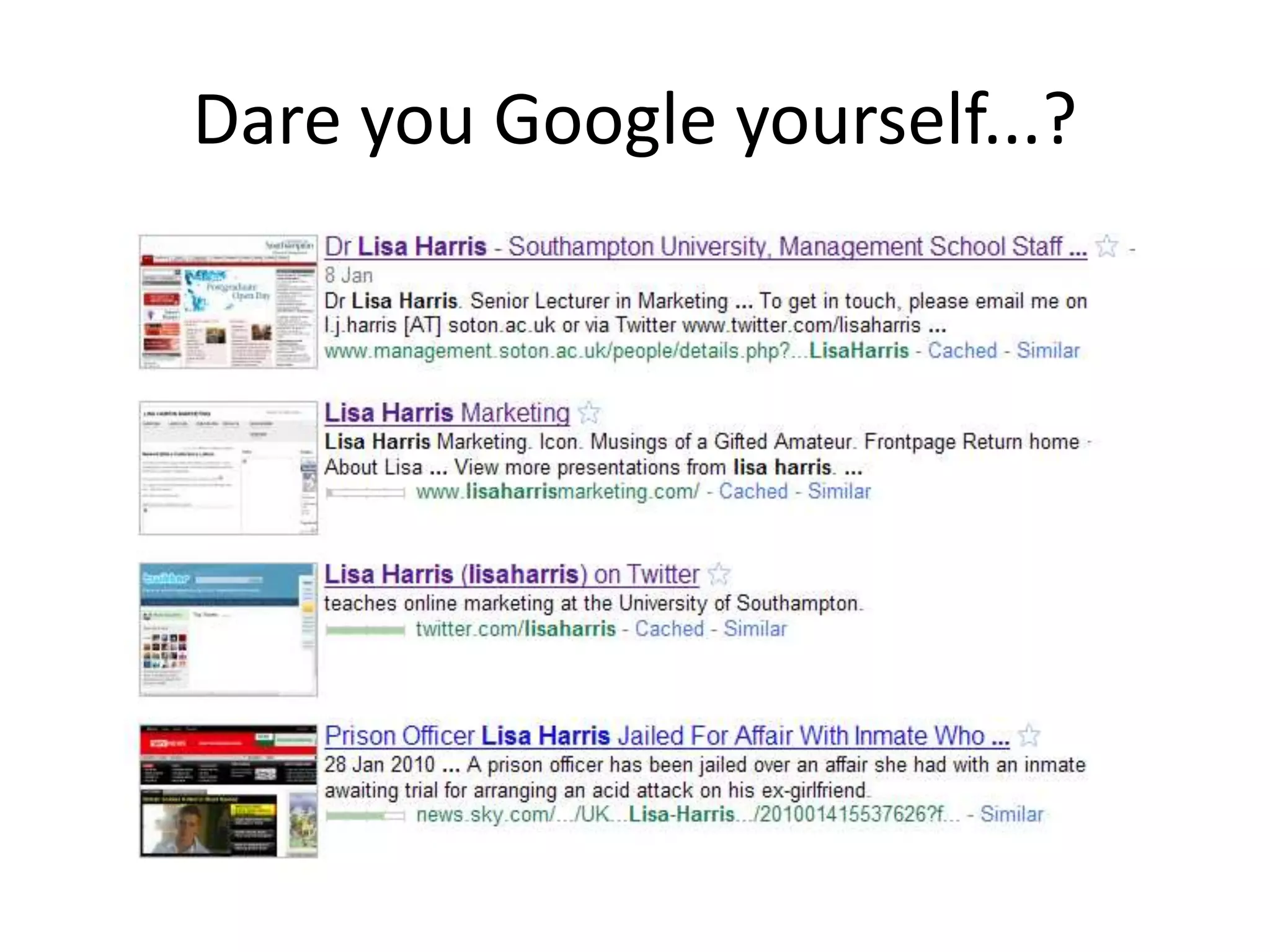
This document outlines the agenda and content for a session on digital literacy and living and working on the web. The session will cover evaluating online information, relevant articles and resources, satire, a student video, and building a professional digital profile. It discusses the scope of digital literacy including information management, creating materials, communication, and online identity and behavior. It provides tips on using social media for employment and setting up a blog.