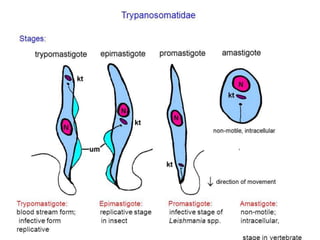
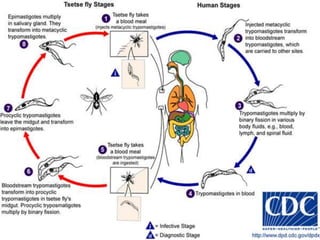
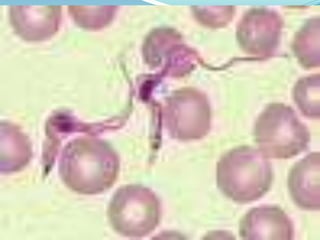
Trypanosoma brucei causes African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness) in humans. It is transmitted through bites from infected tsetse flies. In the first stage, symptoms may include fever and swollen lymph nodes. Later stages can affect the central nervous system, with symptoms like severe headaches, poor coordination, and changes in sleep patterns or behavior. Diagnosis involves examining blood, lymph node fluid, or spinal fluid under a microscope for the parasites. Treatment depends on the stage of disease and may include drugs like suramin, pentamidine, or eflornithine. Control efforts focus on reducing tsetse fly habitats and quickly treating infected people.