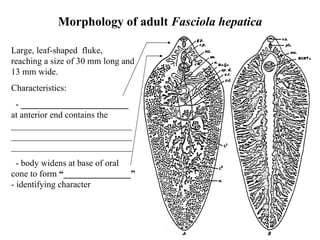
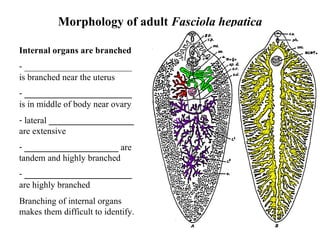
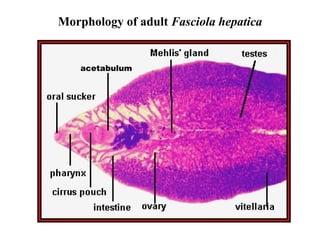
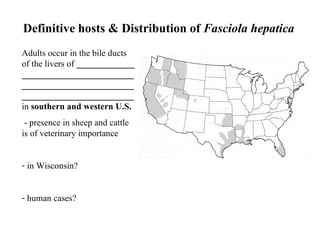
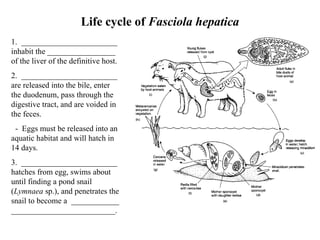
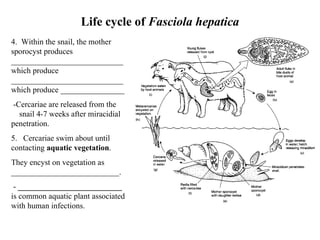
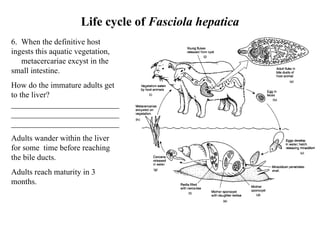
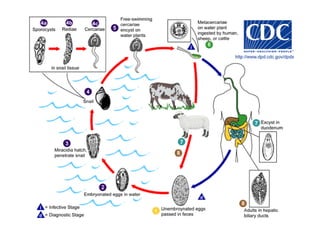
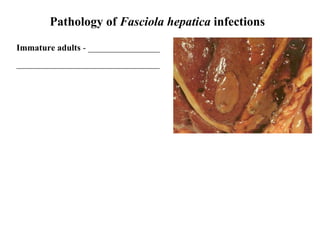
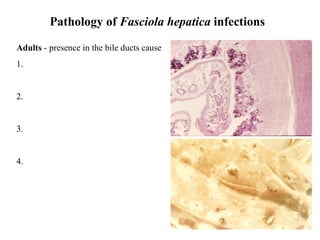
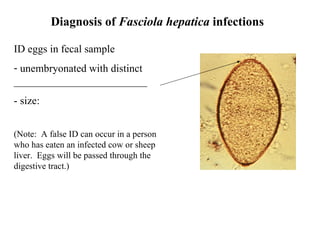
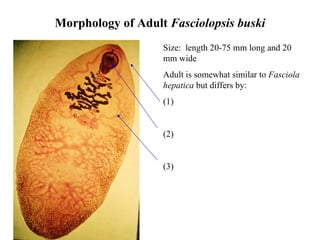
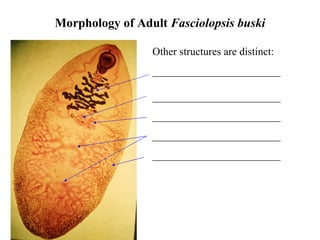
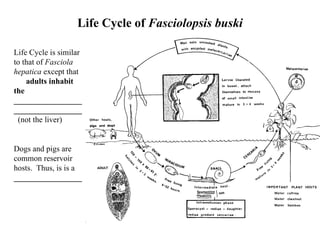
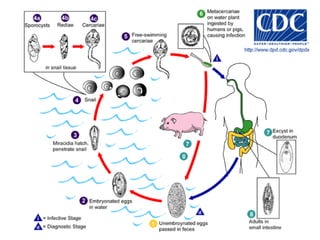
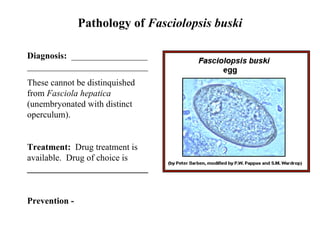
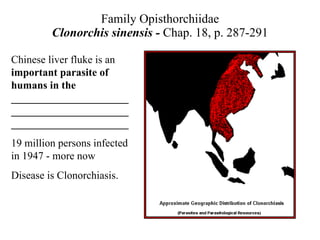
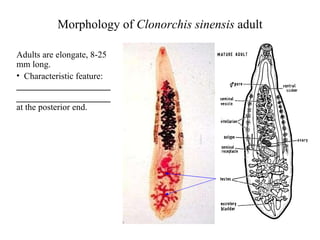
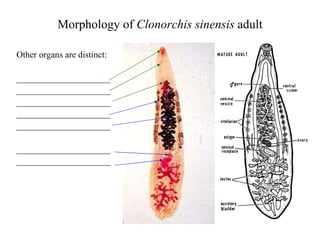
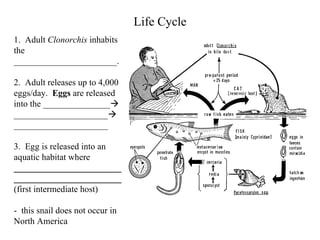
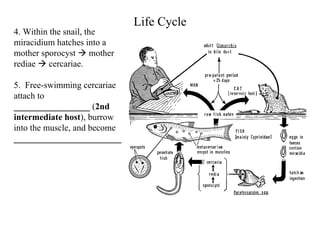
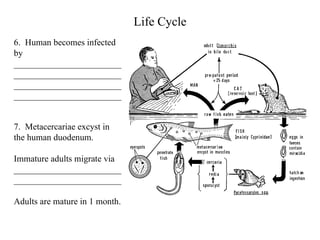
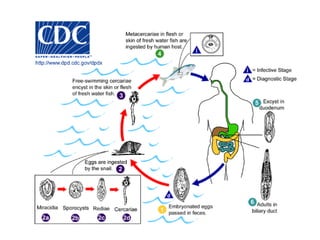
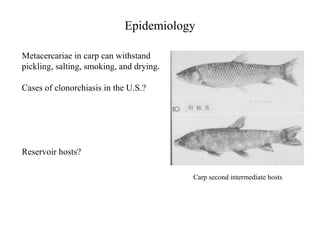
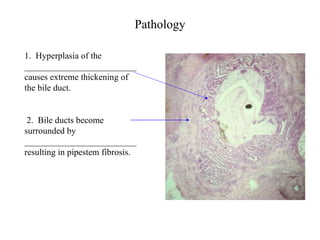
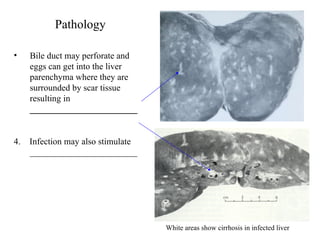
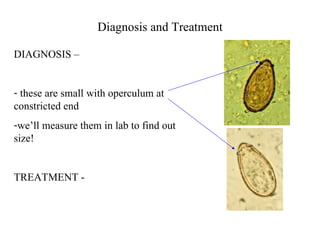
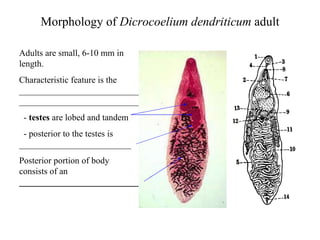
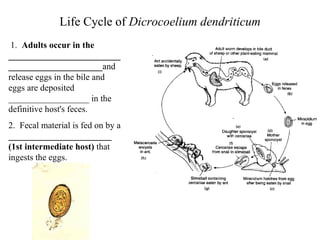
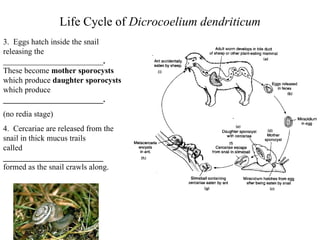
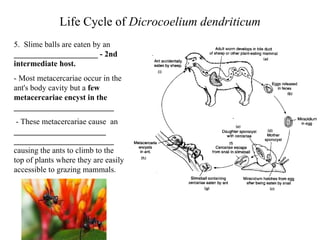
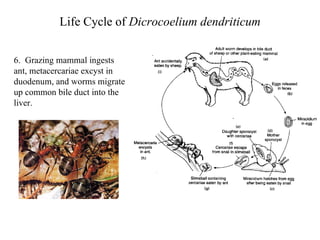
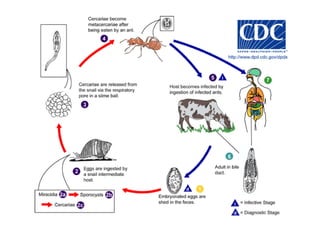
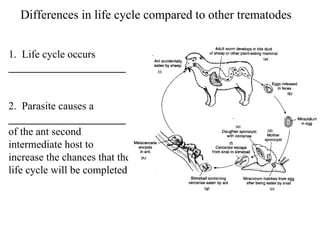
This document summarizes several important digenetic trematodes (flukes) that infect mammals in different organs. It describes the morphology, life cycles, pathology and epidemiology of liver flukes (Fasciola hepatica, Fascioloides magna), intestinal flukes (Fasciolopsis buski), lung flukes, and reproductive system flukes. Key details are provided for each fluke, including the definitive host, intermediate hosts, sites of infection, and symptoms caused.