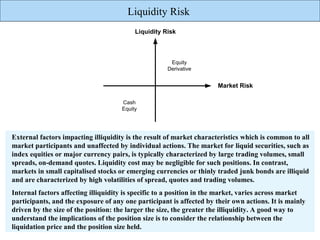
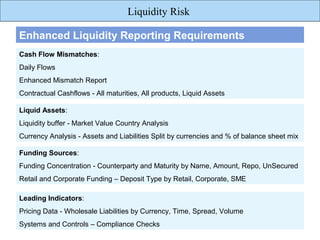
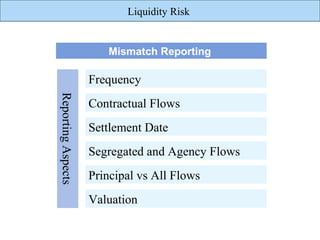
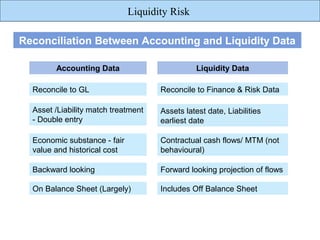
The document discusses liquidity risk, which can be defined as a bank's ability to meet its short-term obligations. It is measured over a specific time horizon and depends on factors like a bank's cash inflows and outflows. Liquidity risk is affected by both external market characteristics and internal factors specific to a bank's positions. Reporting on liquidity risk involves reconciling accounting and liquidity data, projecting contractual cash flows, and analyzing liquid assets, funding sources, and leading indicators of liquidity issues.