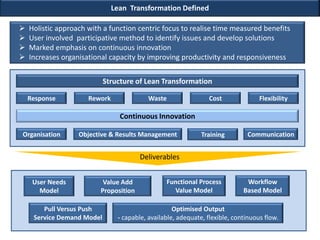
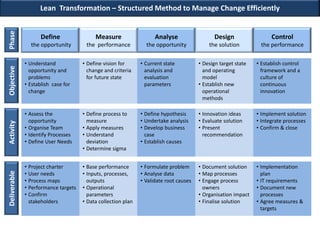
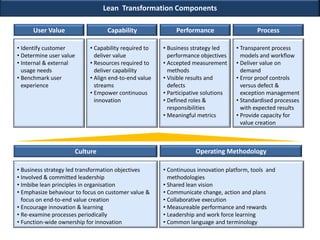
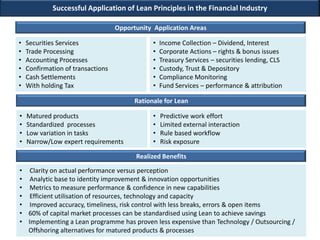
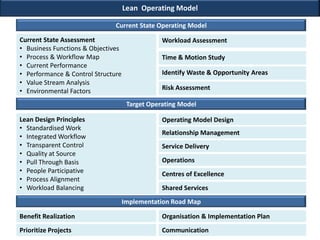
This document discusses applying lean principles to transform organizations. It defines lean transformation as a holistic, function-centric approach that emphasizes continuous innovation to improve productivity, responsiveness, and reduce waste and costs. The document outlines a structured 5-phase method to manage lean transformation: define, measure, analyze, design, and control. It also discusses key components of lean transformation including user value, capability, performance, process, culture and operating methodology. The document provides an example of successfully applying lean principles in the financial industry and outlines a lean operating model and implementation approach.