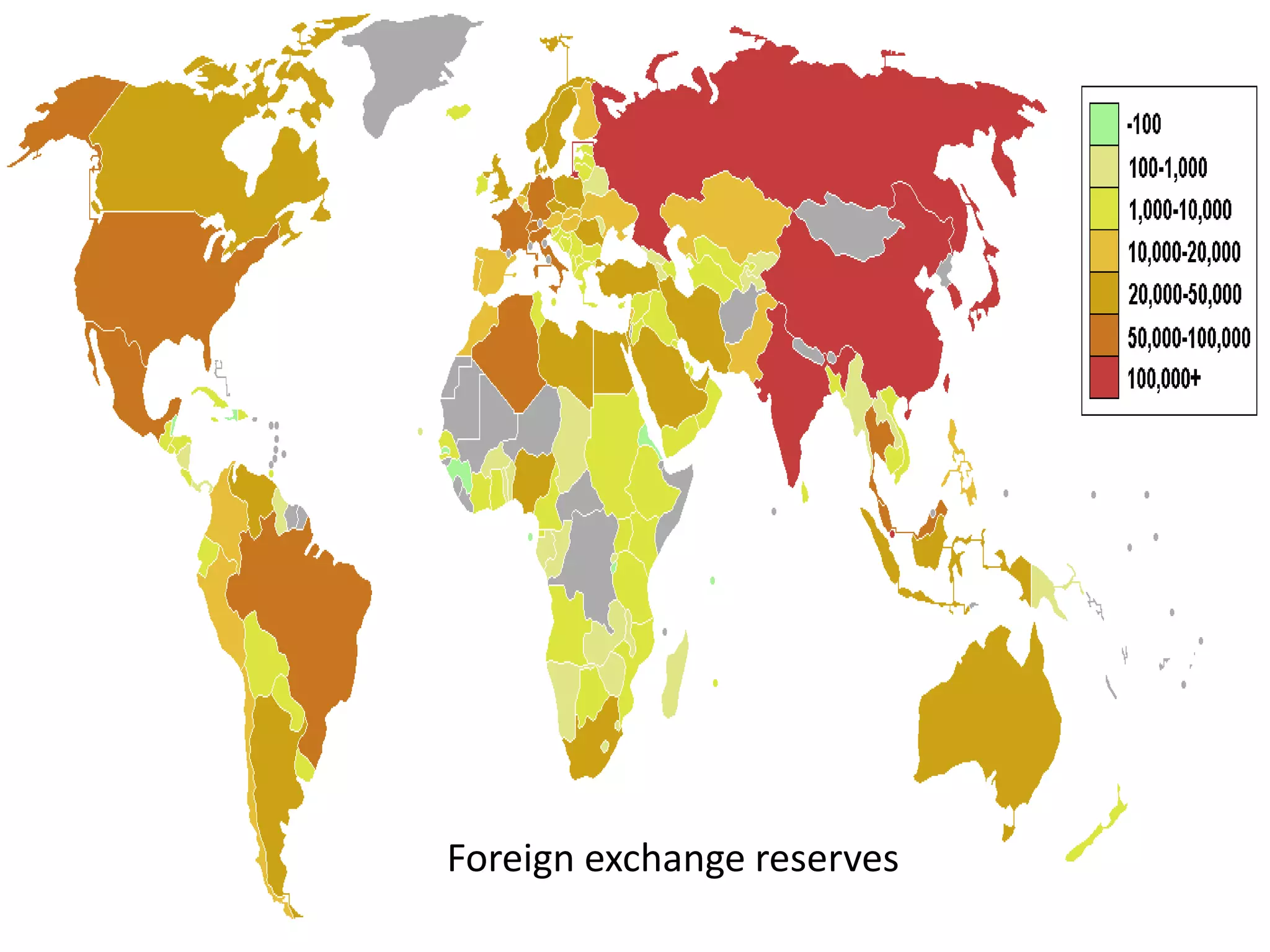
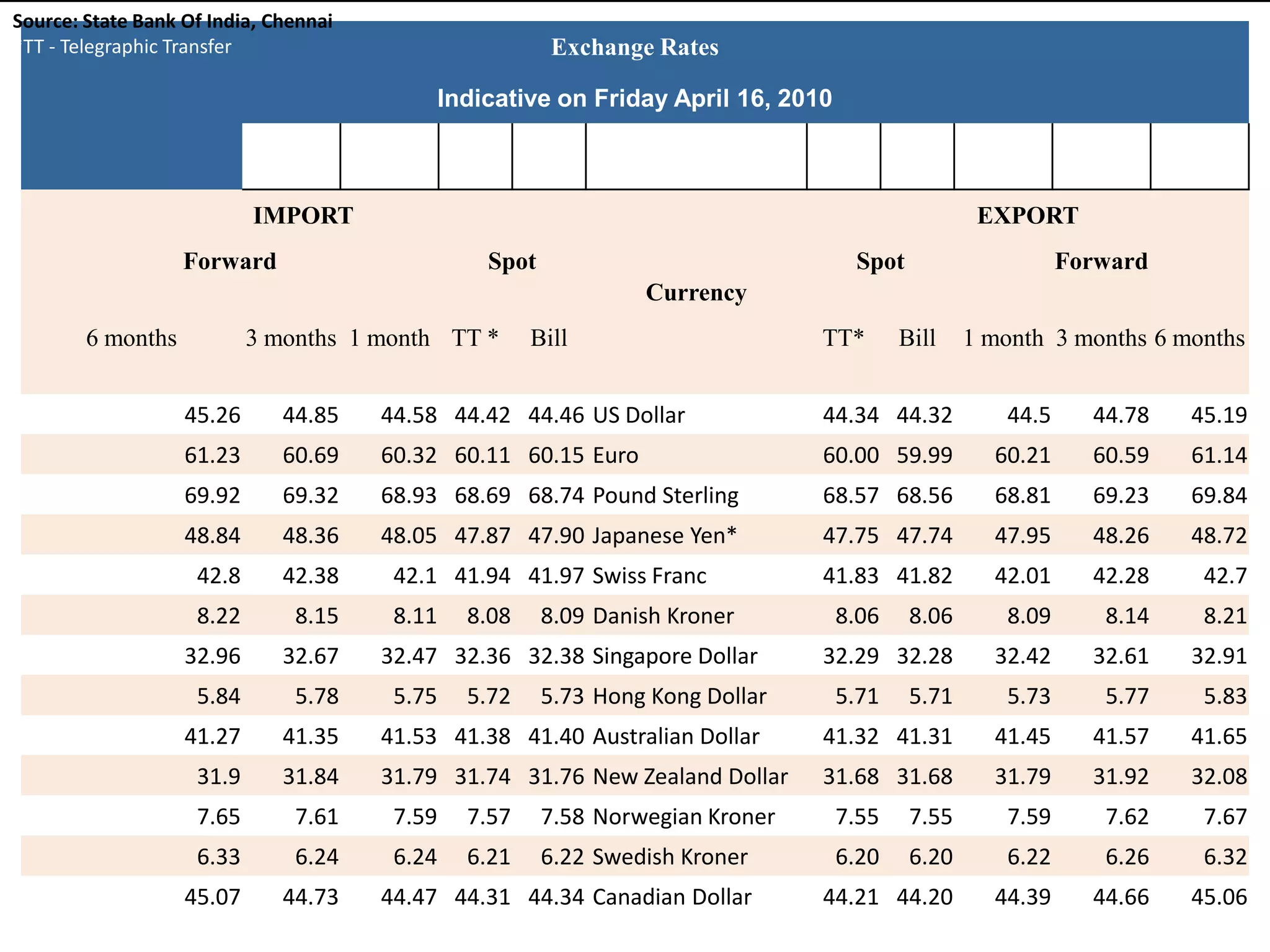
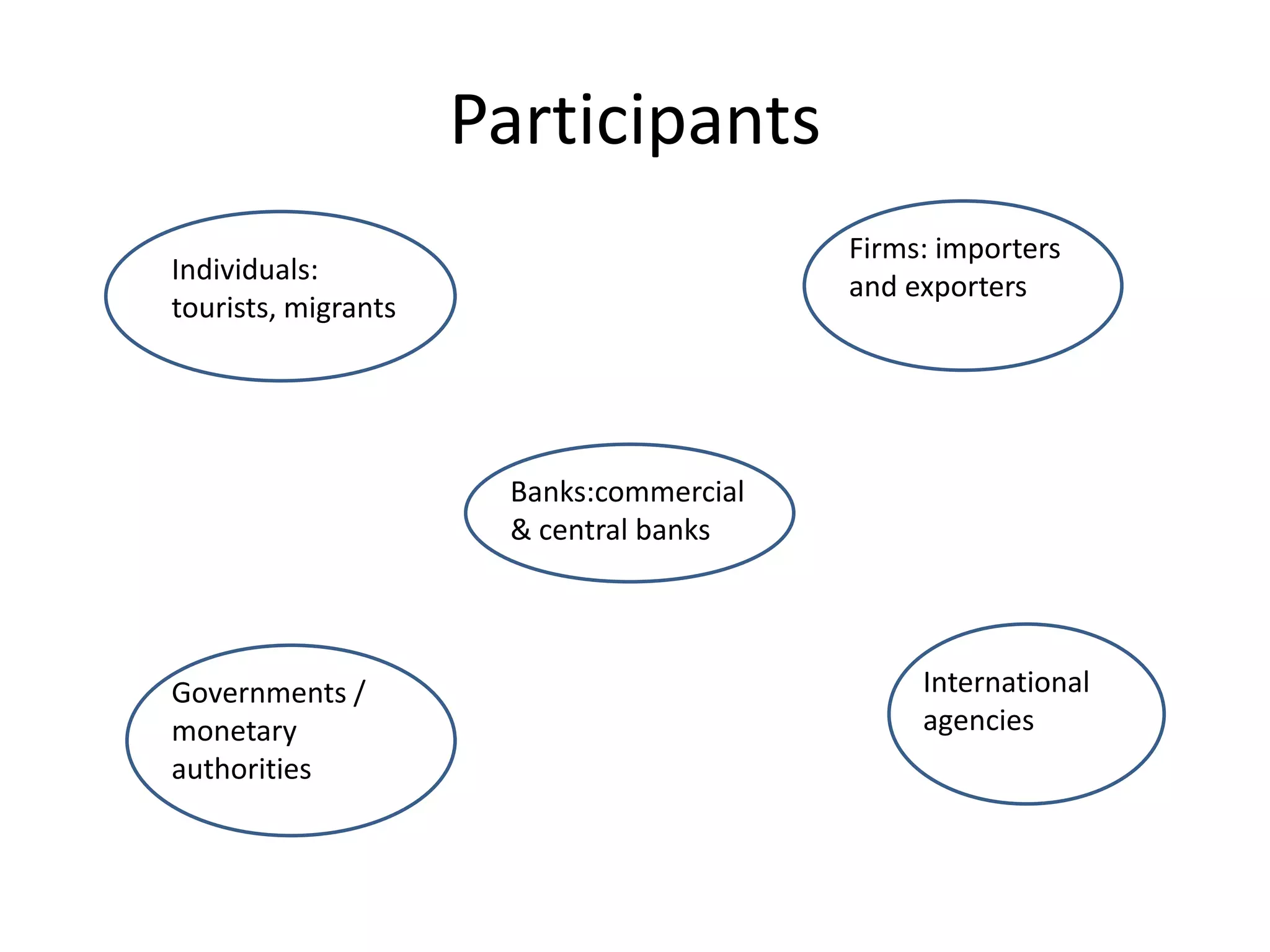
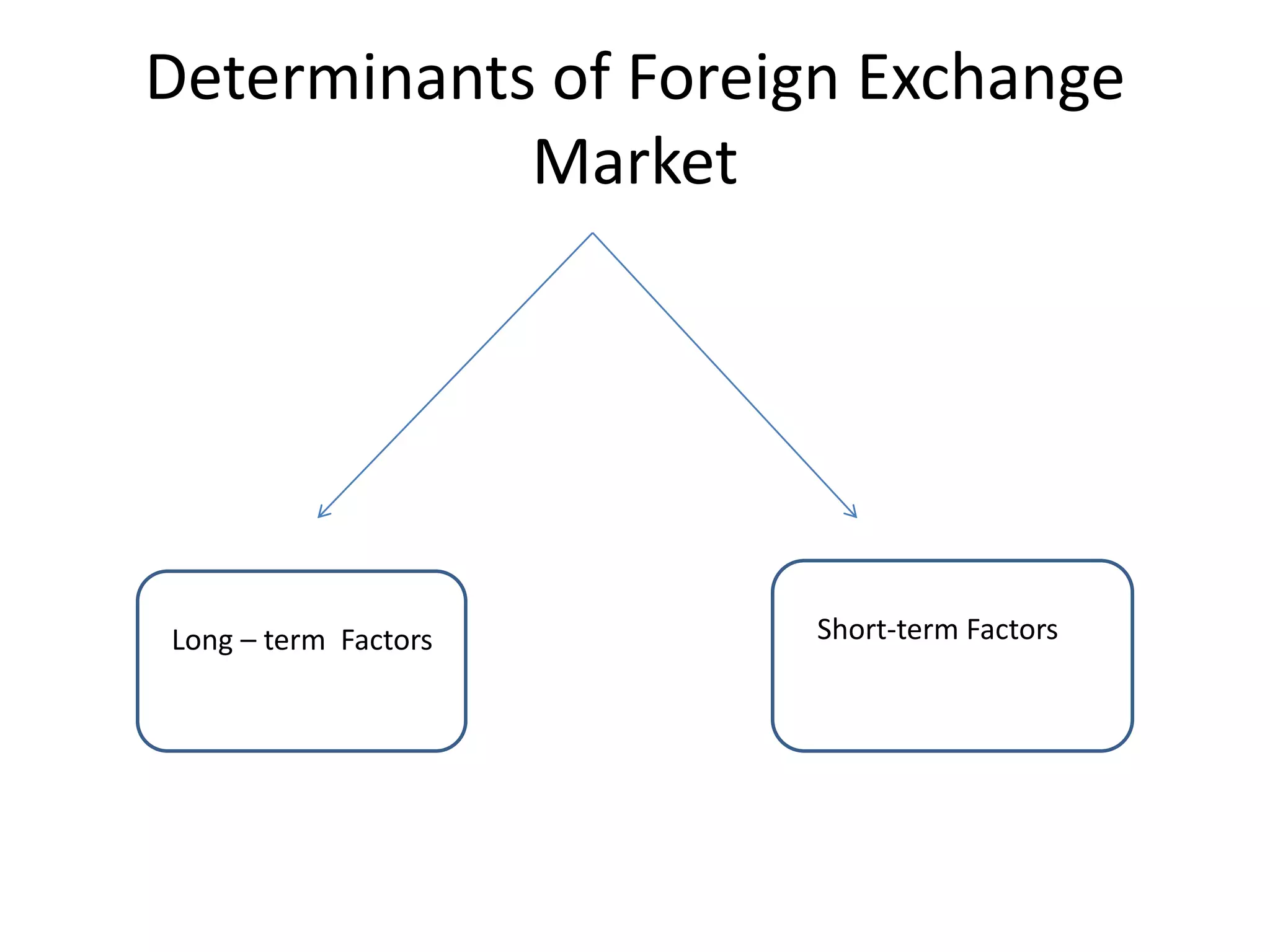
The document defines foreign exchange and foreign exchange markets. It discusses the key participants in foreign exchange markets including individuals, firms, banks, governments, and international agencies. It also outlines some of the main functions and determinants of foreign exchange markets. Long-term determinants include balance of payments, relative economic strength, interest rates, inflation, money supply, and national income. Short-term determinants include central bank intervention, export/import payments and flows, foreign investment flows, political factors, speculation, and capital movements. The document also provides context on the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) in India.