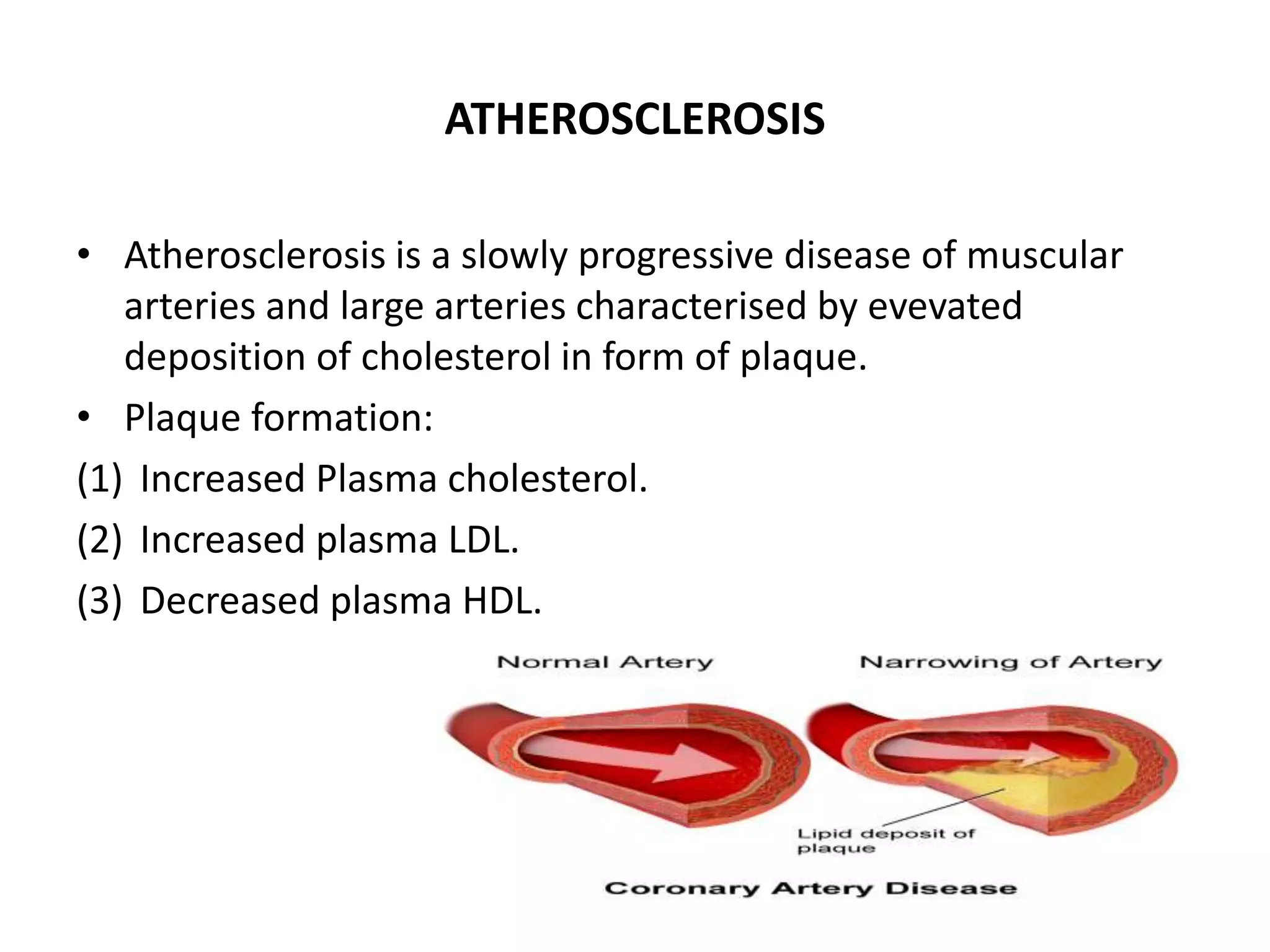
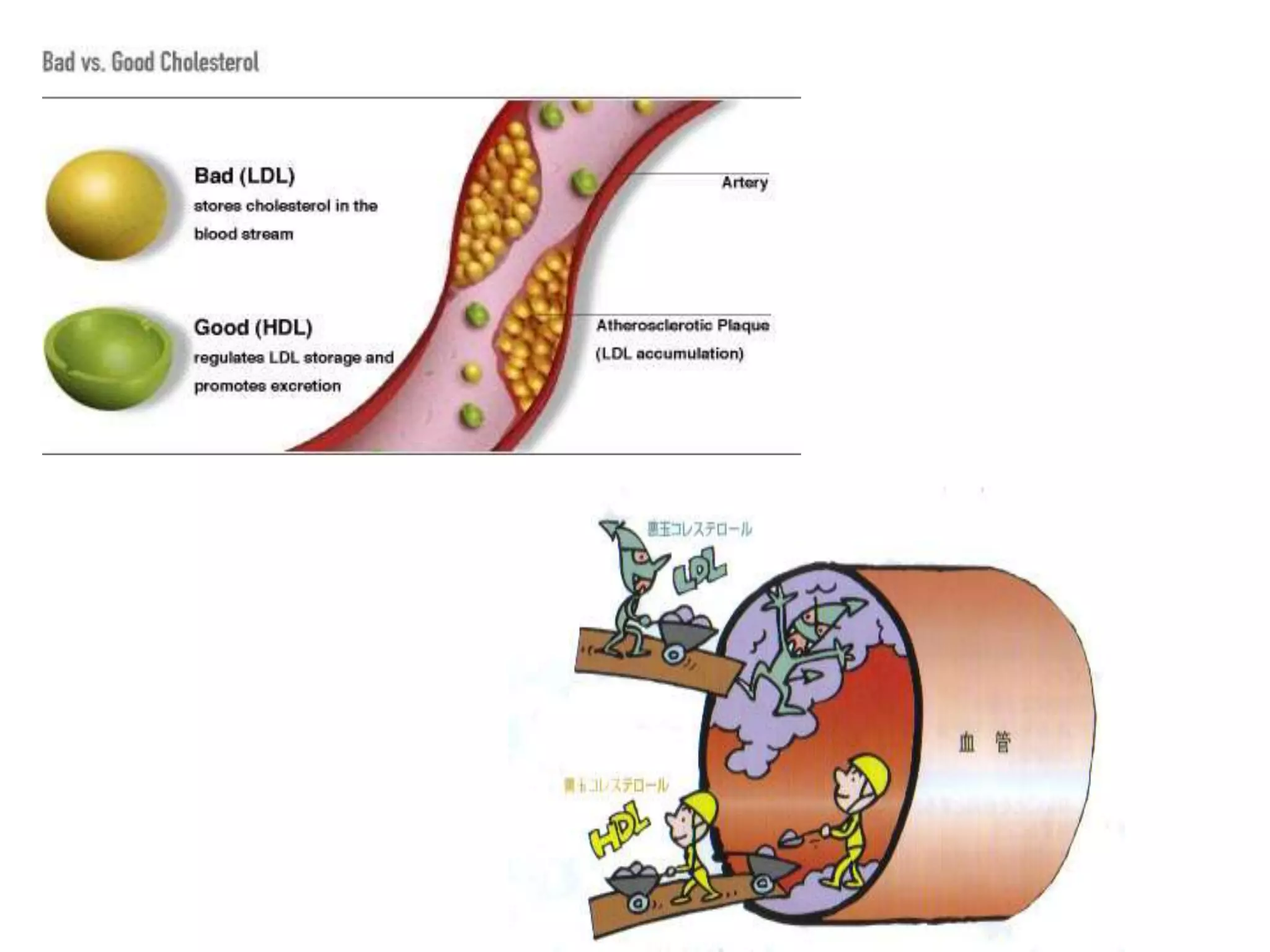
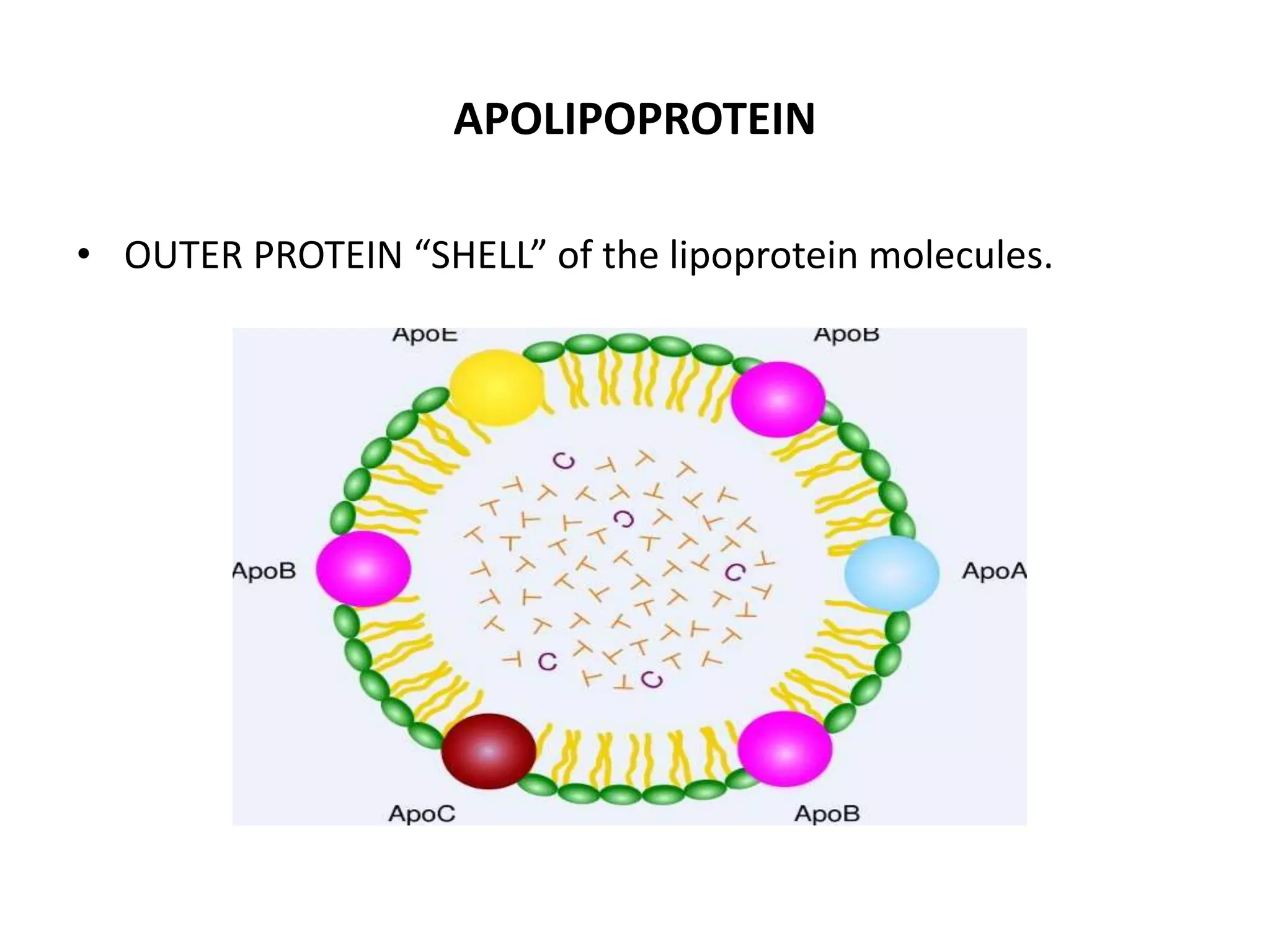
Lipoproteins are complexes that transport water-insoluble fat molecules in plasma, consisting of lipids and apolipoprotein components. They are classified by density into chylomicrons, VLDL, IDL, LDL, and HDL, each varying in lipid-protein composition and function. Clinical disorders related to lipoproteins include hyperlipoproteinaemias, atherosclerosis, and the unique lipoprotein(a), which poses higher risks for heart disease.























![LIPOPROTEIN (a) [LP(a)]
• It is a special type of lipoprotein not present in all people.
• In normal individuals it may be present only in 20% of the
population.
• In 20% of normal individuals , if present , it is found to be
more than 30 mg/dl. When present , it is attached to apo-
B100 by a disulphide bond.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipoprotein-200515081515/75/Lipoprotein-29-2048.jpg)