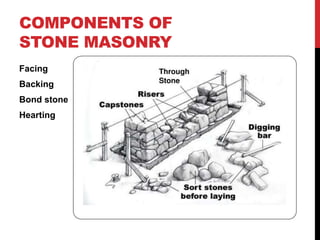
The document provides a comprehensive overview of stone masonry, including its definitions, classifications, and essential components, such as facing, backing, and types of bond stones. It covers various types of masonry like dry rubble, coursed rubble, and ashlar masonry, along with construction principles, selection criteria for stones, and important construction practices. Additionally, it discusses the use of mortar types in masonry, emphasizing the importance of skilled workmanship for durability and strength.