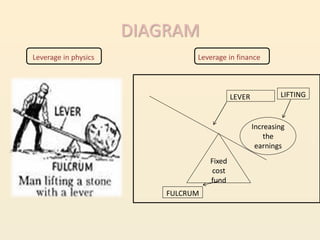
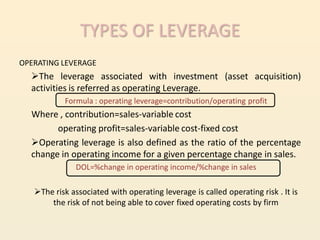
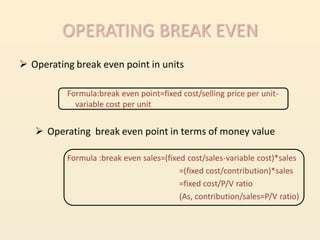
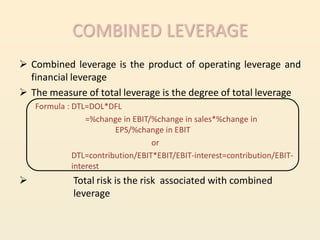
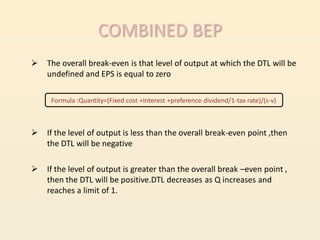
Leverage refers to using fixed costs to increase returns for owners. In finance, leverage allows firms to use fixed-cost funds like debt and preferred shares to increase earnings for equity shareholders. There are three types of leverage: operating, financial, and combined. Operating leverage measures how fixed costs affect operating income with sales changes. Financial leverage measures how interest expenses affect EPS. Combined leverage multiplies operating and financial leverage to measure total leverage.