This document provides an overview of key concepts in statistics for management, including:
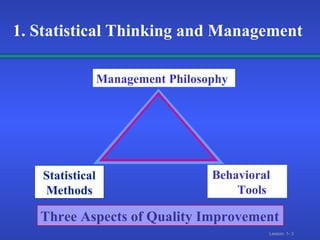
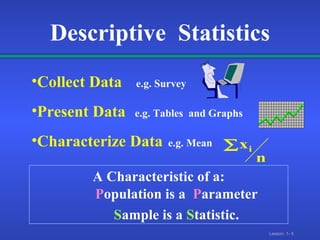
1. Descriptive statistics involve collecting and describing data through tables and graphs, while inferential statistics allow making decisions about populations based on sample data using estimation and hypothesis testing.
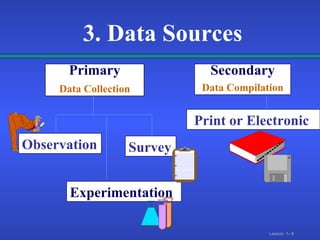
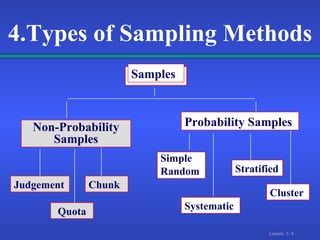
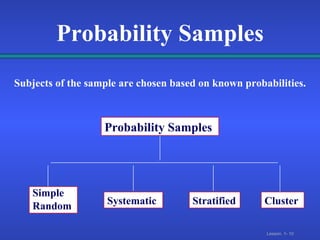
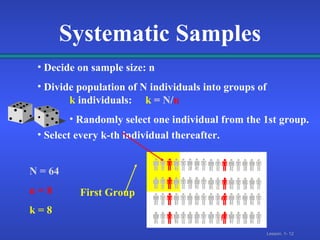
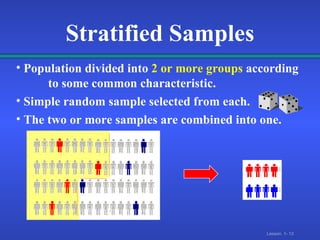
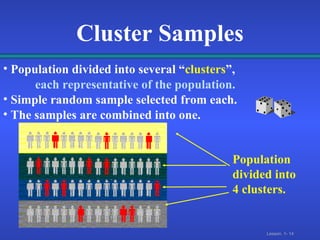
2. There are different types of data that can come from primary sources like surveys or secondary compiled sources, and different sampling methods like simple random, systematic, and stratified sampling that select subjects with known probabilities.
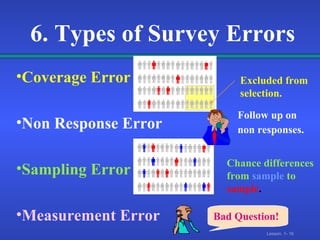
3. Surveys can be conducted through interviews, observation, or experiments, but are subject to errors like non-response, sampling, and measurement errors that can impact the quality of statistical analysis.