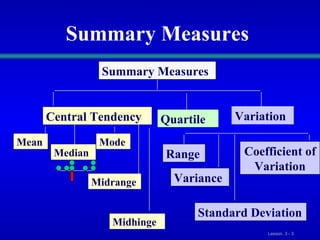
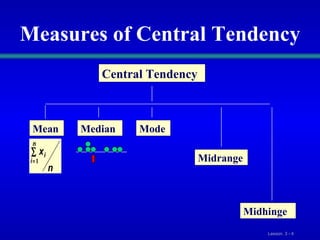
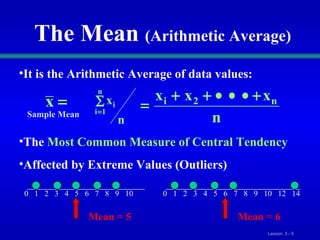
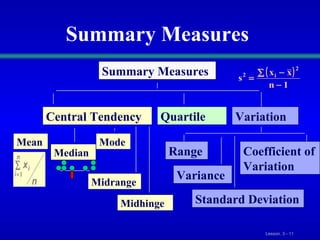
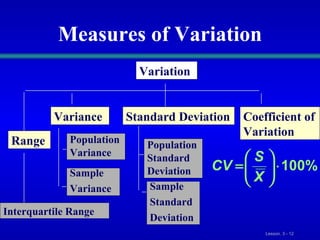
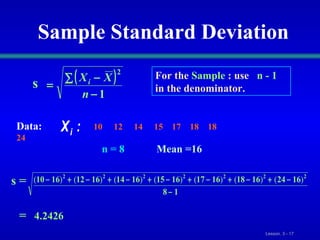
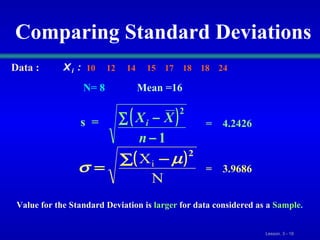
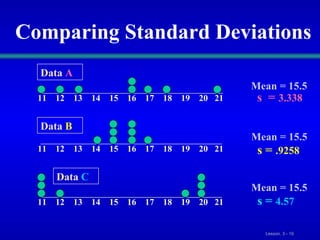
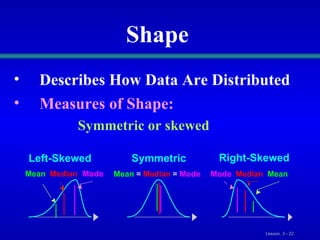
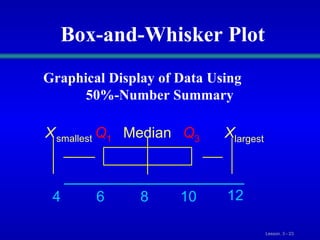
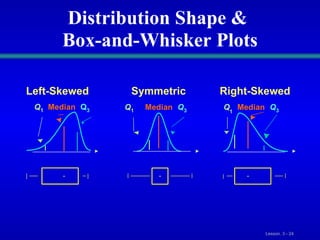
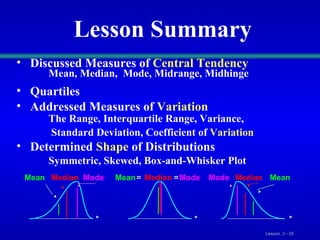
This document discusses various statistical measures for summarizing and describing numerical data, including measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode, midrange, quartiles), measures of variation (range, interquartile range, variance, standard deviation, coefficient of variation), and shape of distributions (symmetric vs. skewed). It provides definitions and formulas for calculating each measure and describes how to interpret them. Box-and-whisker plots are introduced as a graphical way to display data using the median, quartiles, and range.