Embed presentation
Downloaded 62 times

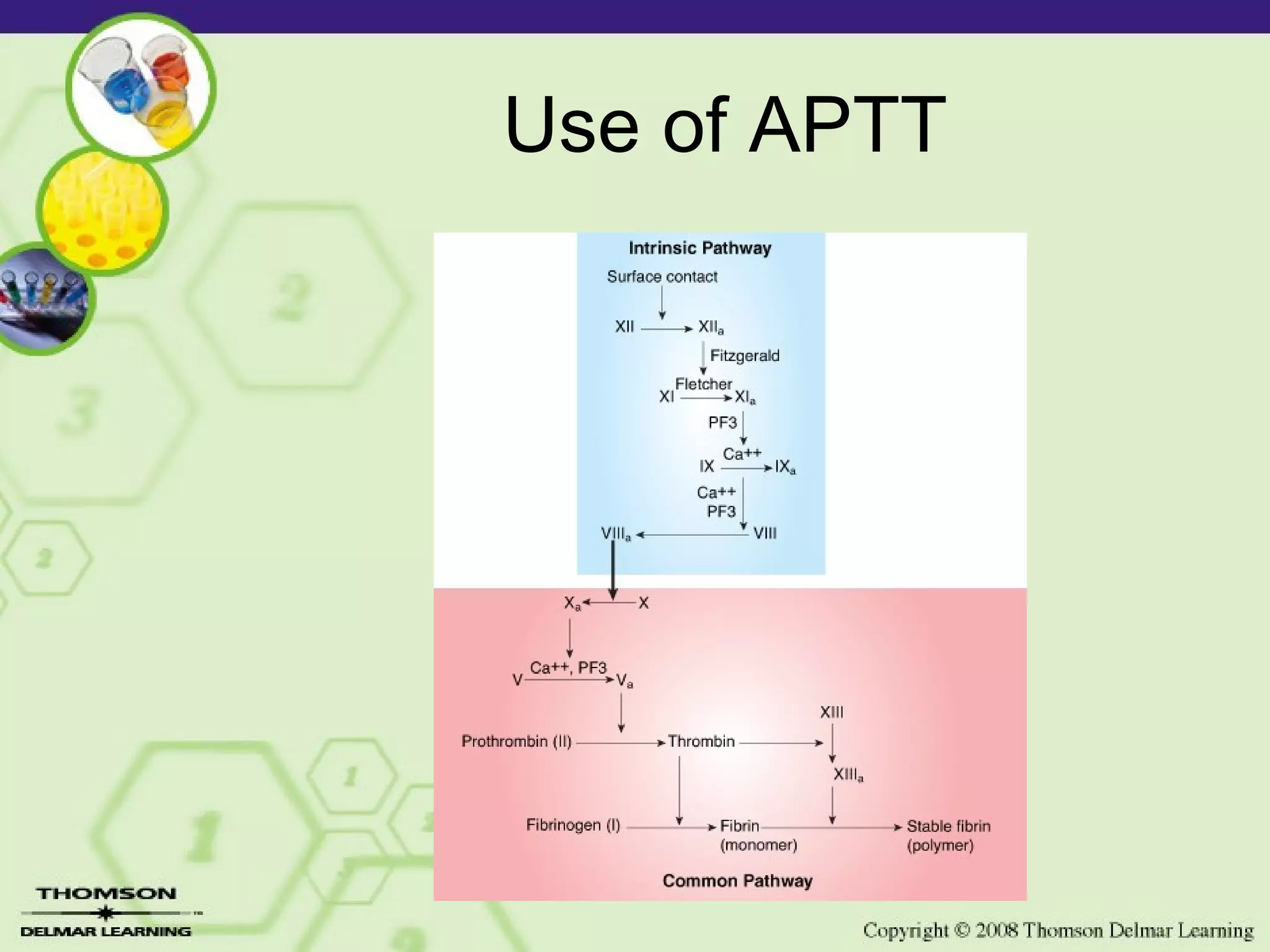


The APTT test screens for deficiencies in the intrinsic coagulation system and the common coagulation pathway. It is more sensitive than PTT and is used to monitor heparin therapy. Prolonged APTT can indicate deficiencies in coagulation factors of the intrinsic system, liver disease, heparin therapy, or DIC. When used together with PT testing, APTT and PT can detect 95% of coagulation defects.






