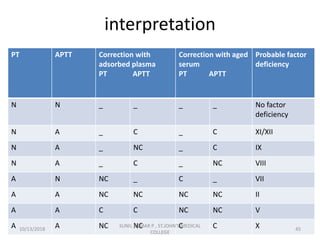
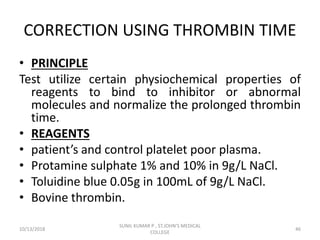
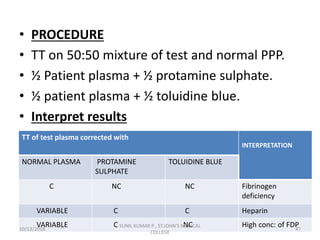
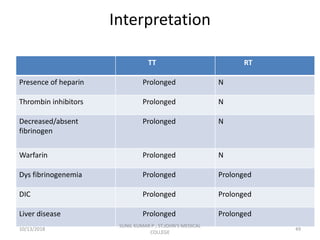
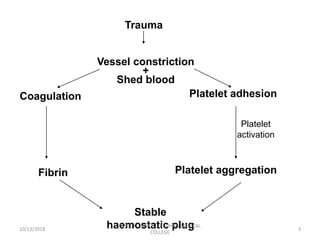
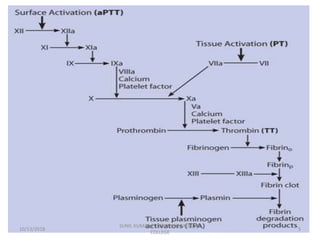
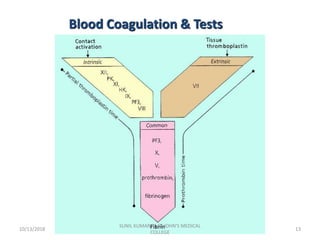
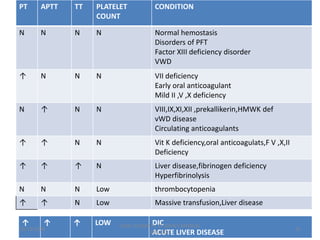
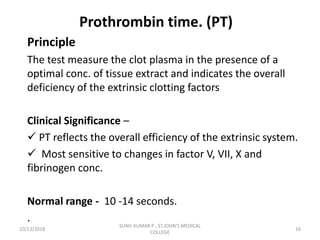
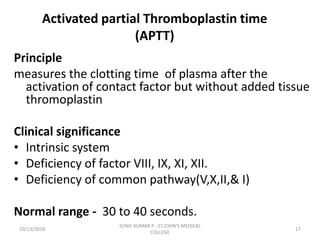
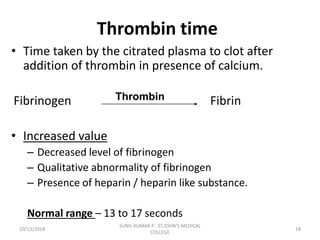
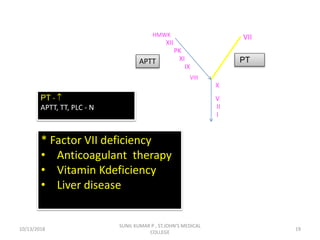
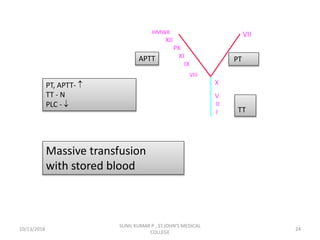
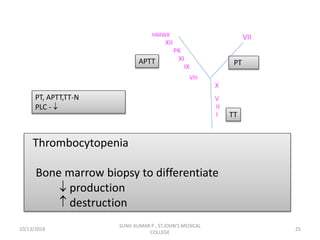
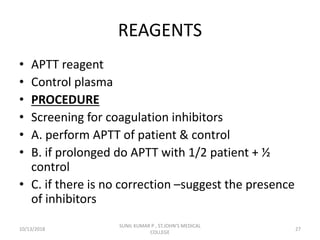
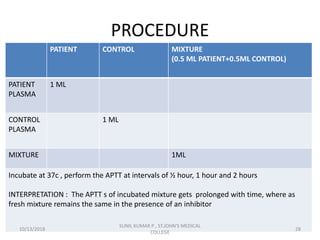
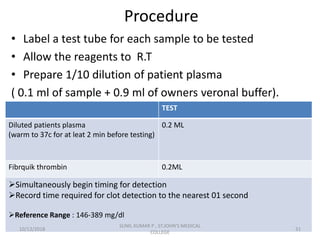
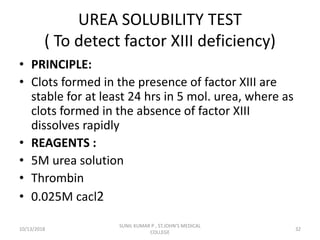
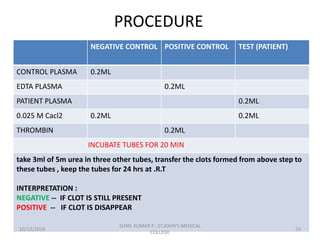
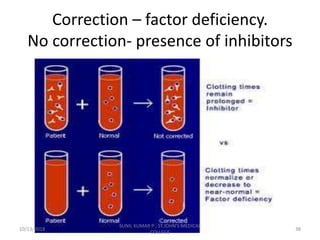
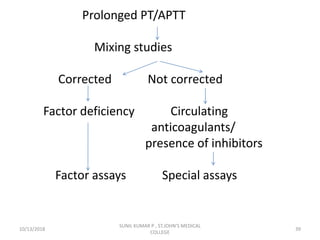
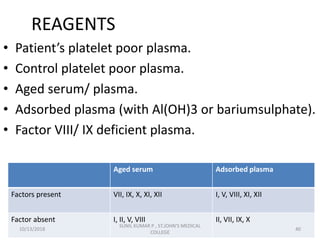
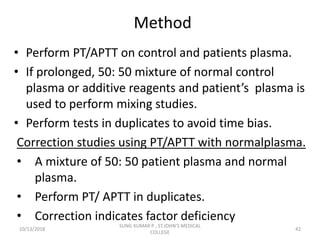
This document discusses laboratory approaches to evaluating bleeding disorders and mixing studies. It begins by explaining haemostasis and the coagulation cascade. It then discusses evaluating patients by obtaining a history, physical exam, and laboratory tests. A variety of screening and specific laboratory tests are outlined to identify abnormalities in coagulation factors, platelets, fibrinogen and the presence of inhibitors. The principles, reagents and procedures for performing various coagulation tests like PT, APTT, thrombin time and mixing studies are detailed.















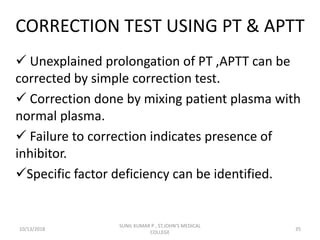



![If APTT corrects by more than 50% of the difference
between clotting times of normal plasma and test
plasma good correction.
A poor correction ie, prolonged APTT on mixing
indicates presence of an inhibitor.
Eg:-
APTT test =60˝
Control = 35˝ 100%
• Correction with ½ patient +
½ control = 42˝ [50%]
60˝- 35˝ =25˝ [100%]
25/2 = 12.5˝ [50%] with out correction.
10/13/2018 43
SUNIL KUMAR P , ST.JOHN'S MEDICAL
COLLEGE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtobleedingdisorders-181013135808/85/Approach-to-bleeding-disorders-43-320.jpg)
![60˝- 42˝ =18˝ [50%] after correction.
18˝ >12.5˝ Good correction.
• ½ patient + ½ control = 52˝ [50%]
60˝ - 52˝ = 8˝ [50%]
8˝ < 12.5˝ poor or no correction
2) Using aged serum.
½ patient serum + ½ aged serum.
Perform PT/APTT in duplicates.
Interpret the result.
10/13/2018 44
SUNIL KUMAR P , ST.JOHN'S MEDICAL
COLLEGE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtobleedingdisorders-181013135808/85/Approach-to-bleeding-disorders-44-320.jpg)