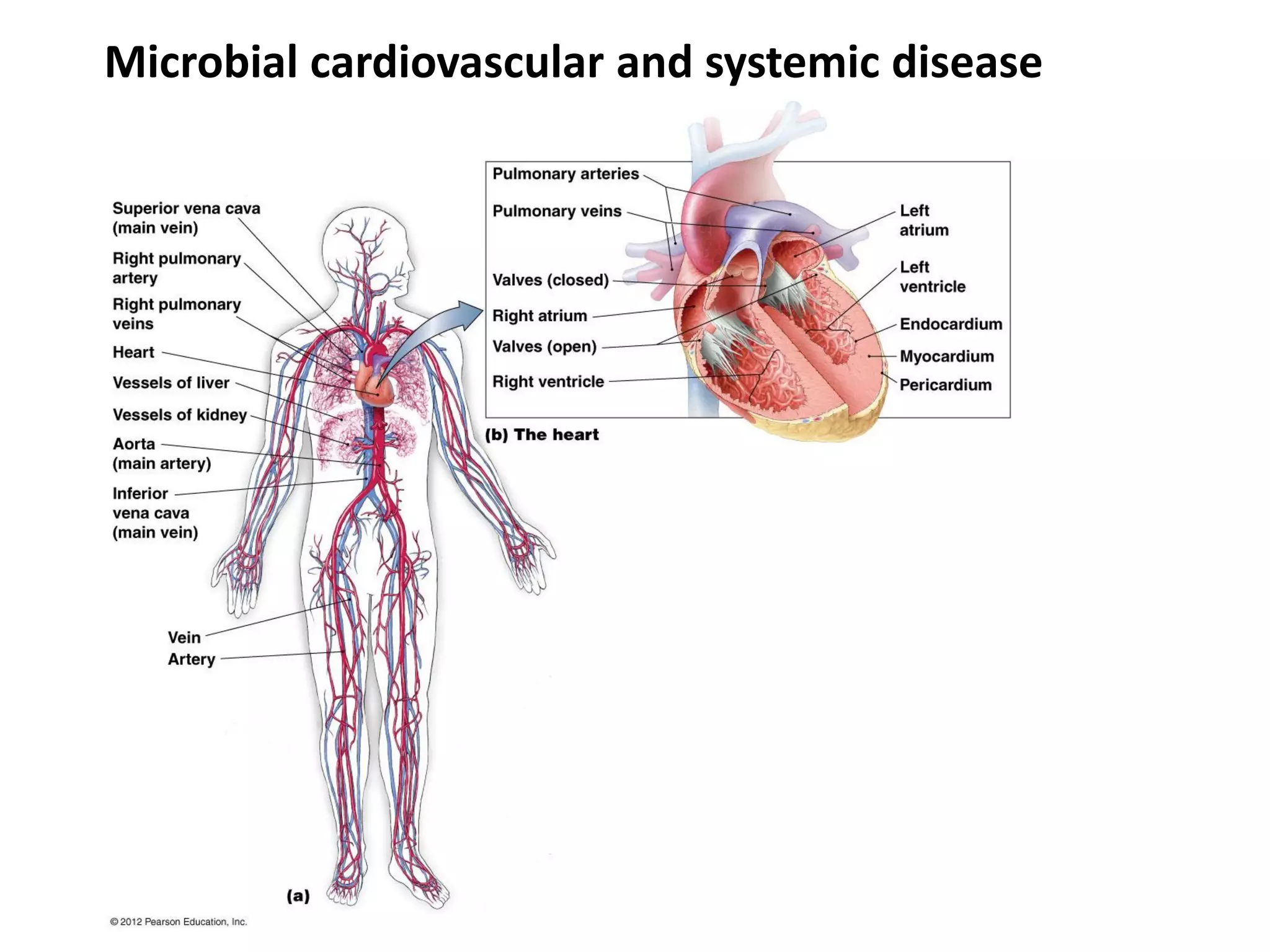
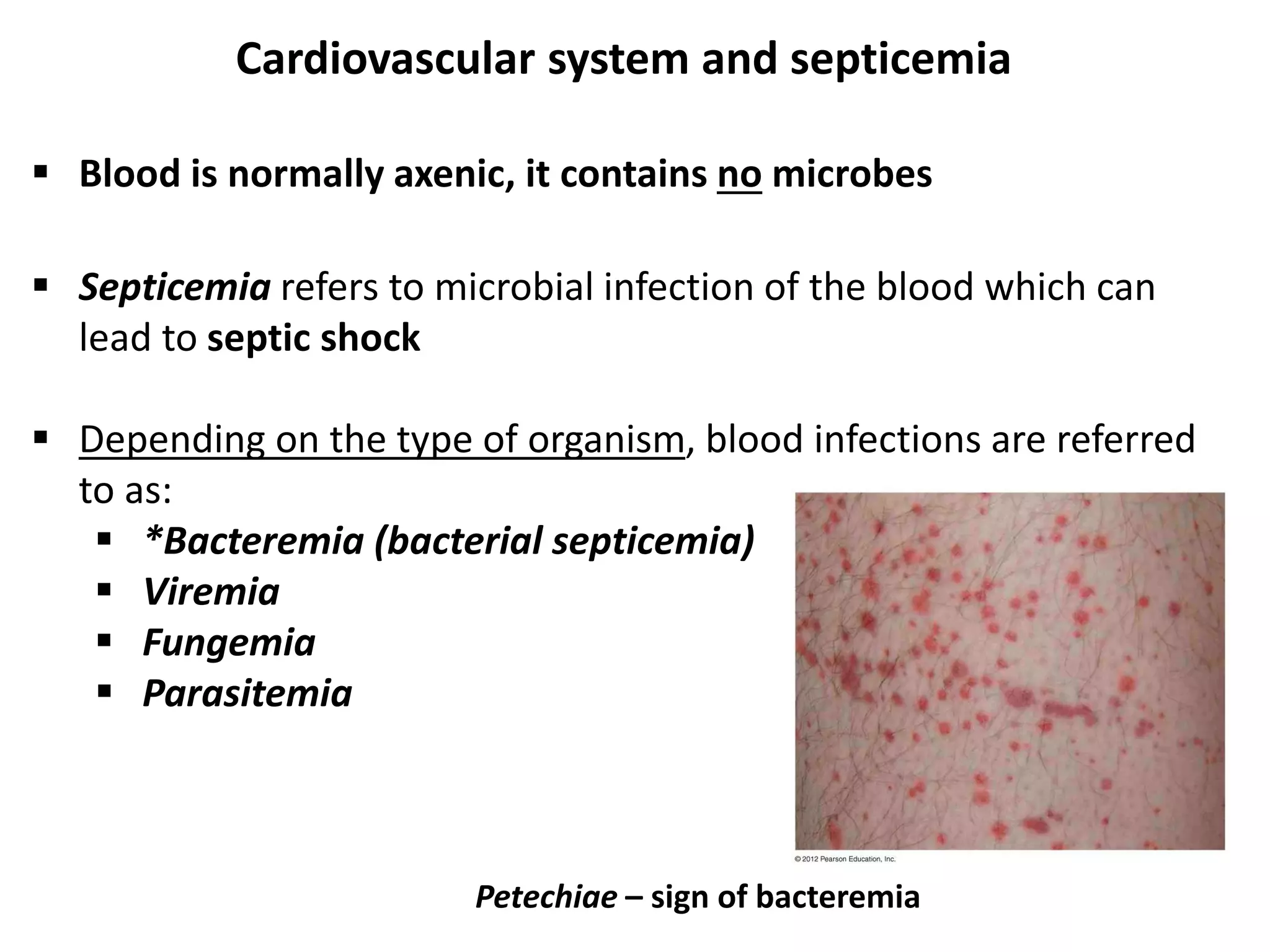
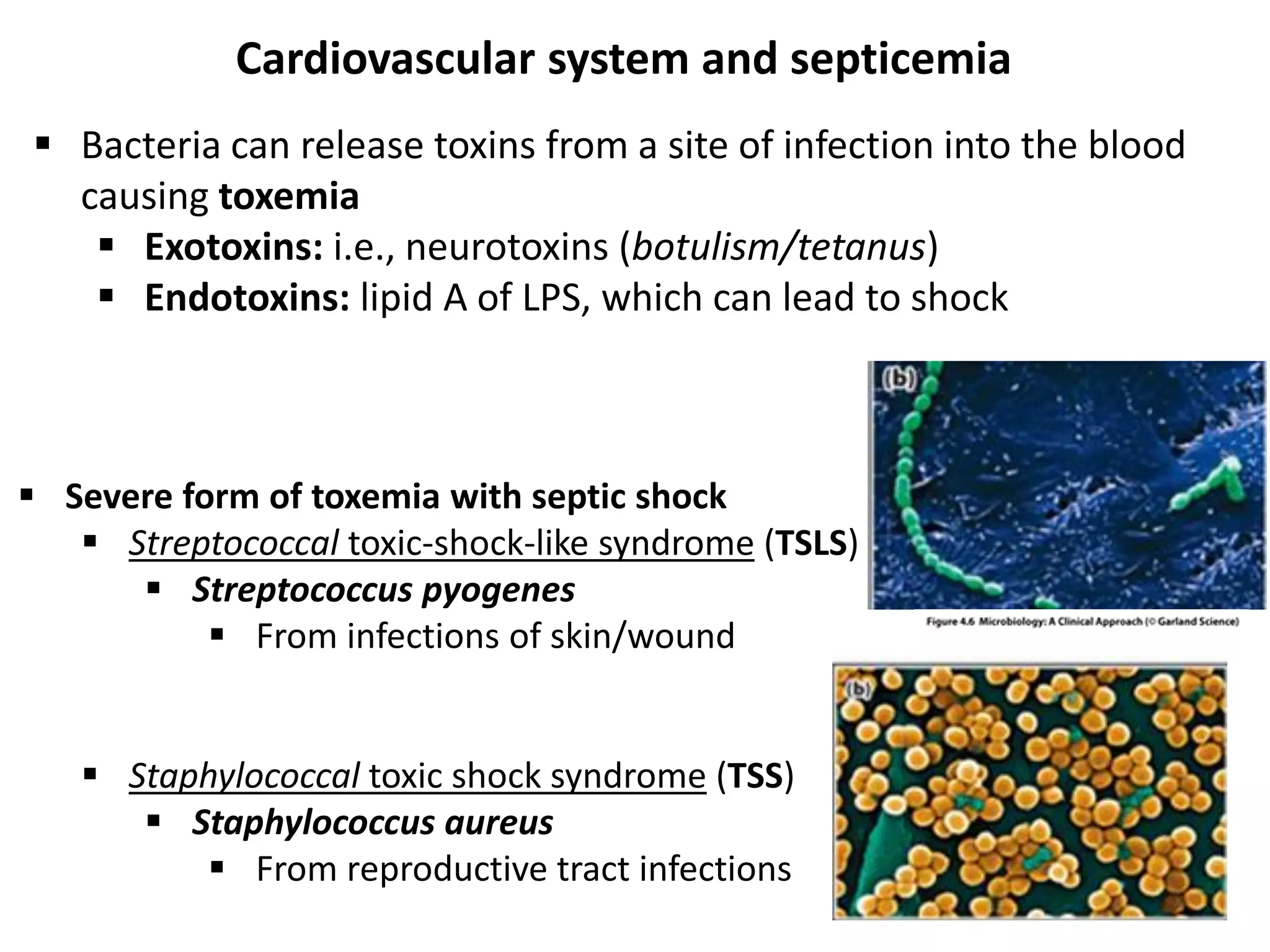
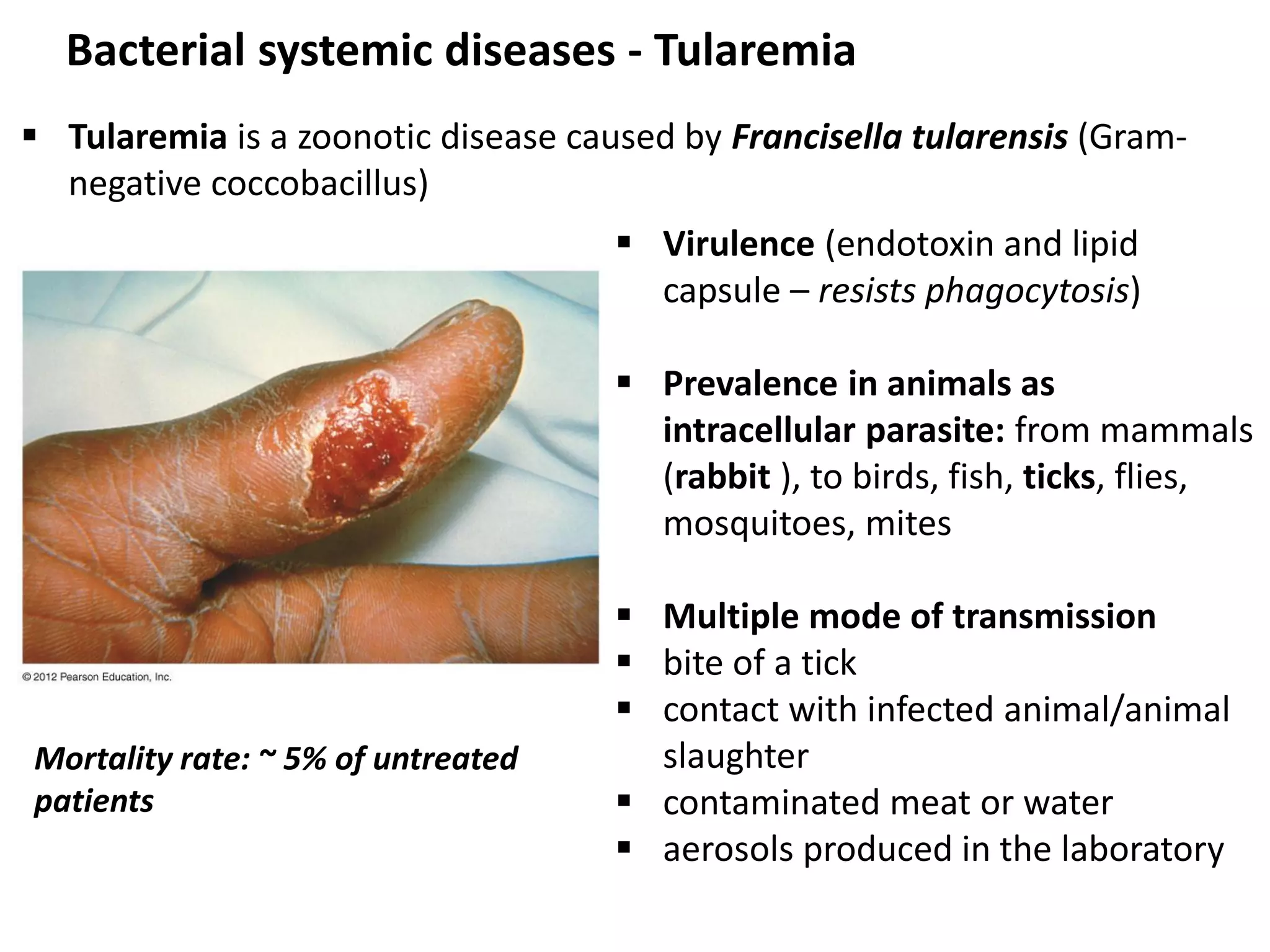
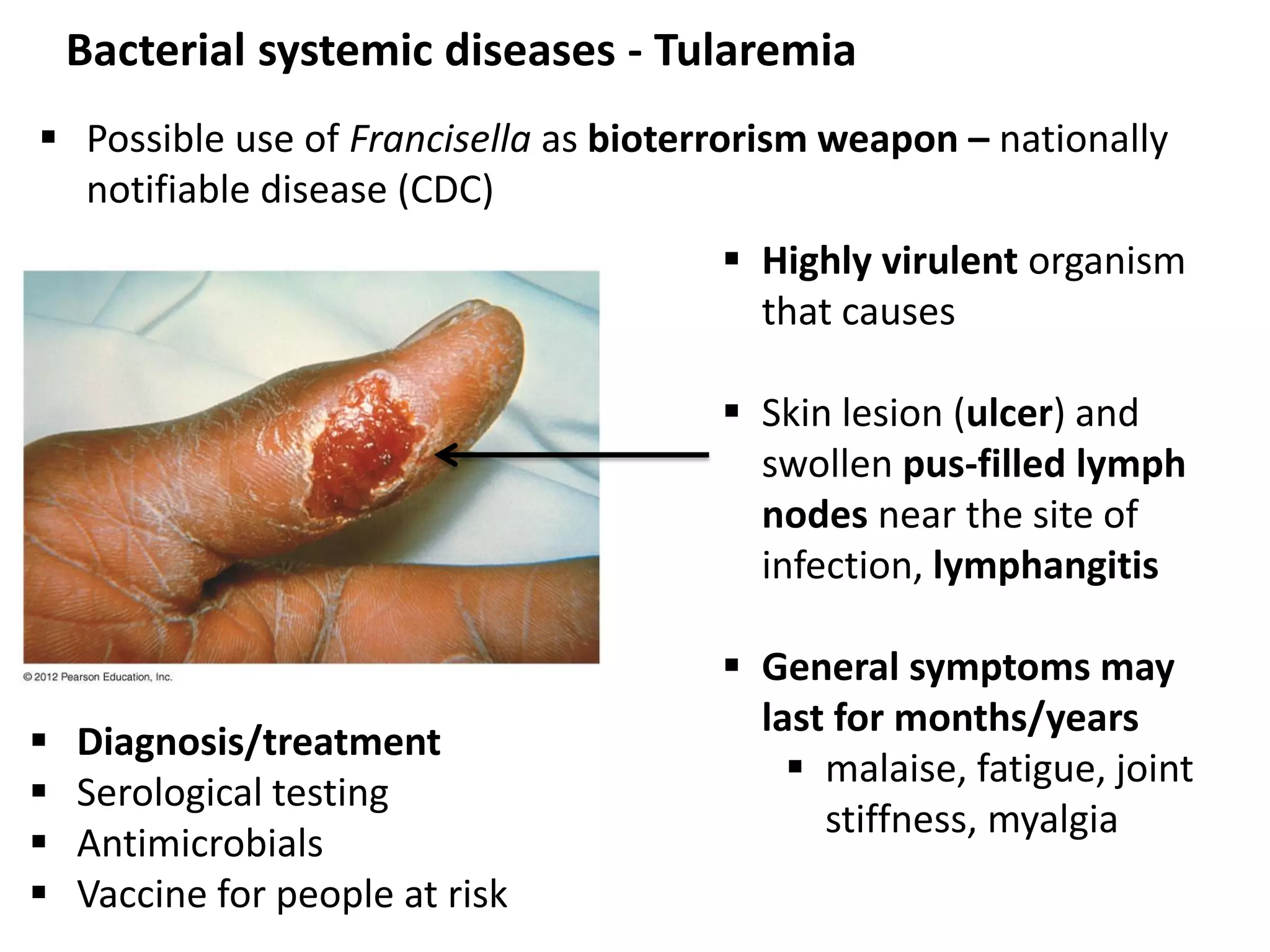
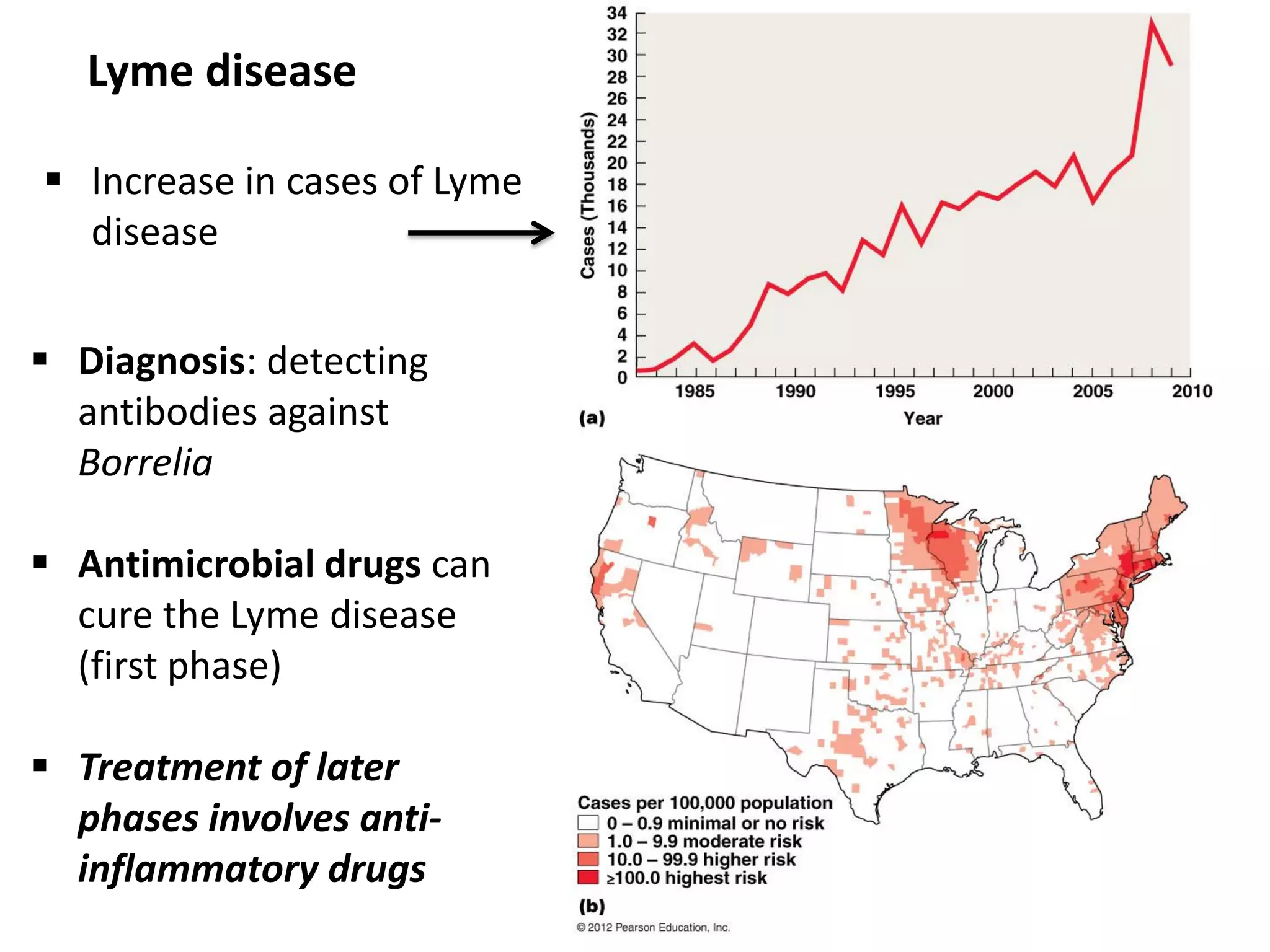
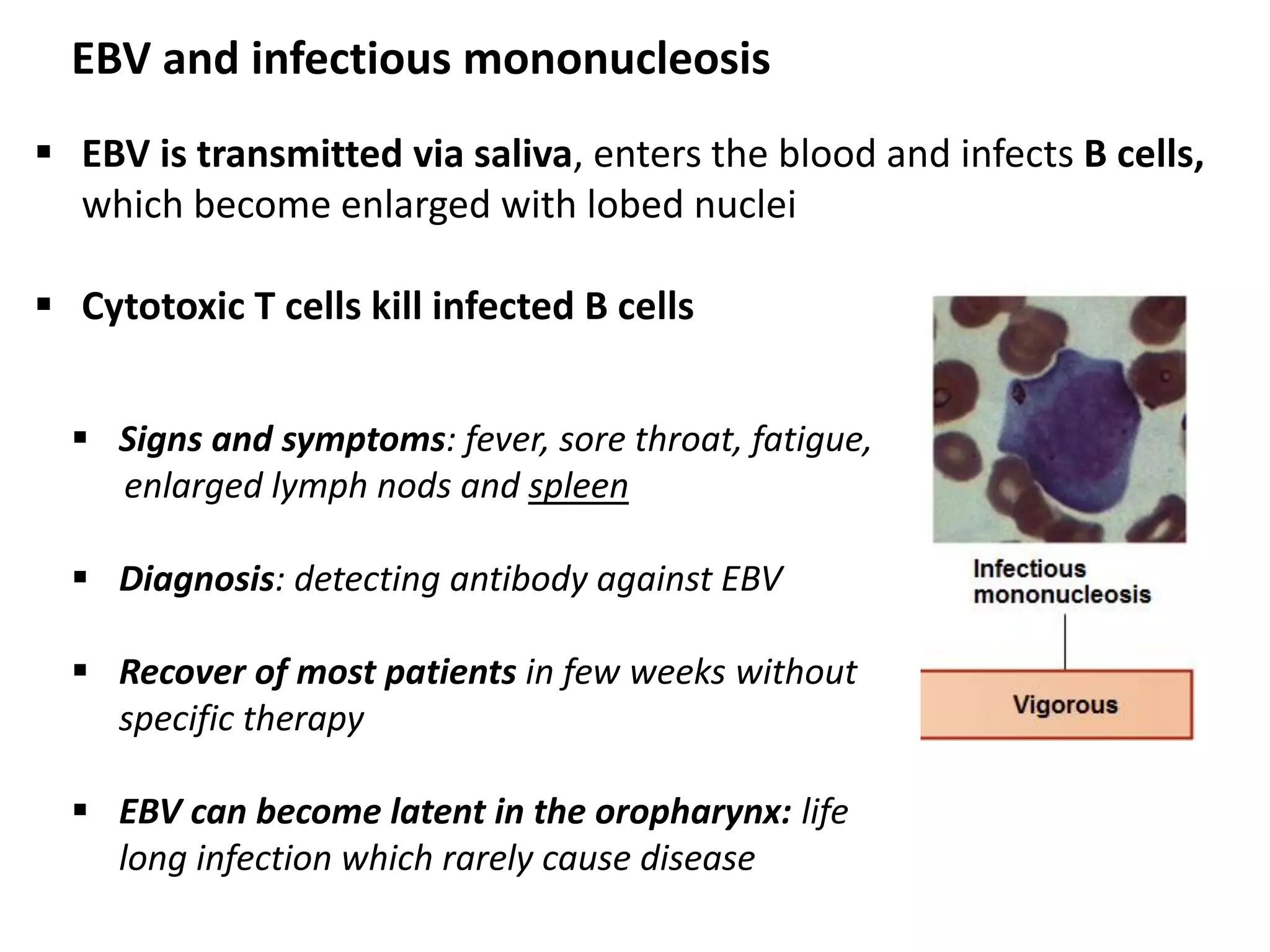
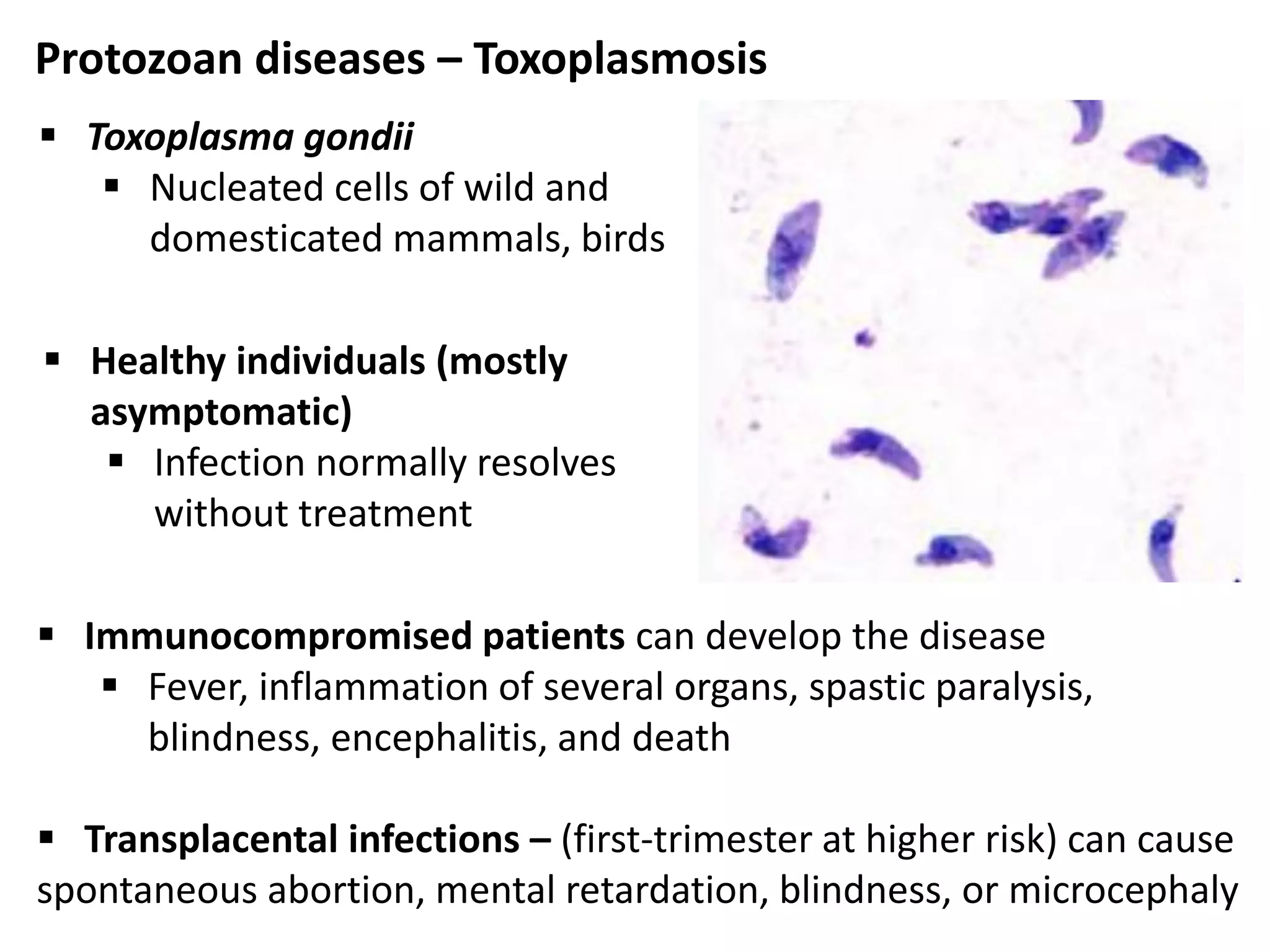
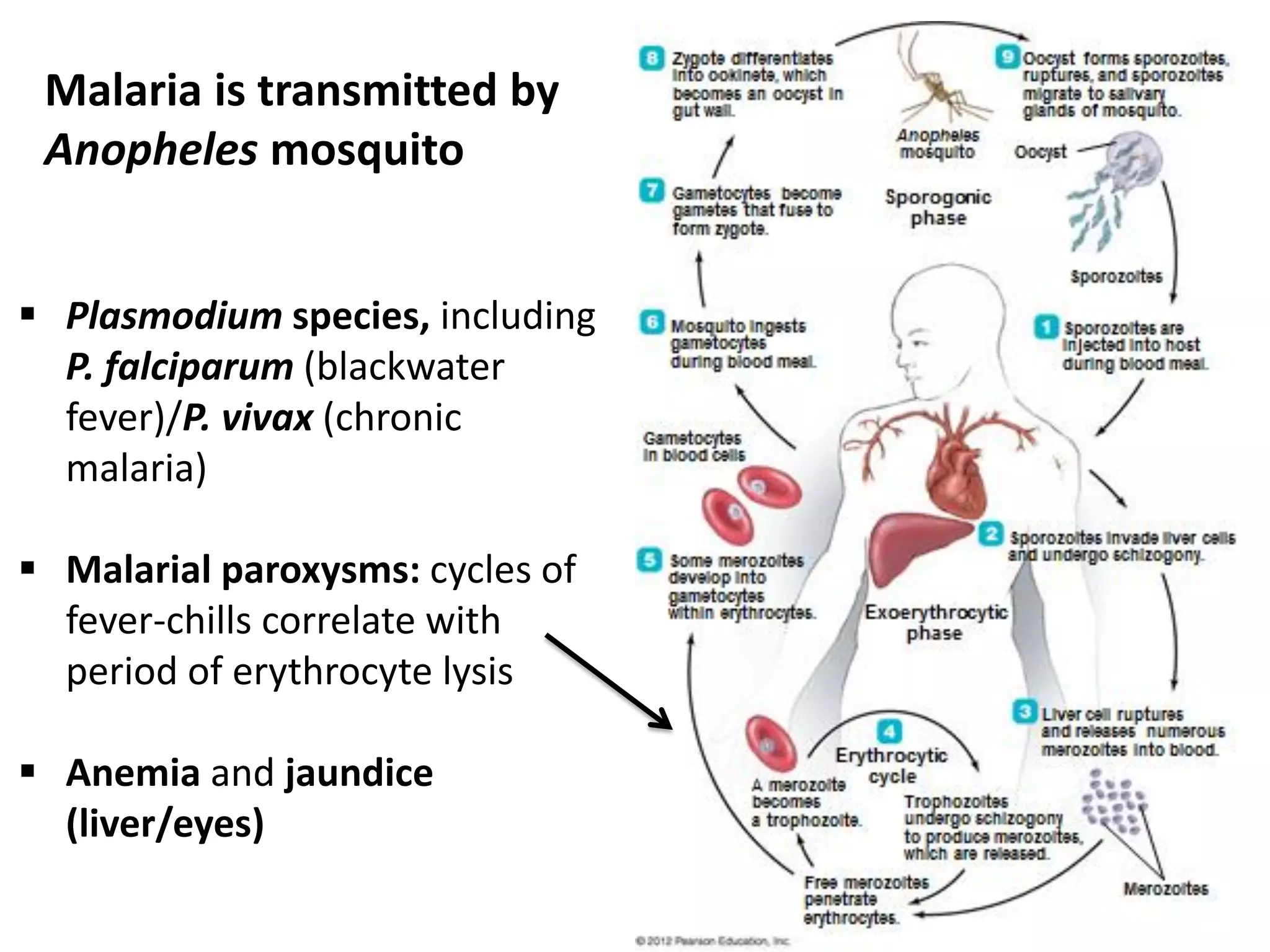
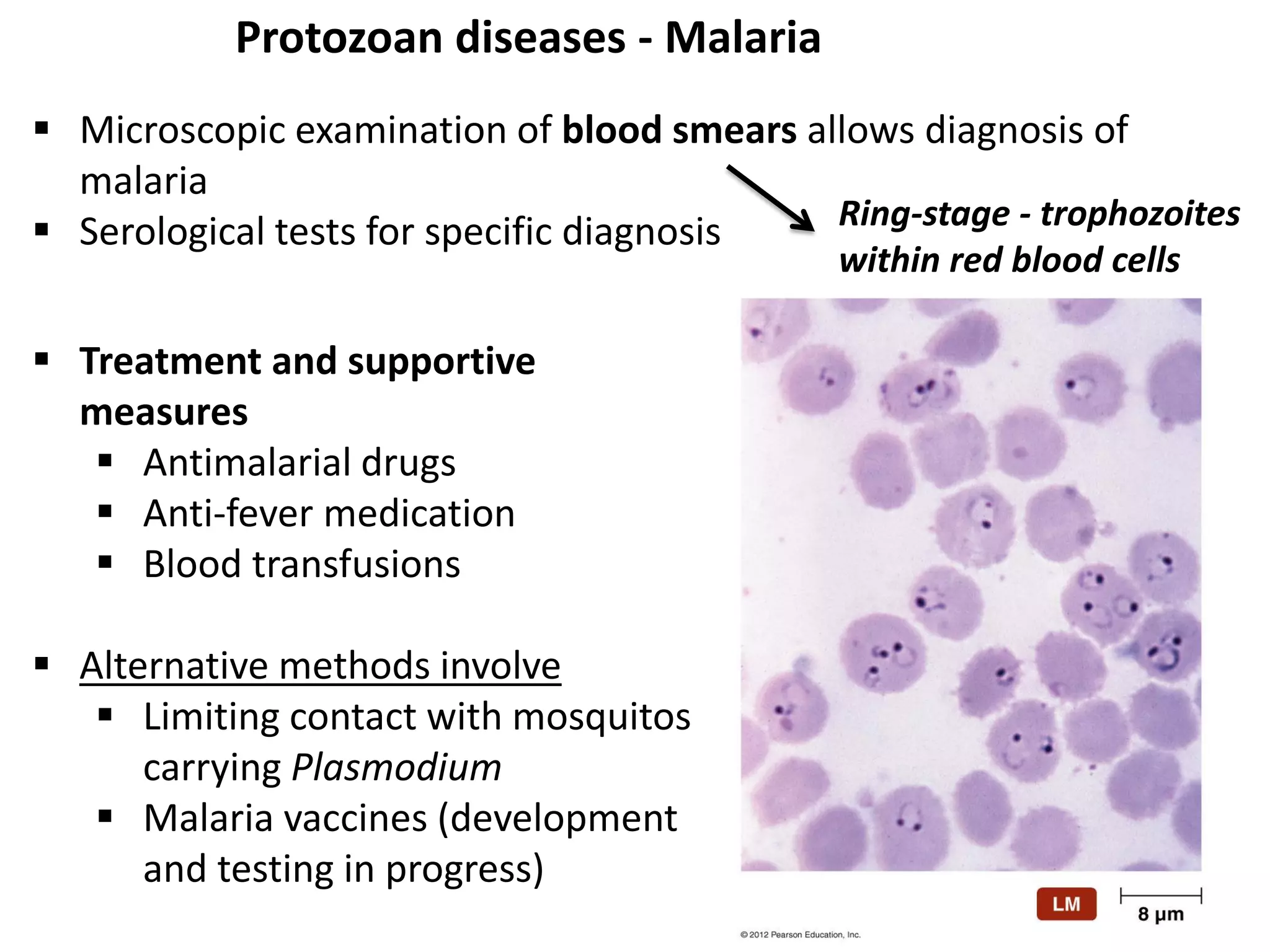
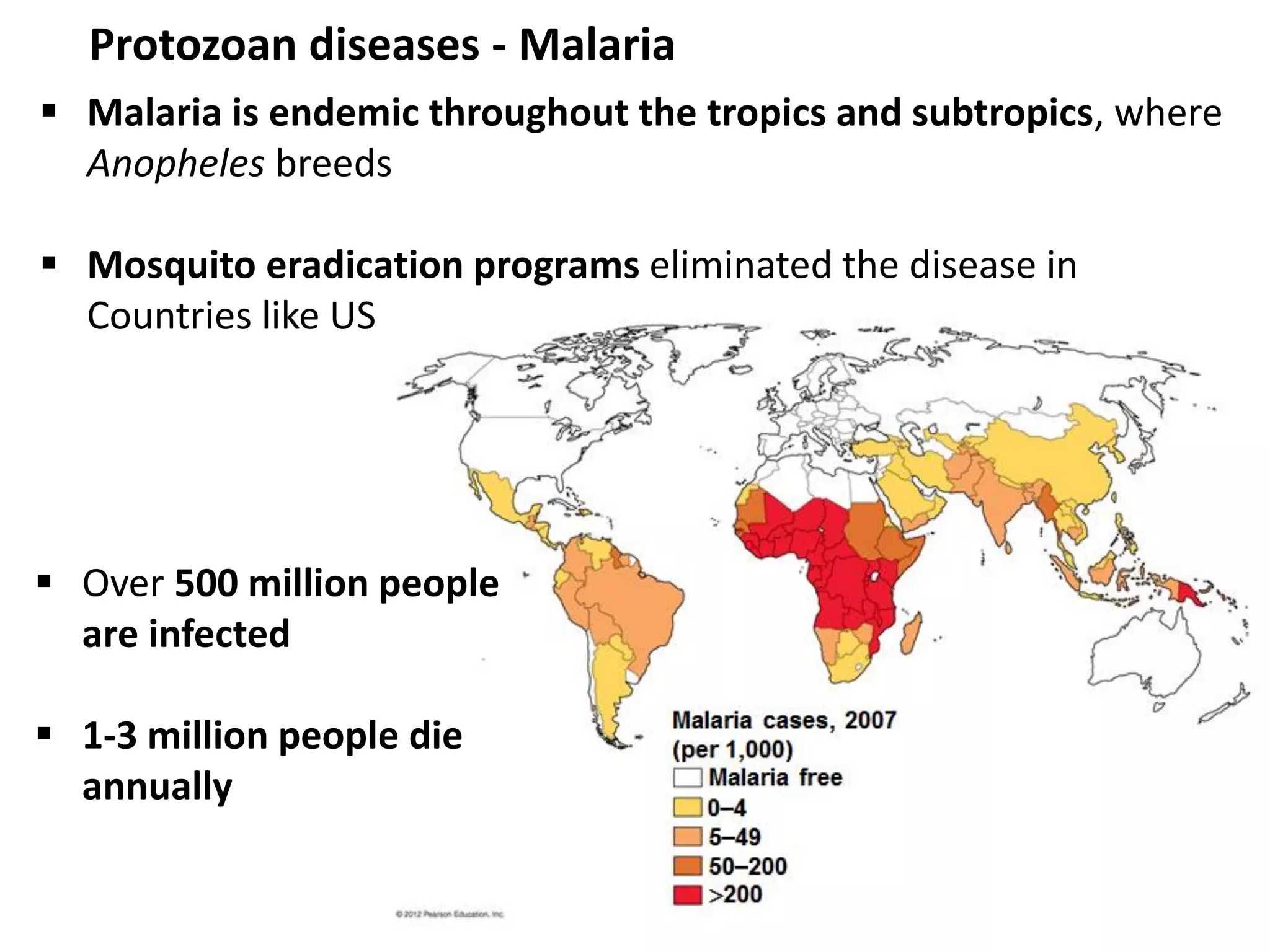
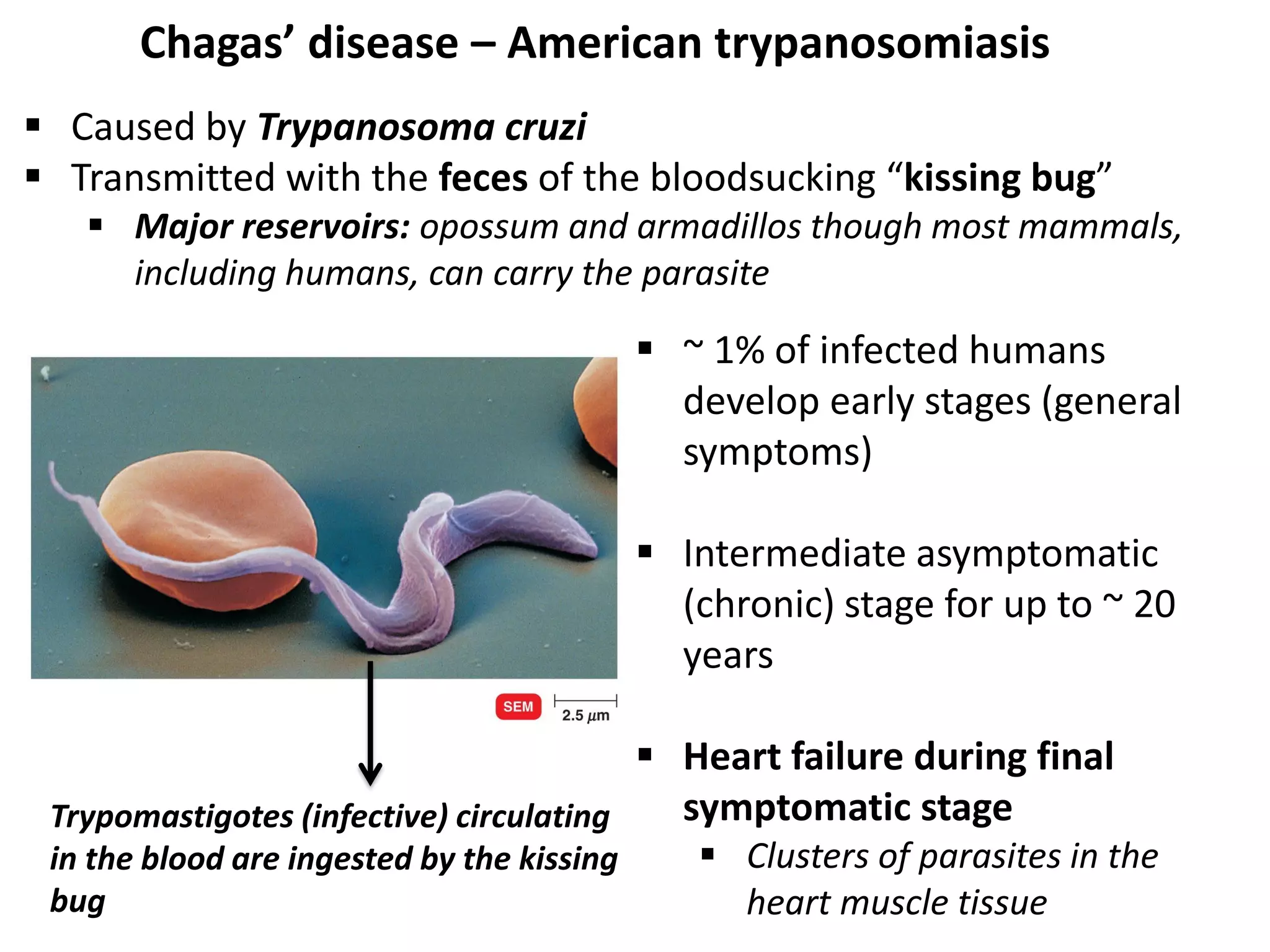
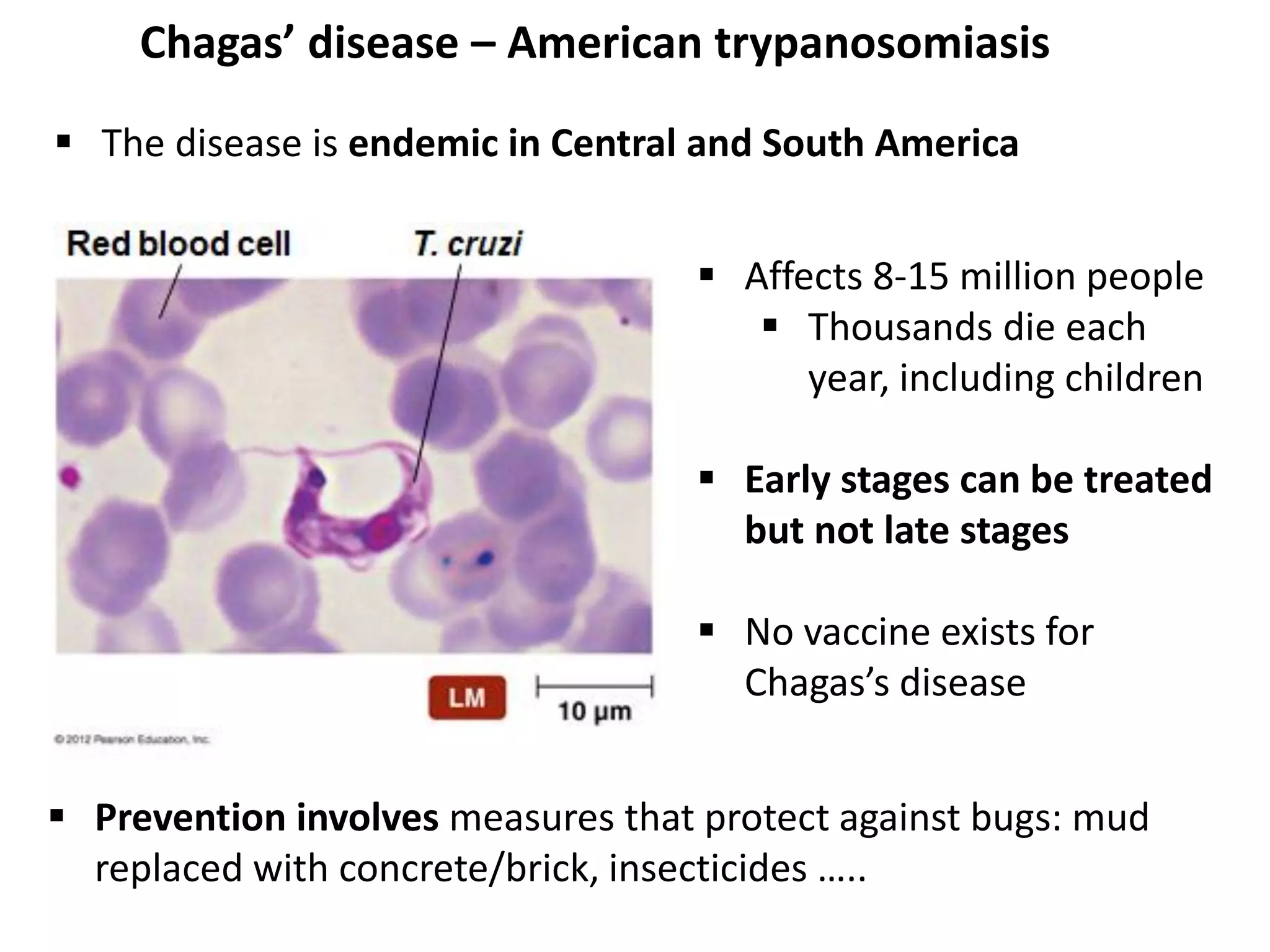
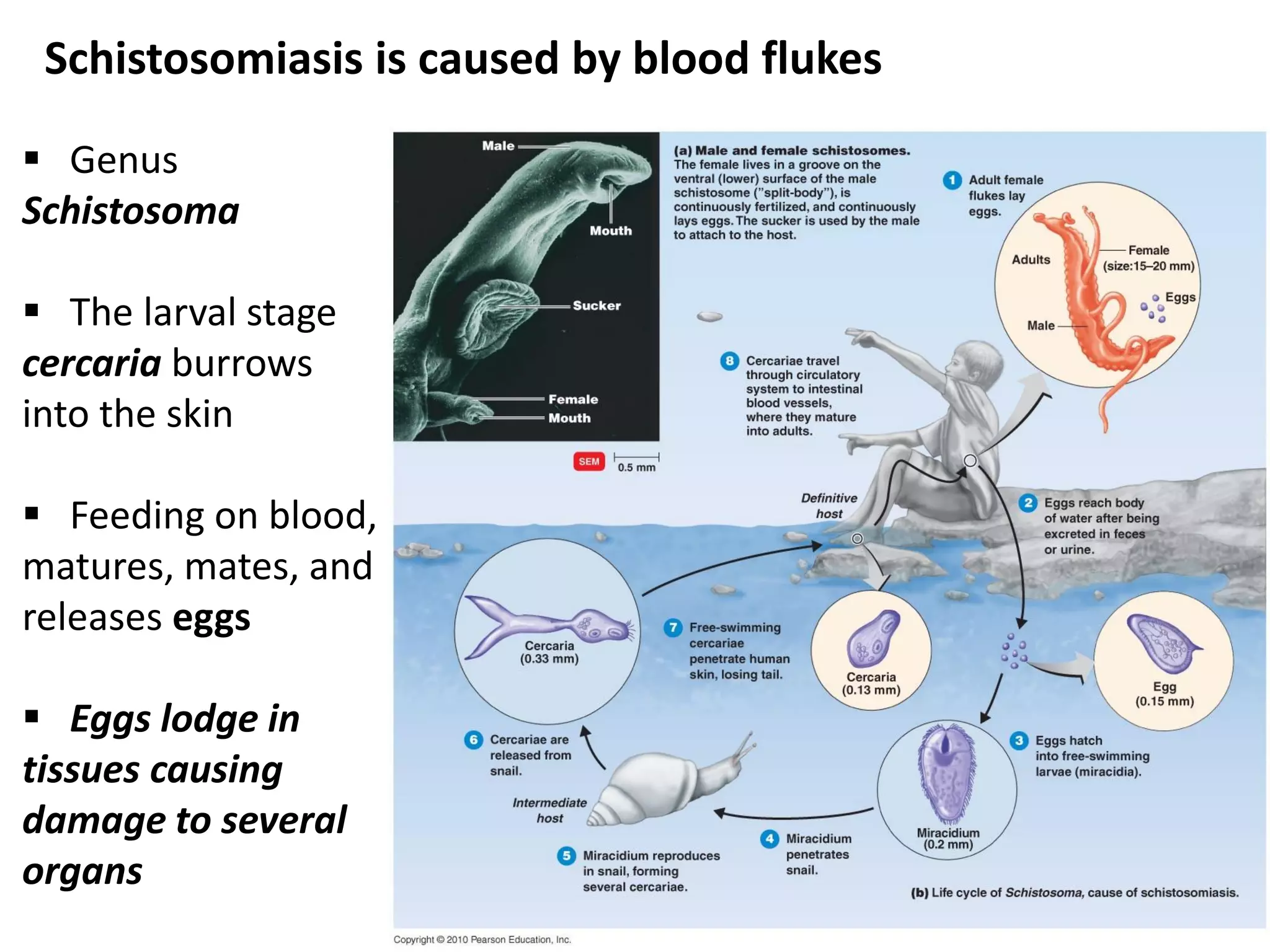
This document discusses various microbial pathogens that can cause cardiovascular and systemic diseases. It describes how bacteria, viruses, protozoa and helminths can infect the bloodstream (septicemia) and spread throughout the body, potentially infecting multiple organ systems. Examples discussed in detail include bacteremia, viral infections like Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus, and parasitic diseases such as toxoplasmosis, malaria, Chagas disease, schistosomiasis and others. For each pathogen, the document outlines the causative agent, transmission, signs and symptoms, diagnosis and available treatments.