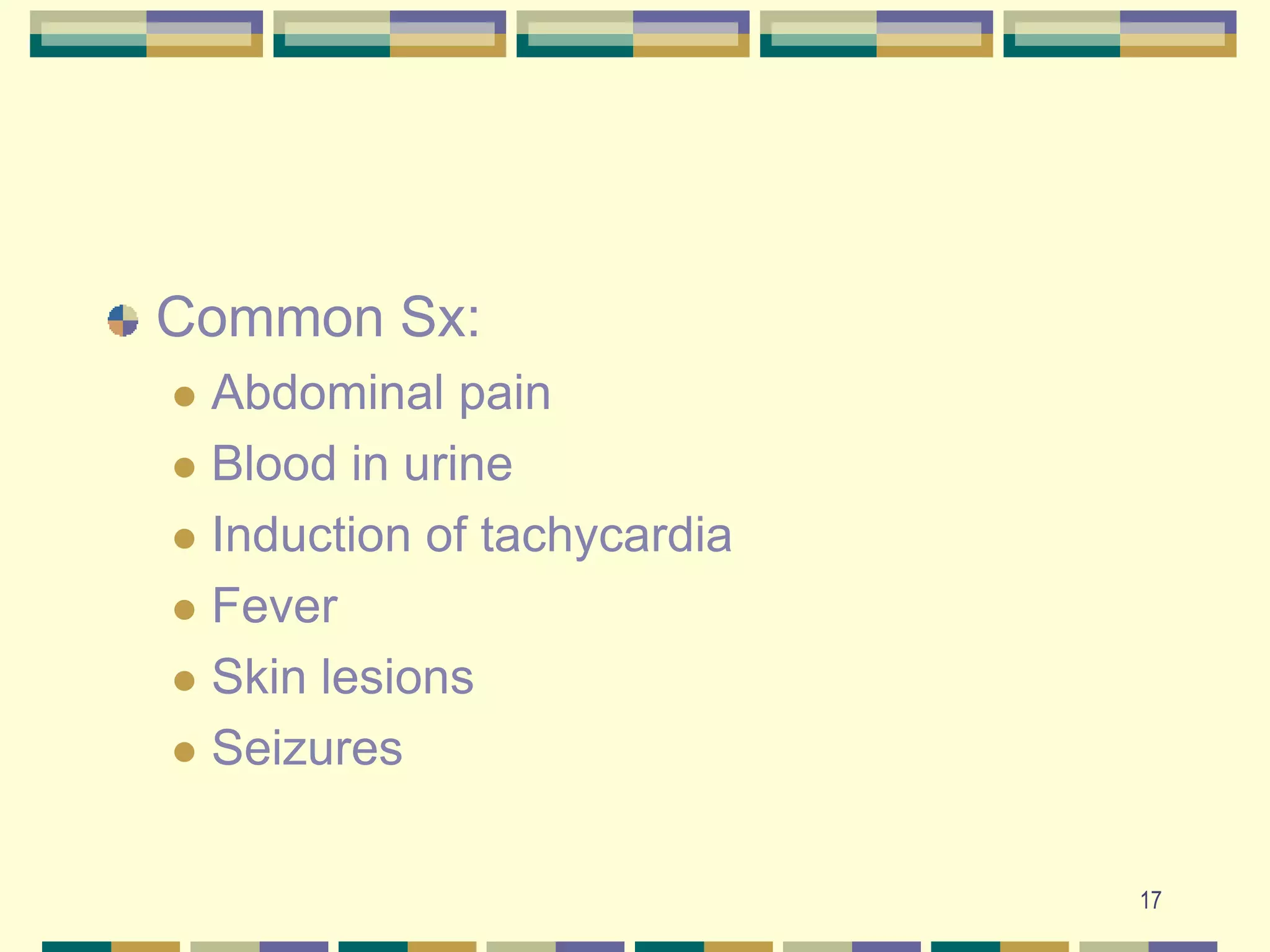
This document provides an overview of somatoform and dissociative disorders. It describes the major classifications in the DSM-IV including somatization disorder, conversion disorder, hypochondriasis, body dysmorphic disorder, pain disorder, and undifferentiated somatoform disorder. Key characteristics, differential diagnoses, treatments, and prognoses are outlined for each disorder. Paraphilias are also discussed including types such as pedophilia, voyeurism, and fetishism. Gender identity disorder and homosexuality are differentiated from paraphilias.



![5Somatoform disorders are more common in female except for Hypochondrasis, which is found equally in both50% of patients also have another mental disorder [depression and anxiety]Patient unconsciously expresses an unacceptable emotion as a physical symptom so he does not have to deal with the emotion [primary gain]Symptoms allows the patient to get attention from others or avoid responsibility [secondary gain]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psychlecture7somatoform-1ppt-090706120213-phpapp01/75/Psych-Lecture-7-Somatoform-1ppt-5-2048.jpg)



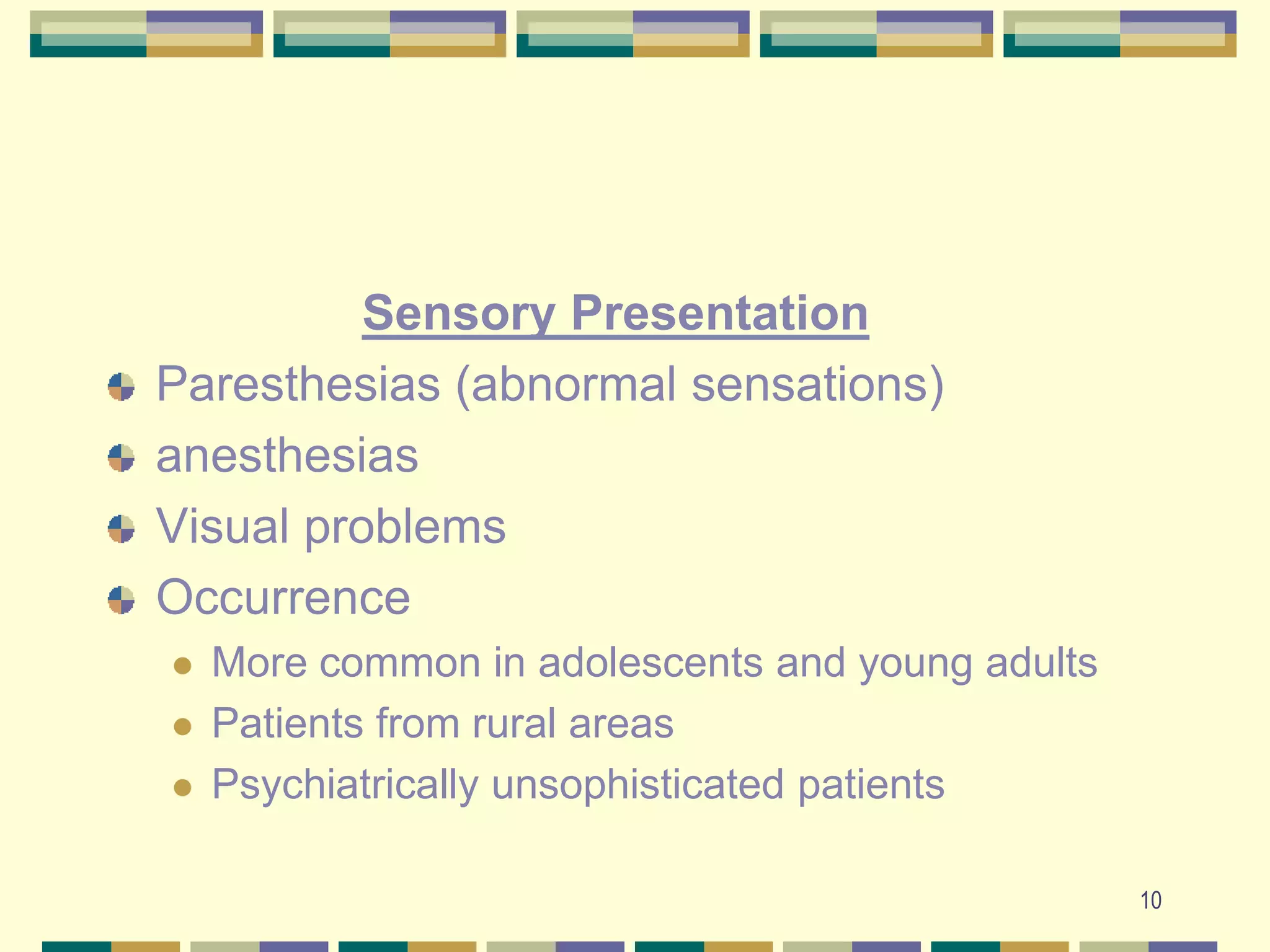
![9Conversion DisorderAbrupt, dramatic loss of motor or sensory function or organ of special senseMotor PresentationParalysis [which shifts to different areas of the body]Seizures, which are often bizarreGlobus hystericus (lump in the throat)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psychlecture7somatoform-1ppt-090706120213-phpapp01/75/Psych-Lecture-7-Somatoform-1ppt-9-2048.jpg)


![13Body Dysmorphic DisorderPatient is preoccupied with a defect in appearance [but has a normal appearance]If defect present it is usually very minorMost often complaint involves slight flaws of the face and headOnset usually in the late teensChronic course with variable levels of concern over time about the physical feature causing distressPlastic surgery or other medical treatment rarely alleviates Sx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psychlecture7somatoform-1ppt-090706120213-phpapp01/75/Psych-Lecture-7-Somatoform-1ppt-13-2048.jpg)















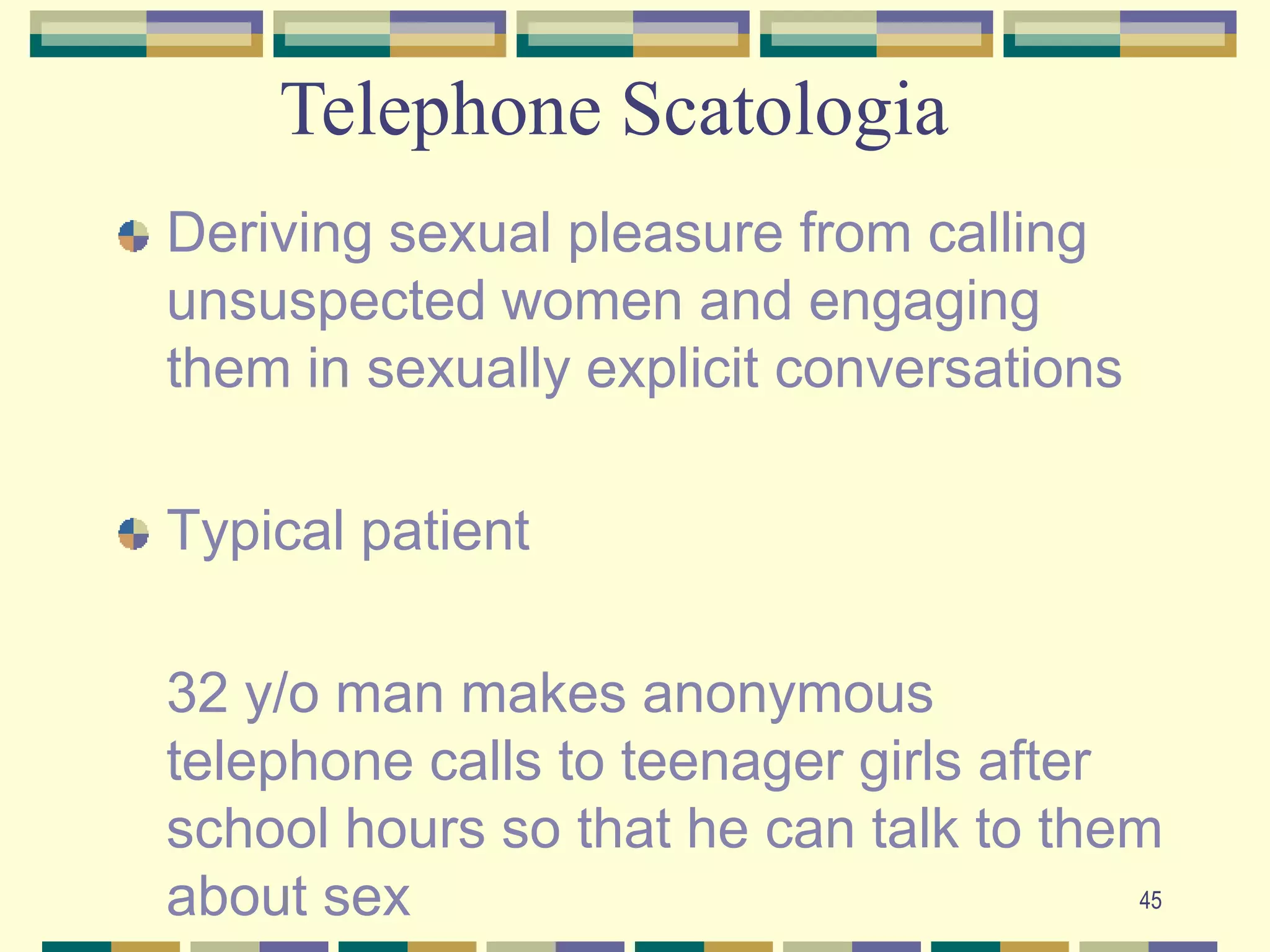
![30Mild forms may resemble borderline personality disorder or schizophreniaMalingering must be ruled out[when the patient presents in a forensic (legal) context]Early traumatic experienceUsually abuse in childhood or adolescenceMost commonly associated with incest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psychlecture7somatoform-1ppt-090706120213-phpapp01/75/Psych-Lecture-7-Somatoform-1ppt-30-2048.jpg)
![31In some cases, integration of the personalities using insight-oriented psychotherapy with or without hypnosisAntidepressants, antianxiety and anticonvulsant agents may be helpfulOften chronic and associated with other psychiatric symptoms [depression and anxiety]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psychlecture7somatoform-1ppt-090706120213-phpapp01/75/Psych-Lecture-7-Somatoform-1ppt-31-2048.jpg)
![32Depersonalization DisorderRecurrent and persistent feeling of detachment from one’s own body or social situation [ if involves environment its called derealization disorder]Sx often present in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, depression, anxiety and histrionic personality disorder](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/psychlecture7somatoform-1ppt-090706120213-phpapp01/75/Psych-Lecture-7-Somatoform-1ppt-32-2048.jpg)