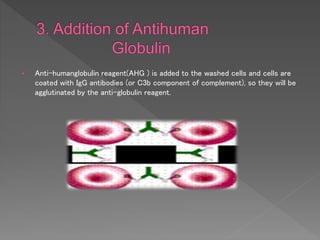
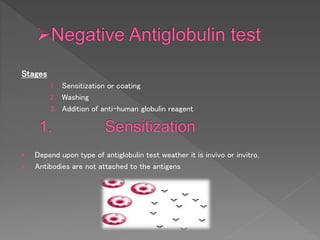
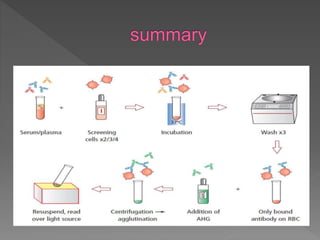
The Coombs test, also known as the direct antiglobulin test (DAT) or indirect antiglobulin test (IAT), detects antibodies or complement coating red blood cells. It involves sensitizing RBCs with patient serum, washing unbound antibodies, then adding anti-human globulin reagent to form a "bridge" and cause agglutination if antibodies or complement are present on the RBCs. Controls like Coombs control check cells are used to validate negative results and detect technical problems. The DAT detects in vivo coating while the IAT detects in vitro coating during antibody screening and identification.