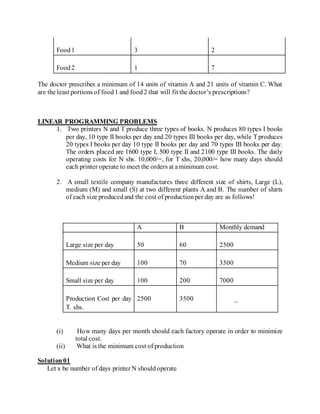
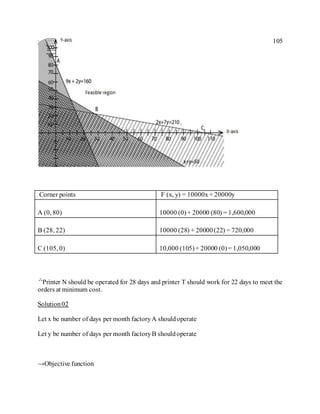
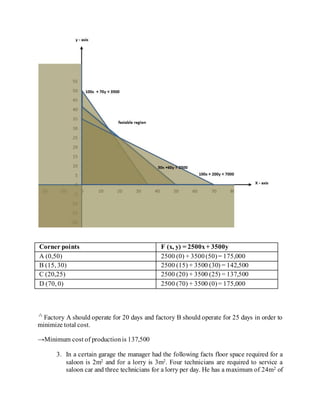
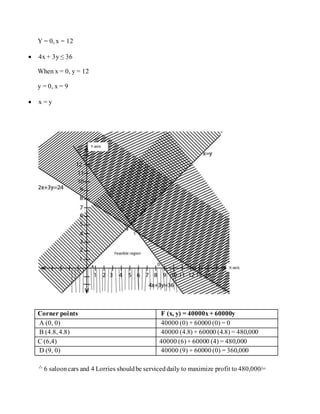
The document defines linear programming as a branch of mathematics used to find the optimal solution to problems with constraints. It provides examples of using linear programming to maximize profit or minimize costs in organizations. It also introduces drawing linear inequalities and solving simultaneous inequalities. The steps to formulate a linear programming problem are identified as defining variables and objectives, translating constraints, finding feasible solutions, and evaluating objectives to find optimal solutions.










![More example
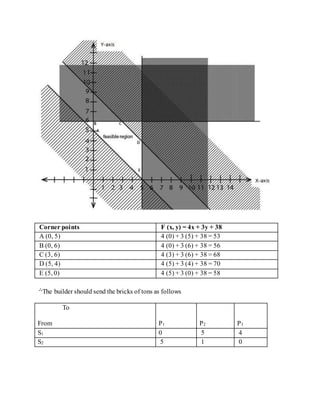
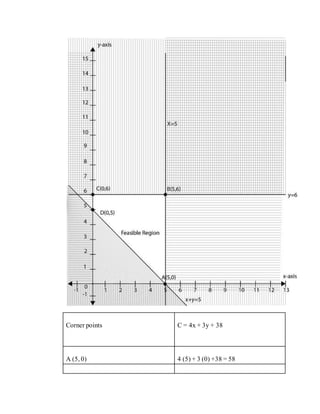
A builder has two stores, one at S1 and the other at S2. He is building houses at P1, P2, and P3.
He needs 5 tons of bricks at P1, 6 tons of bricks at P2 and 4 tons of bricks at P3. The stores
contain 9 tons of bricks at S1 and 6 tons of bricks at S2. The transport cost per ton are shown
in the diagram
To From P1 P2 P3
S1 6/= 3/= 4/=
S2 4/= 2/= 6/=
How does the builder send his bricks at a minimum cost?What is the minimum overall cost?
Solution
Let the builder send x tons of bricks from S1 to P1 and y tons of bricks from S1 to P2
Then the transportationof bricks to P1, P2 and P3 will be as follow: -
To
From P1 P2 P3
S1 X Y 9 – (x +
y)
S2 5 – x 6 – y 4 – [9 –
(x + y)]
The constrains are obtainedas follows
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
9 – (x + y) ≥ 0 i.e. x + y ≤ 9
5 – x ≥ 0 i.e. x ≤ 5
6 – y ≥ 0 i.e. y ≤ 6
4 – [9 - (x + y)} ≥ 0 i.e. x + y ≥ 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linear-190508080813/85/LINEAR-PROGRAMING-21-320.jpg)
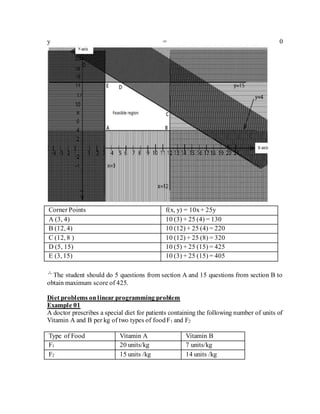
![Objective function
F (x, y) = 6x + 3y + 4(9 - (x + y)) + 4 (5 – x) + 2(6 – y) +6 [4 – (9 - (x + y)]
= 6x + 3y +36 – 4x+ 4y + 20 – 4x+ 12 – 2y + 24 – 54 + 6x+ 6y
F (x, y) = 4x – 3y+ 38
Minimize f (x, y) = 4x – 3y + 38
Subject to x + y ≤ 9
x + y ≥ 5
x ≤ 5, y ≥ 0
y ≤ 6, y ≥ 0
→Equation
x + y = 9
When x = 0, y = 9
y = 0, x = 9
x + y = 5
x = 0, y = 5
y = 0, x = 9
x = 5
y = 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linear-190508080813/85/LINEAR-PROGRAMING-22-320.jpg)