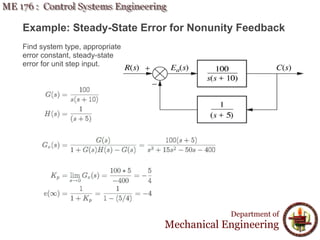
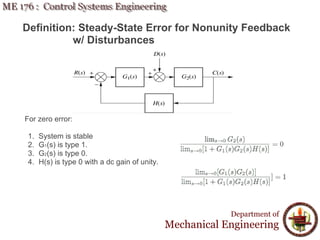
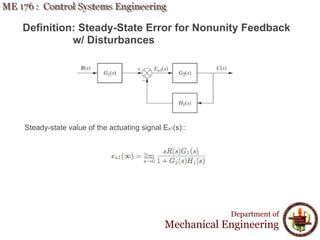
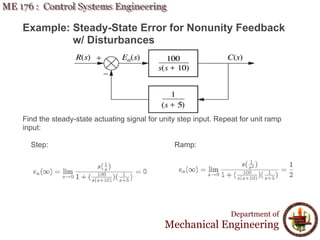
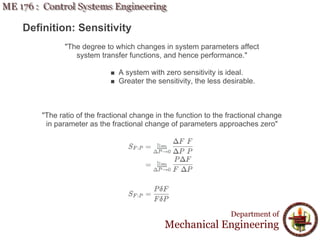
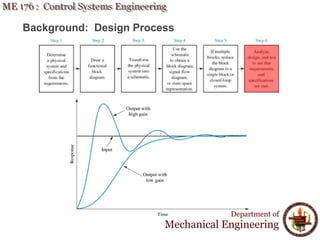
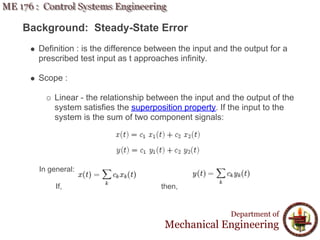
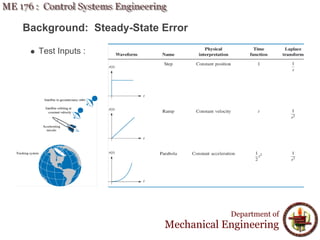
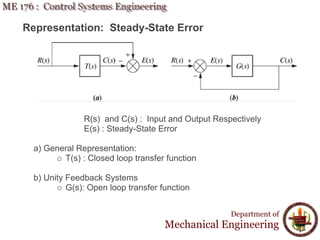
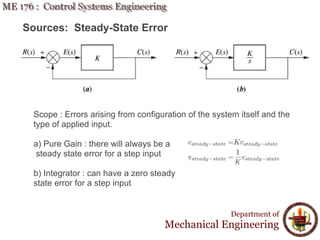
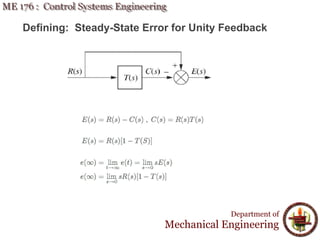
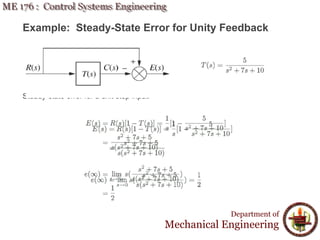
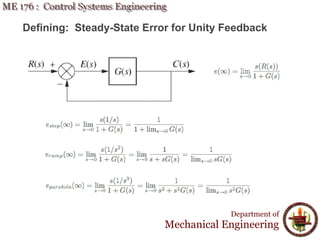
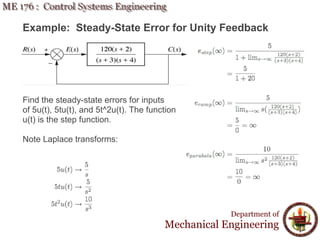
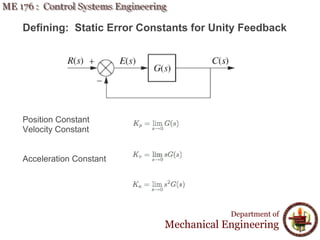
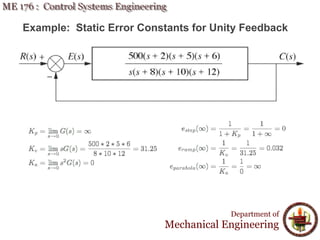
This document discusses steady-state error in control systems. It defines steady-state error and describes how it arises from system configuration and input type. Examples are provided to illustrate calculating steady-state error for various system types and inputs, including step, ramp, and disturbances. Sensitivity analysis is also introduced to analyze how changes in system parameters affect steady-state error.







![Definition: Steady-State Error for Nonunity Feedback
Move R(s) to right
of summing
junction.
Compute resulting
G(s) and H(s).
Add and subtract
unity feedback
paths.
Combine negative
feedback path to H
(s).
Combine feedback
system consisting
of G(s) and [H(s)
-1].
Department of
Mechanical Engineering](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture12me1766steadystateerror-12555290178452-phpapp03/85/Lecture-12-ME-176-6-Steady-State-Error-23-320.jpg)