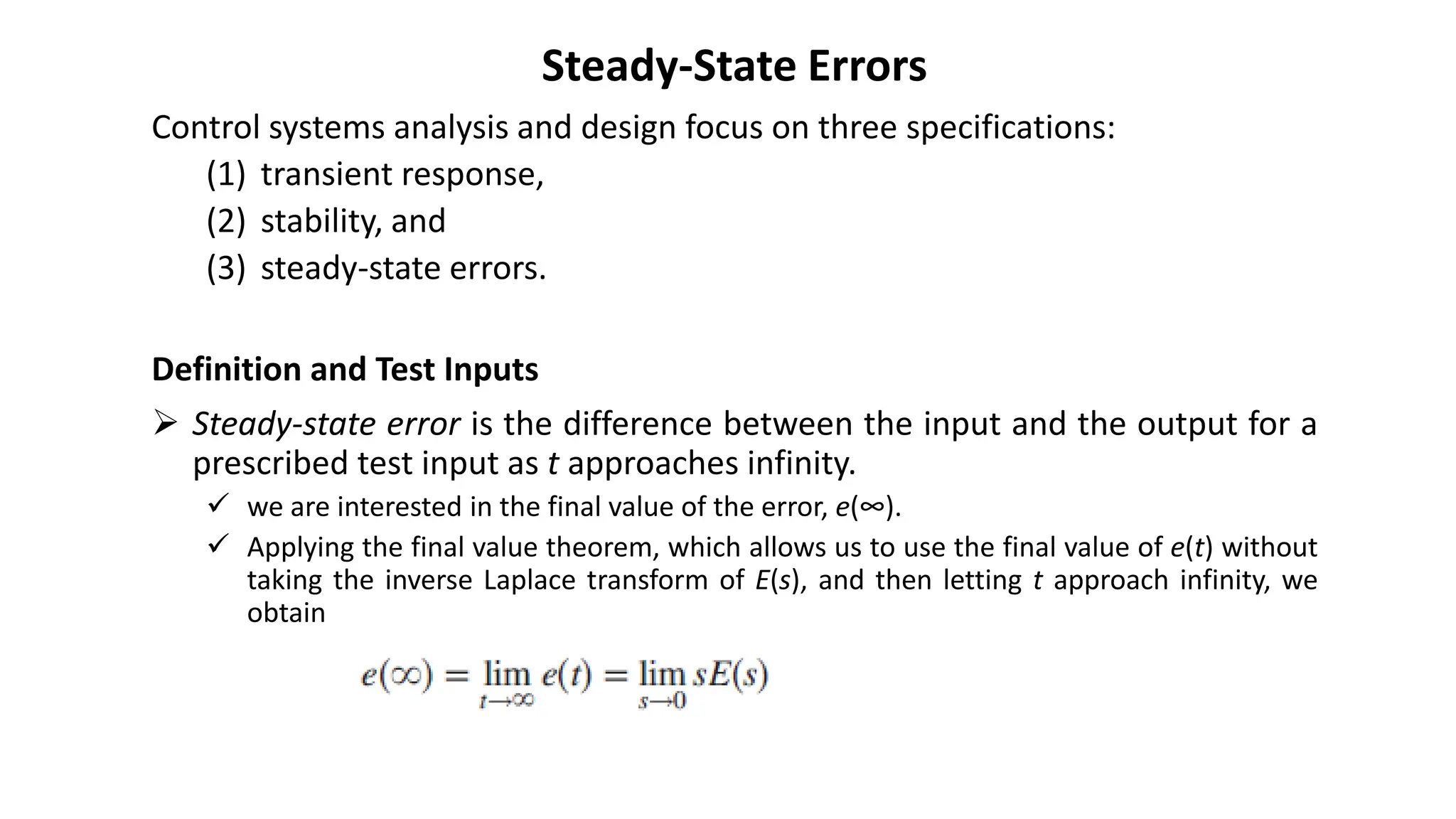
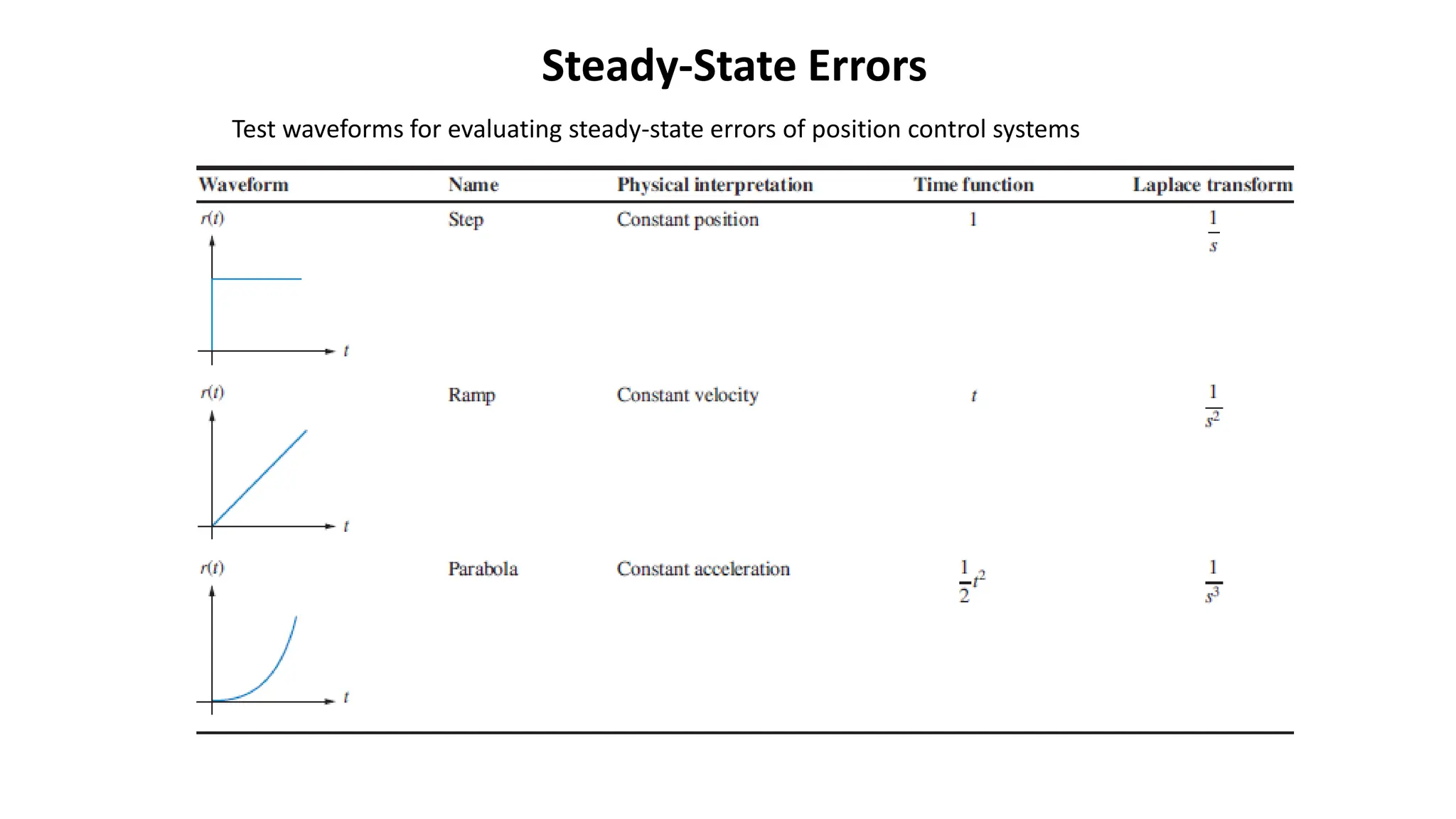
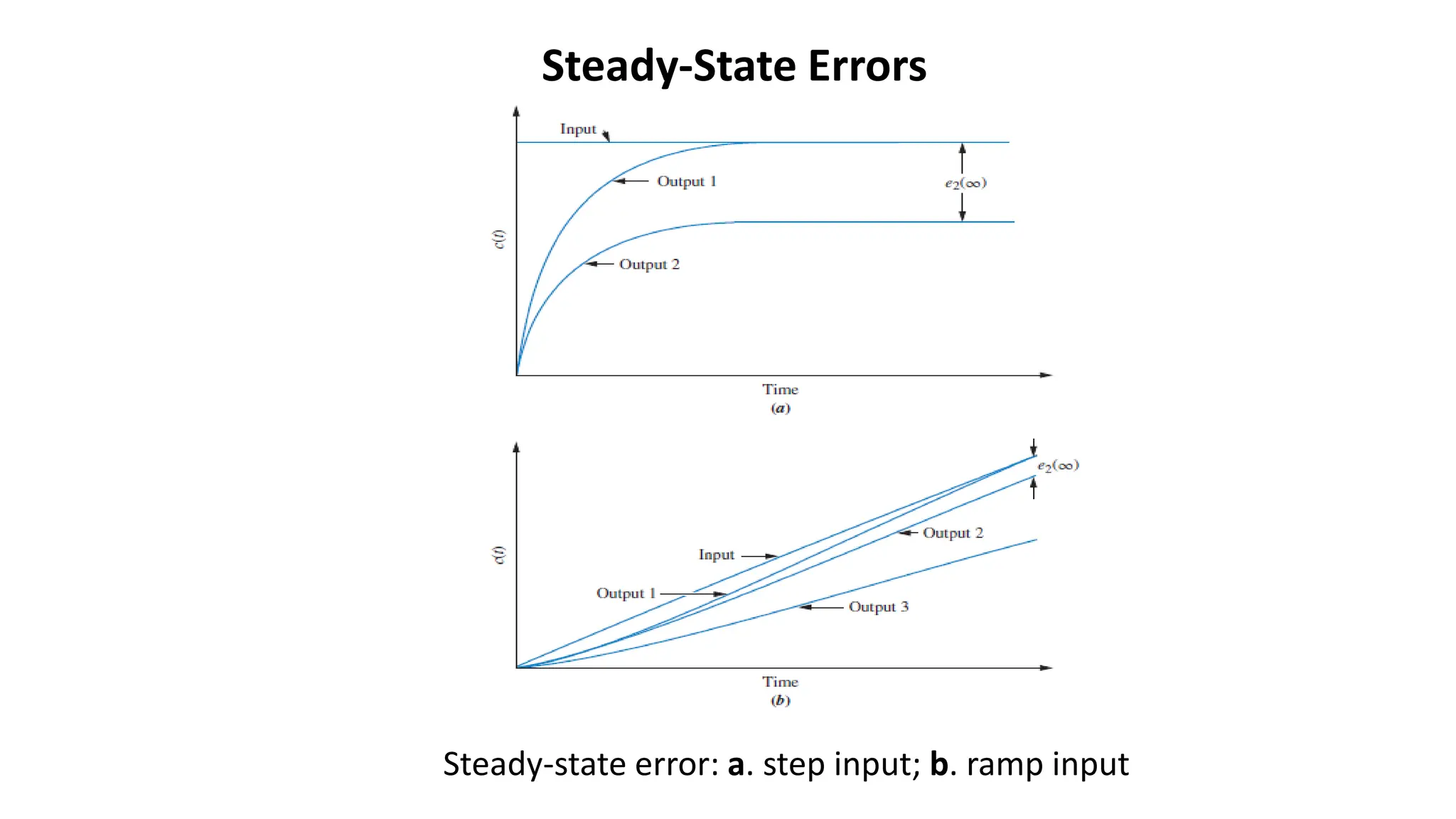
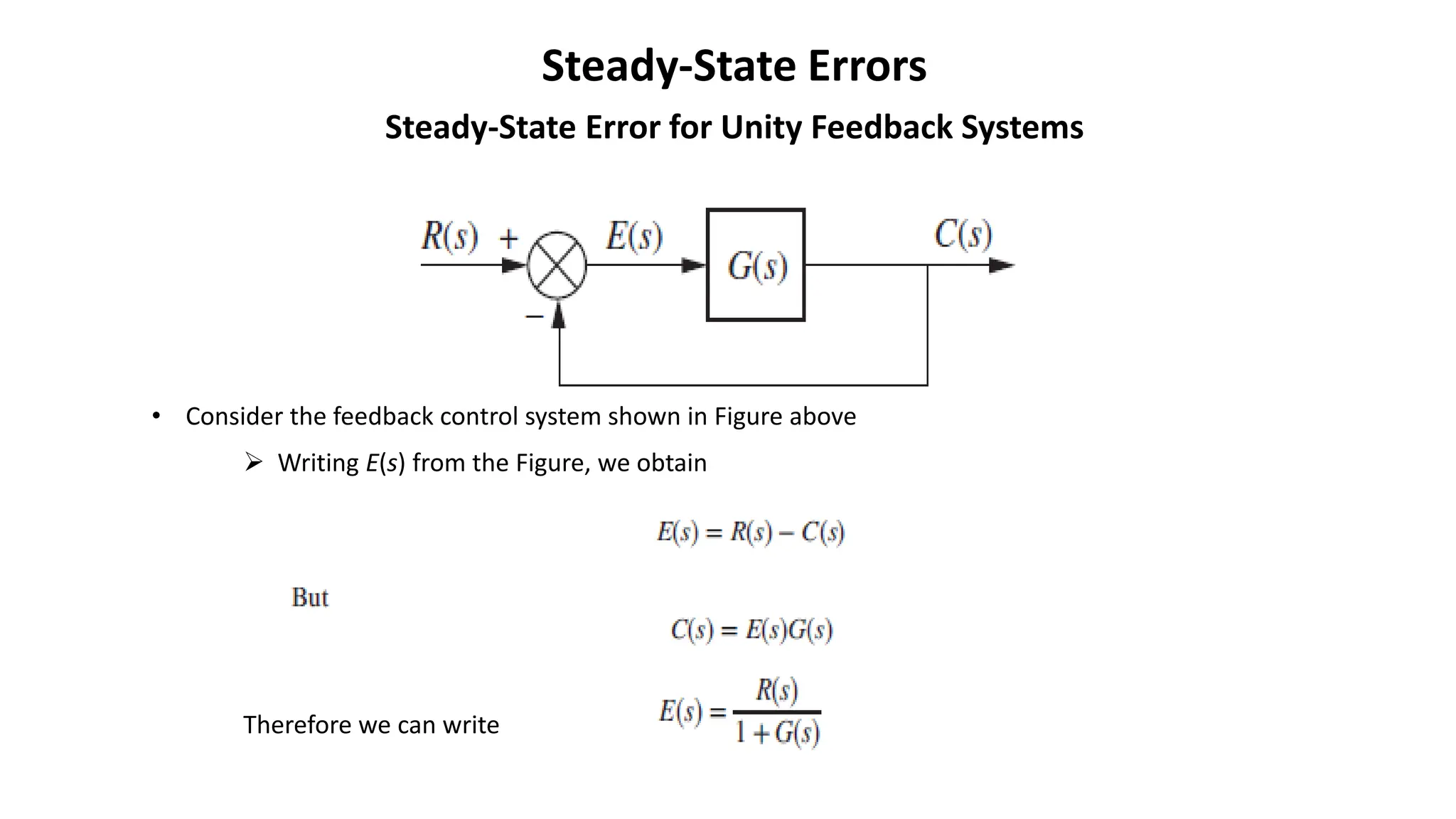
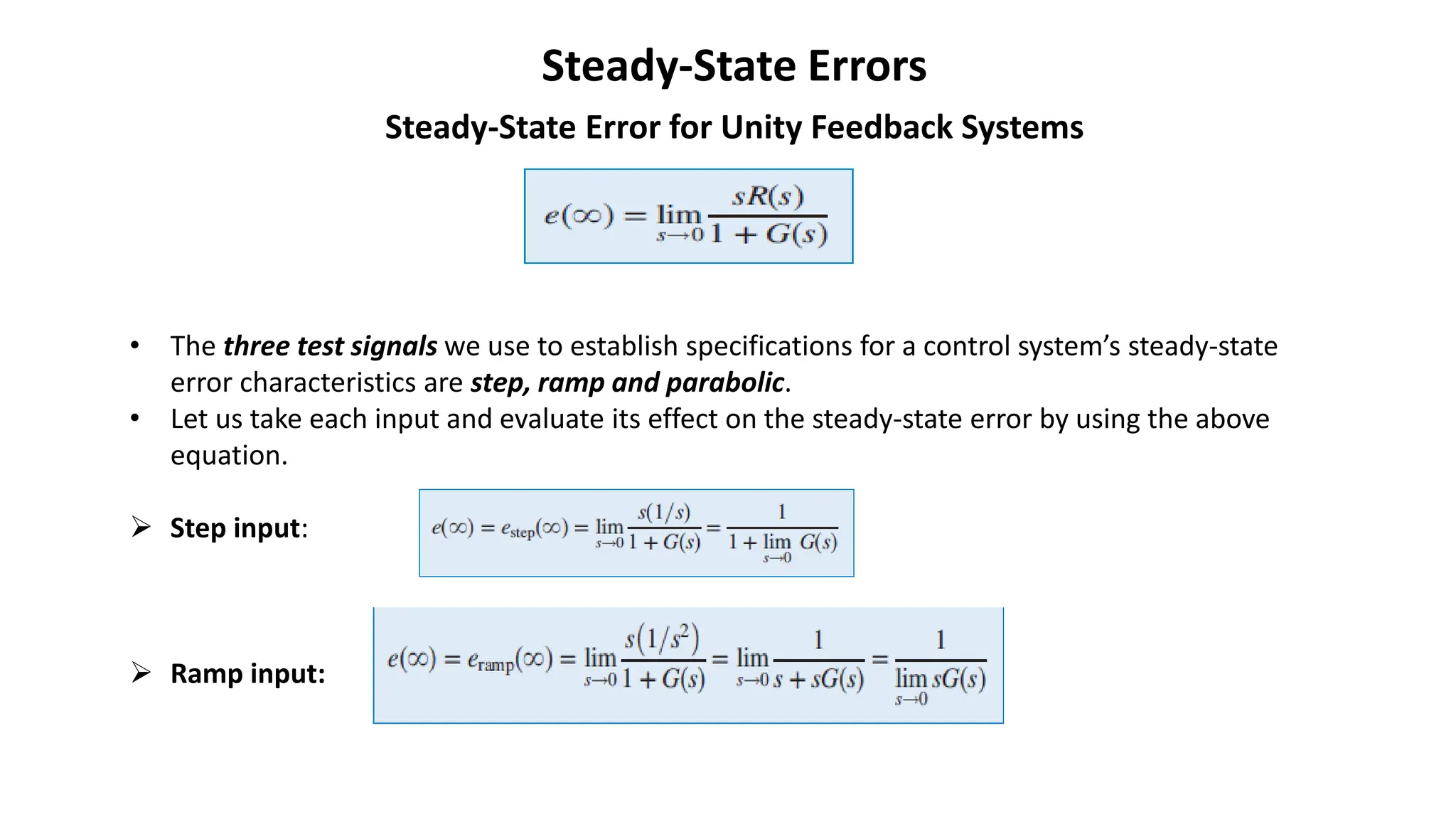
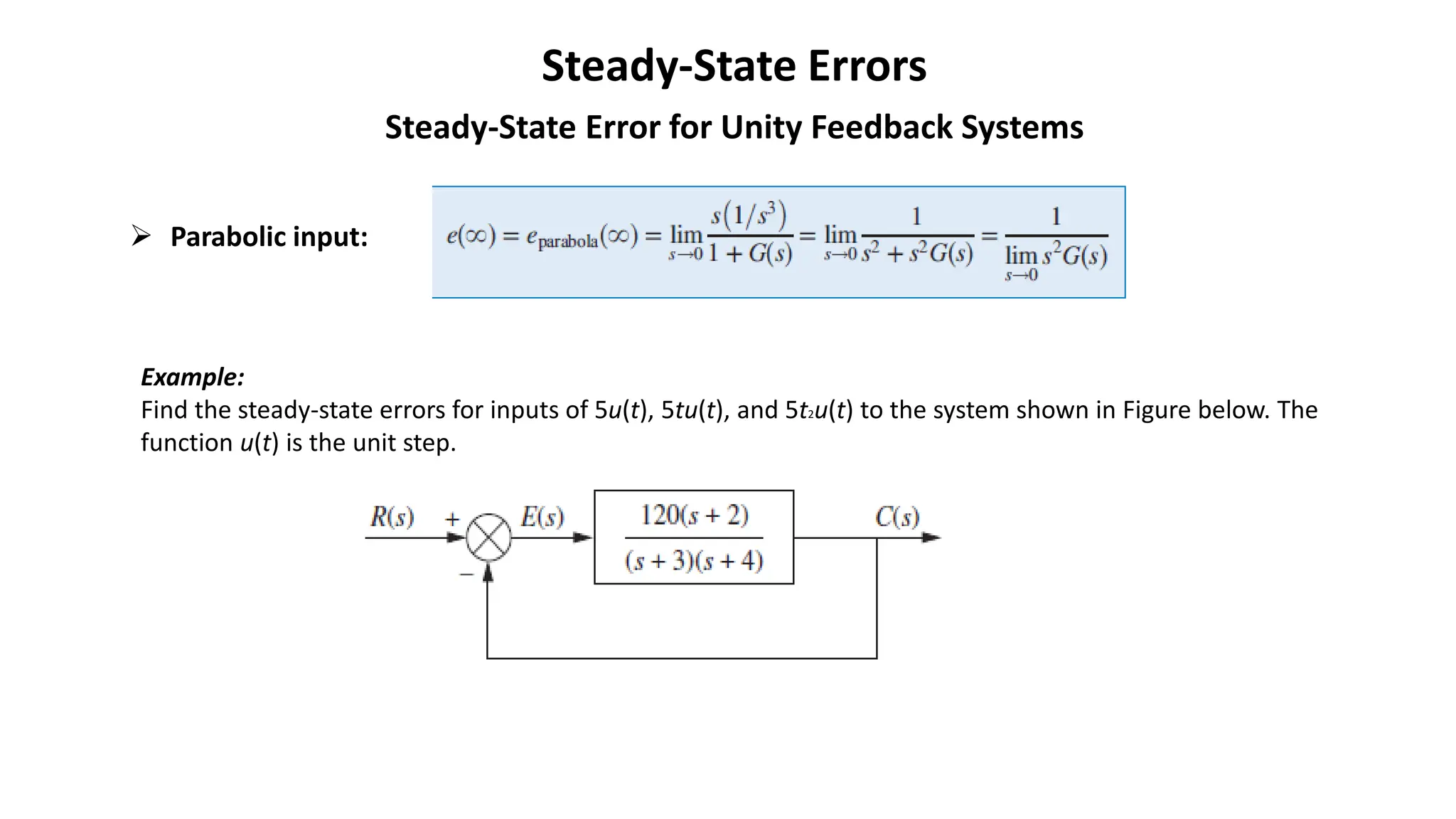
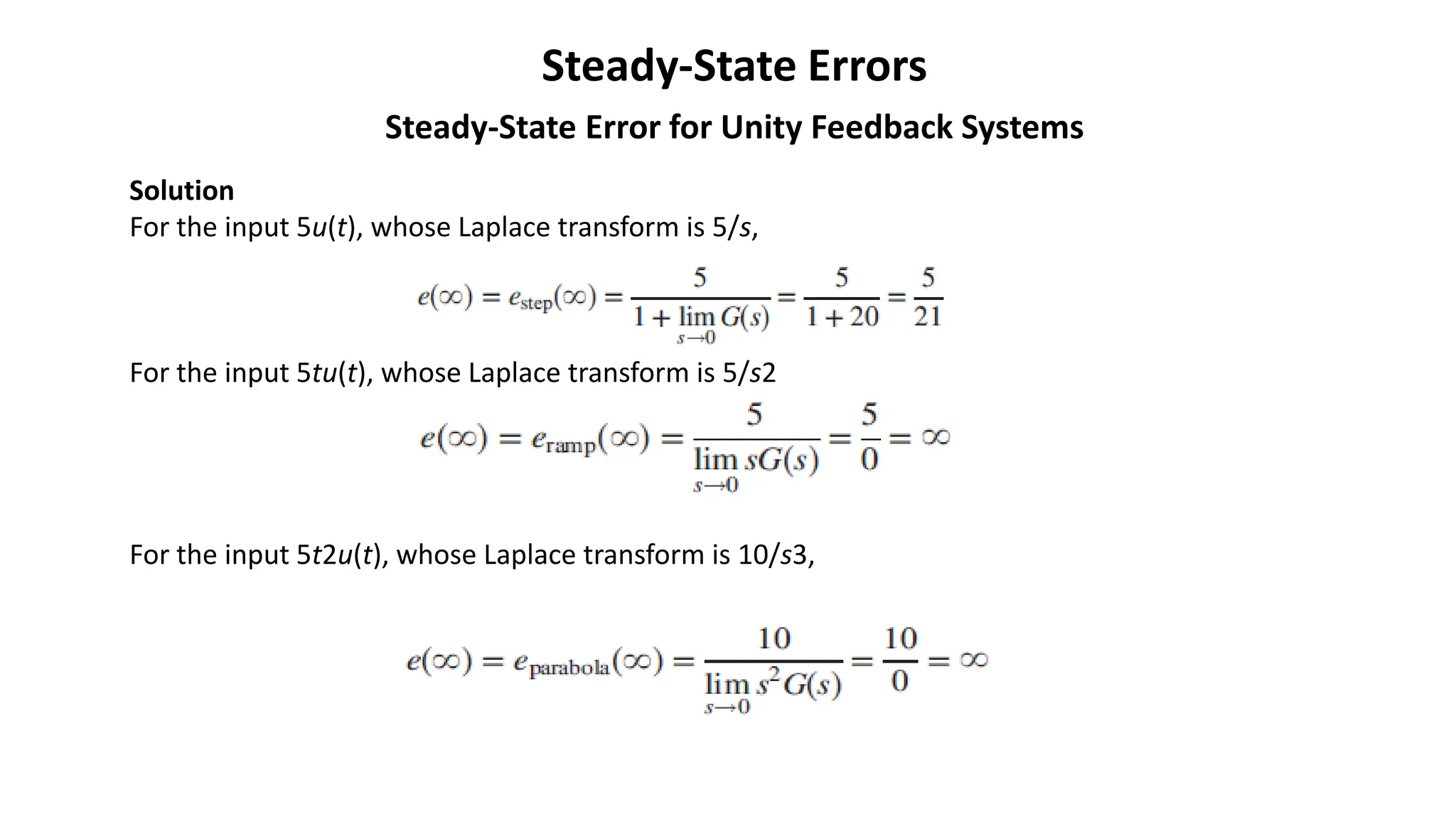
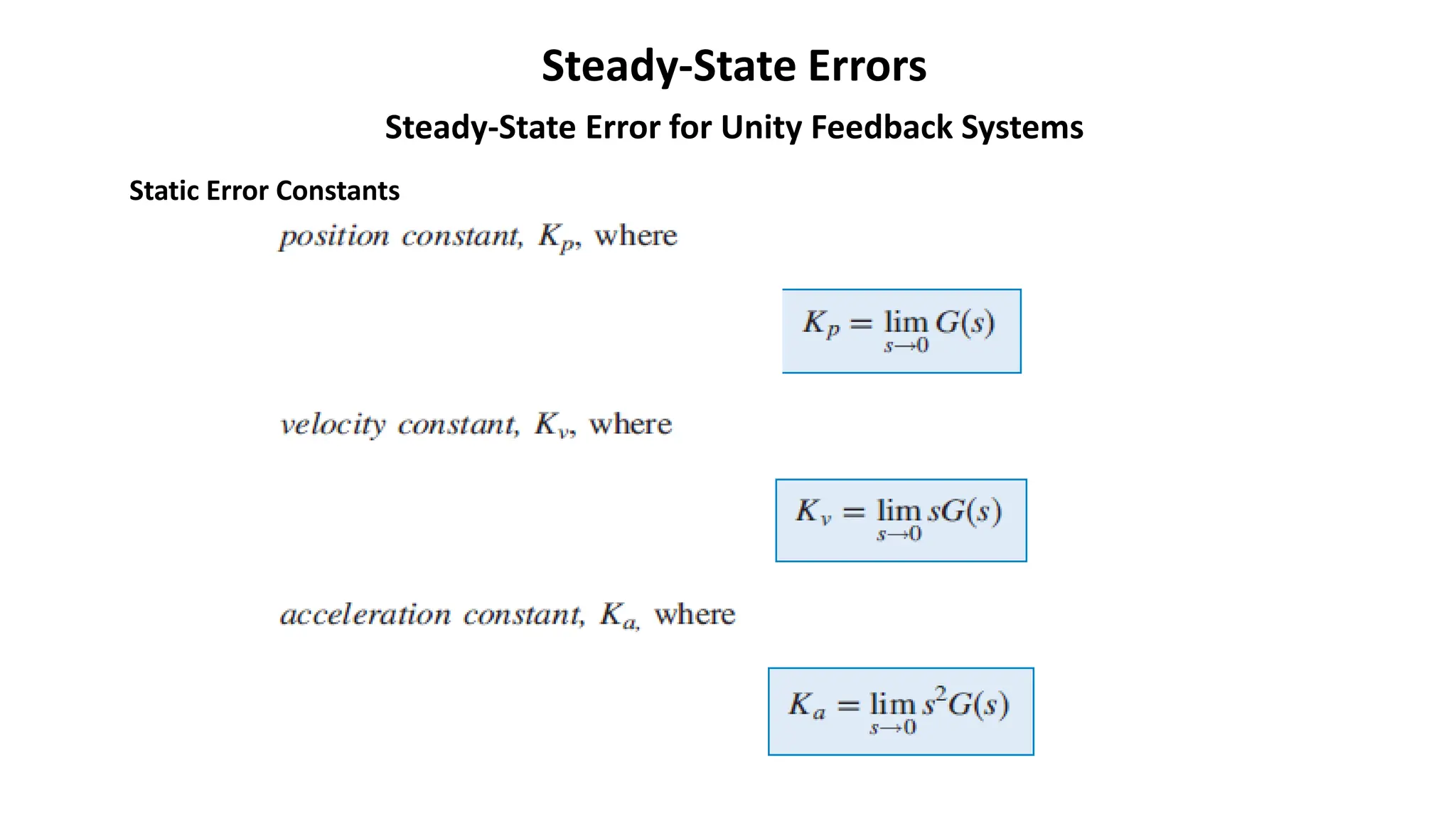
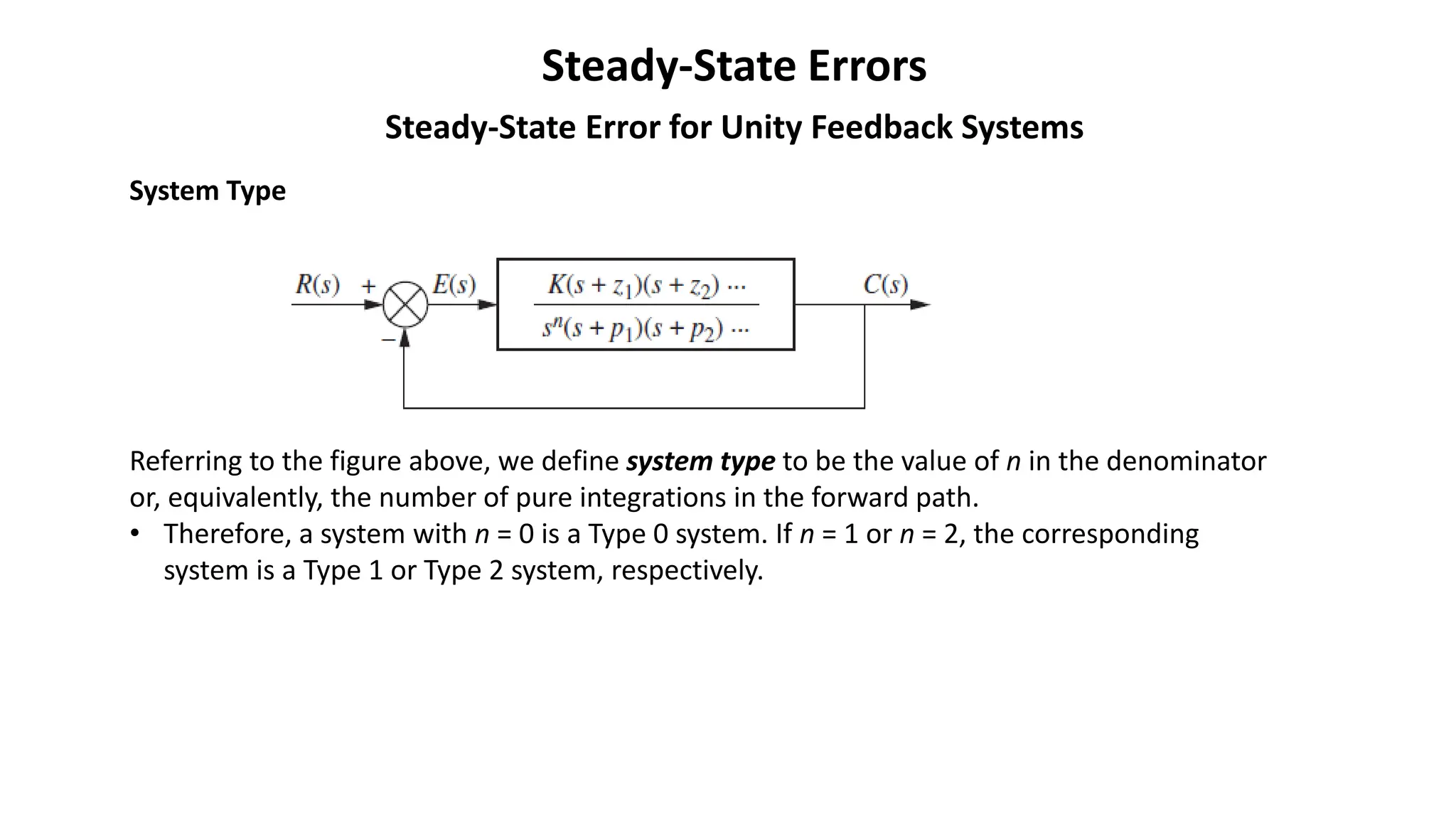
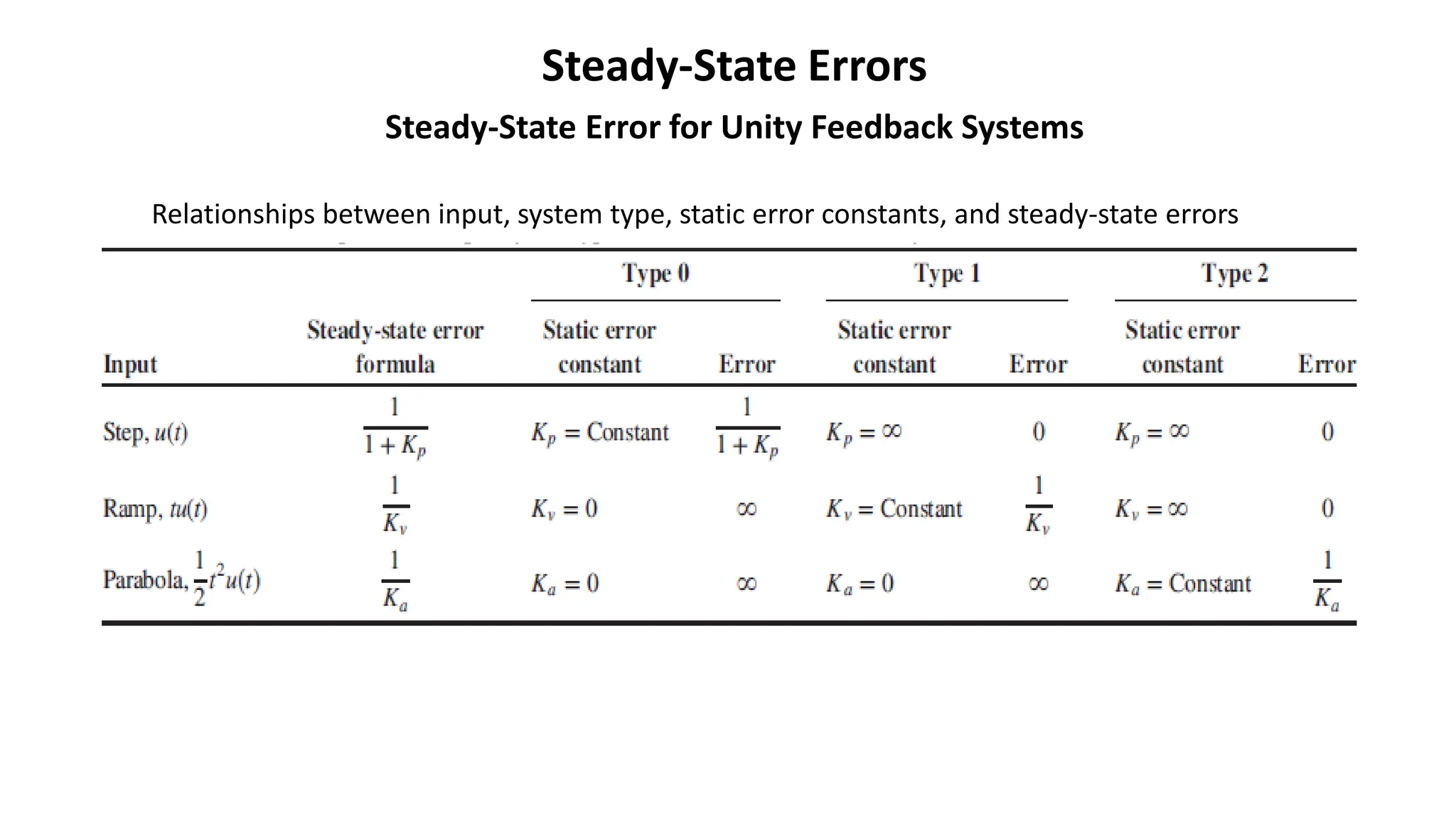
Steady-state error is the difference between the input and output of a system as time approaches infinity. It is evaluated using step, ramp, and parabolic test inputs. The steady-state error for a unity feedback system depends on the system type, which is determined by the number of integrations in the forward path. Higher system types have smaller steady-state errors. Position, velocity, and acceleration constants can be used to specify steady-state error characteristics and determine the system type and appropriate test input.