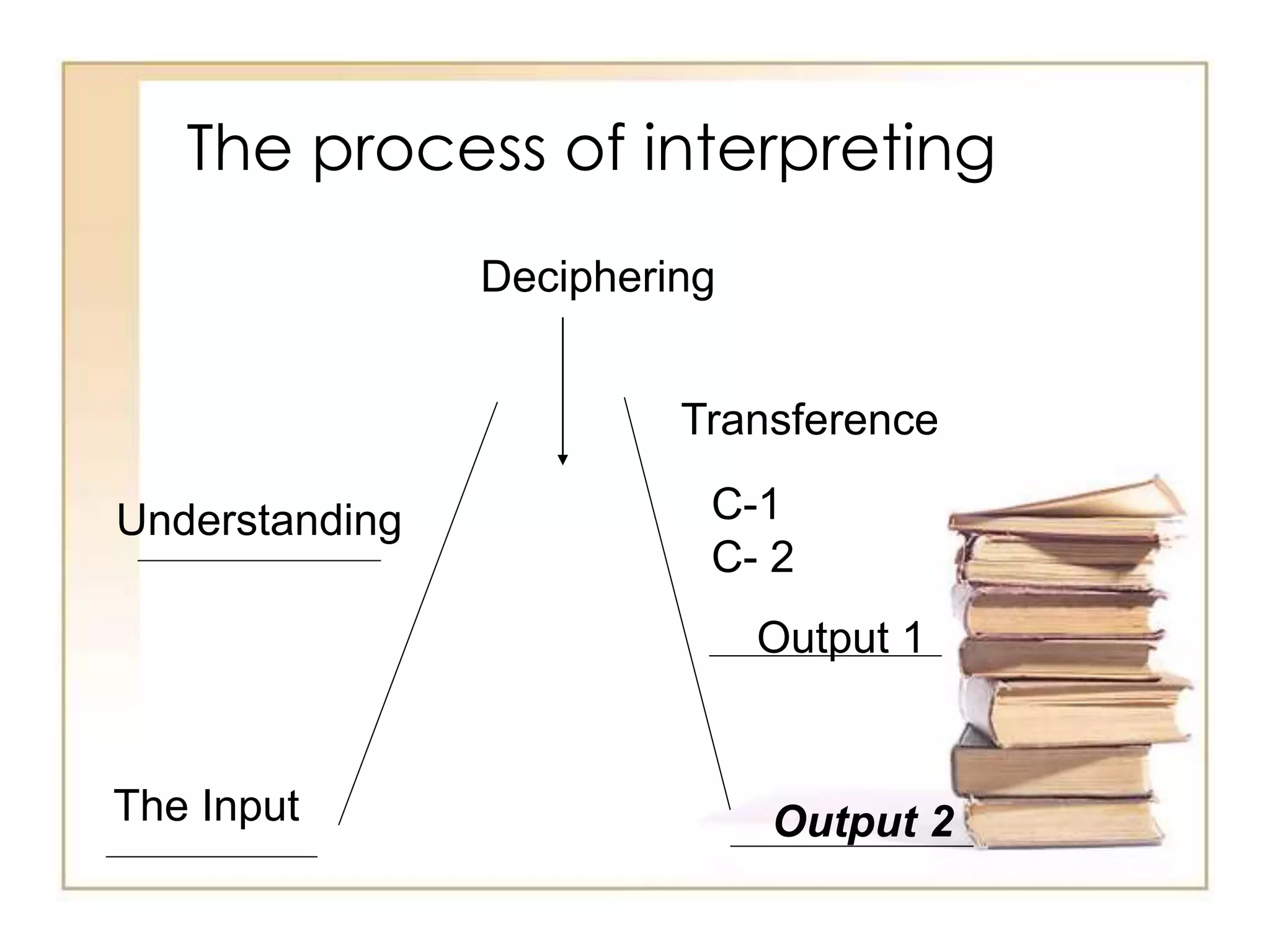
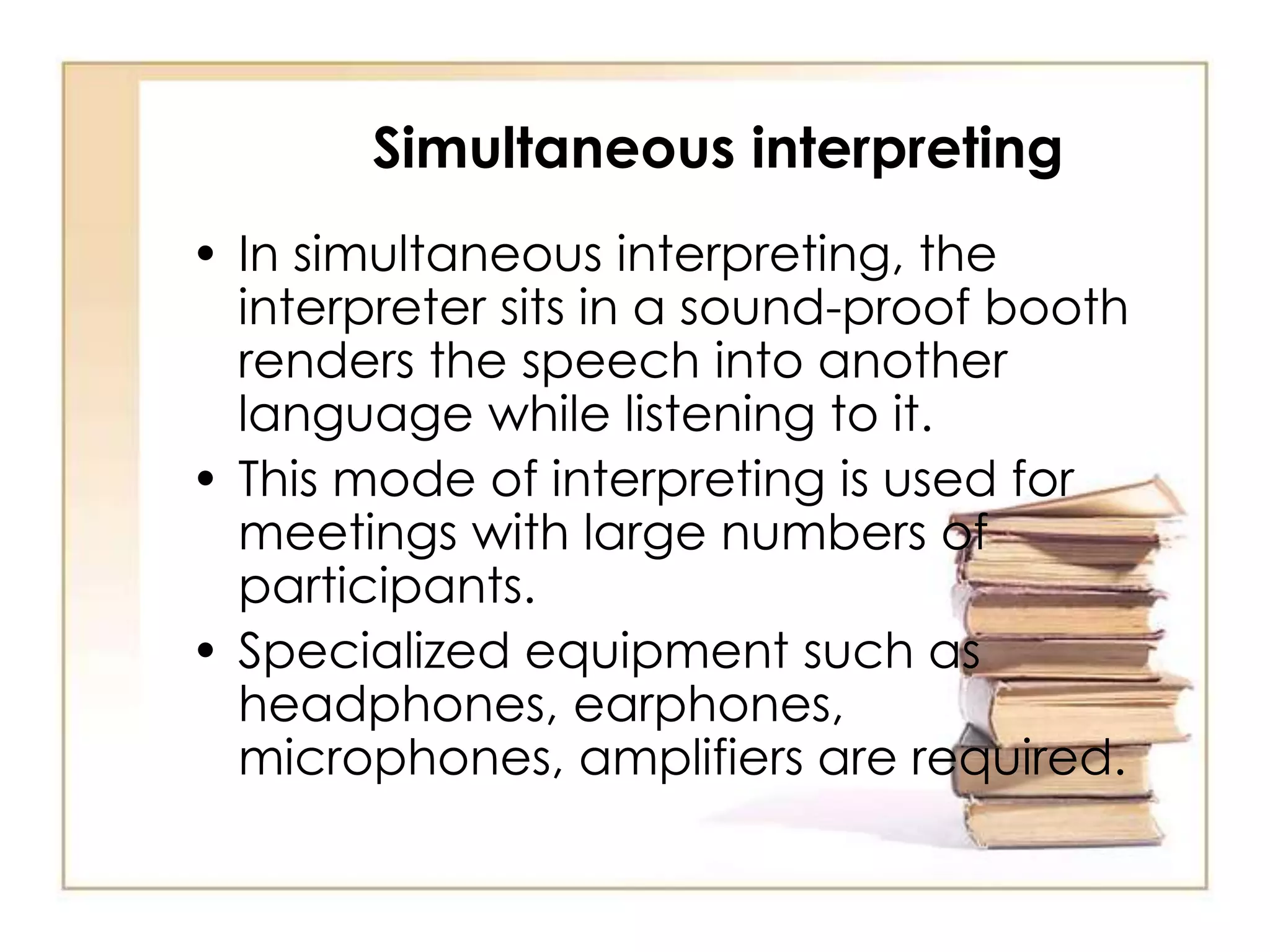
This document discusses the differences between interpreting and translation. Interpreting involves orally communicating the exact meaning and tone of a spoken message between languages, either simultaneously or consecutively. Interpreters must bridge cultural gaps without resources, while translators can research when working with written text. Effective interpreting requires linguistic and cultural knowledge, background information, language skills, and adherence to codes of ethics like impartiality and active listening.