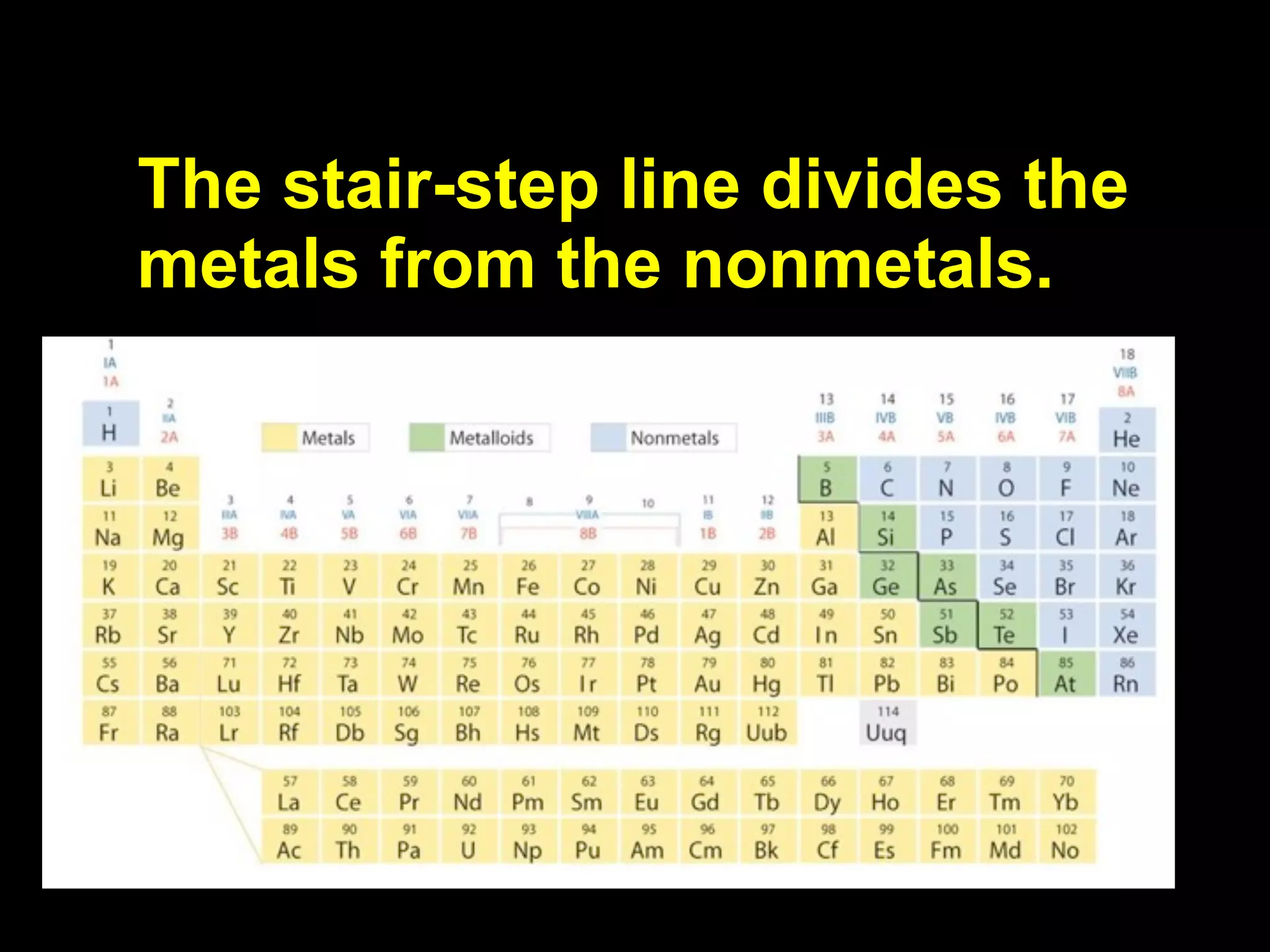
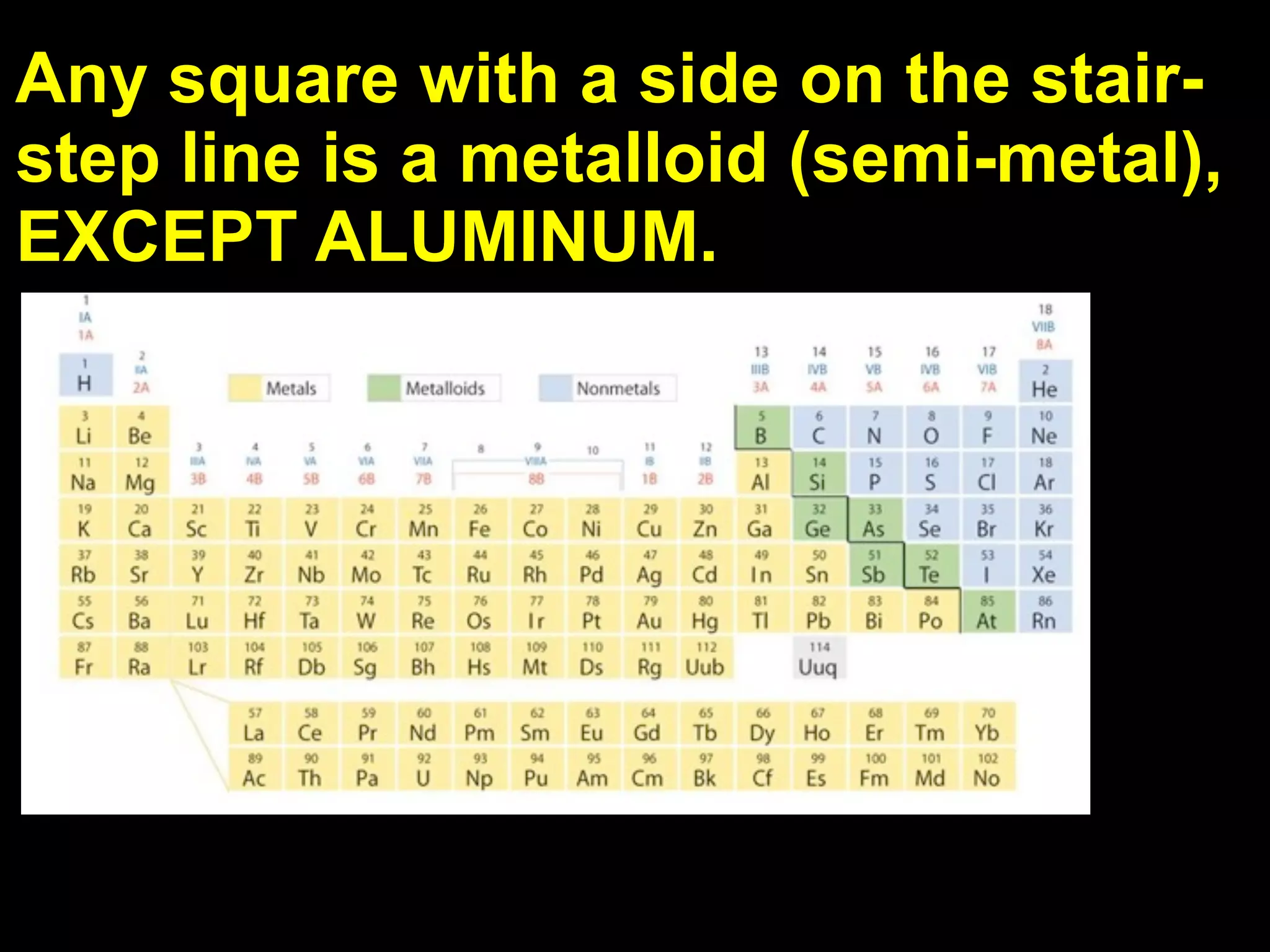
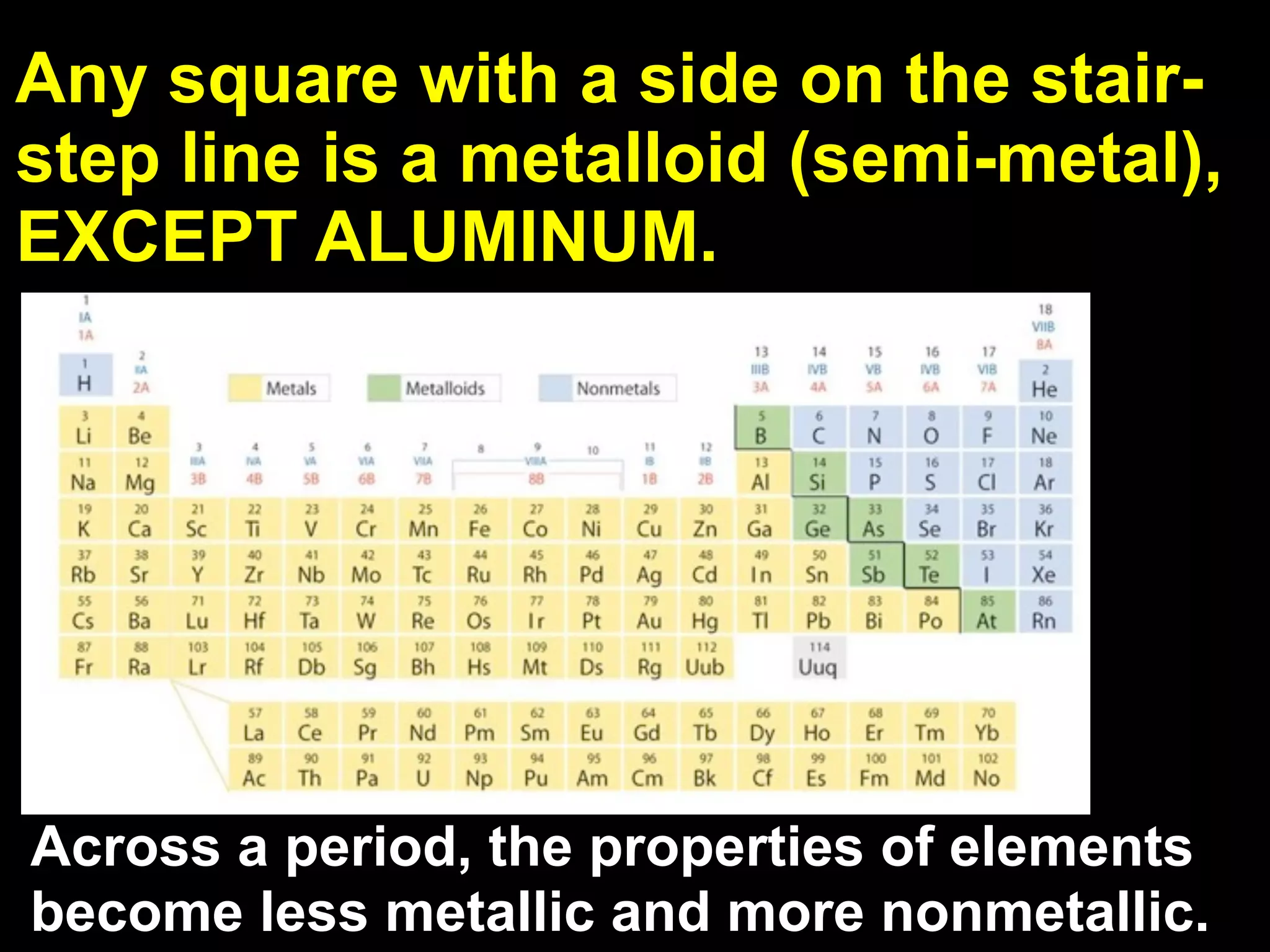
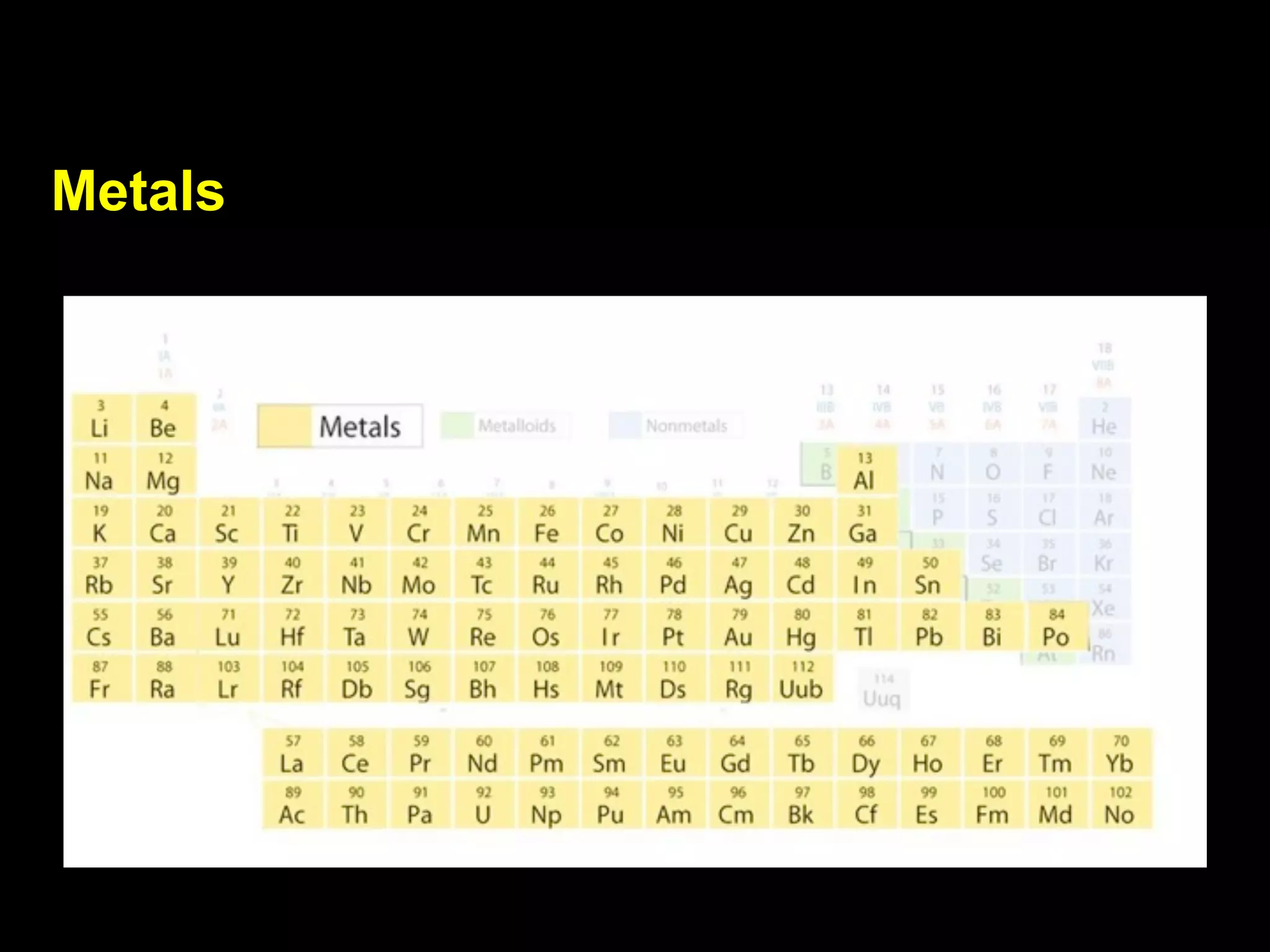
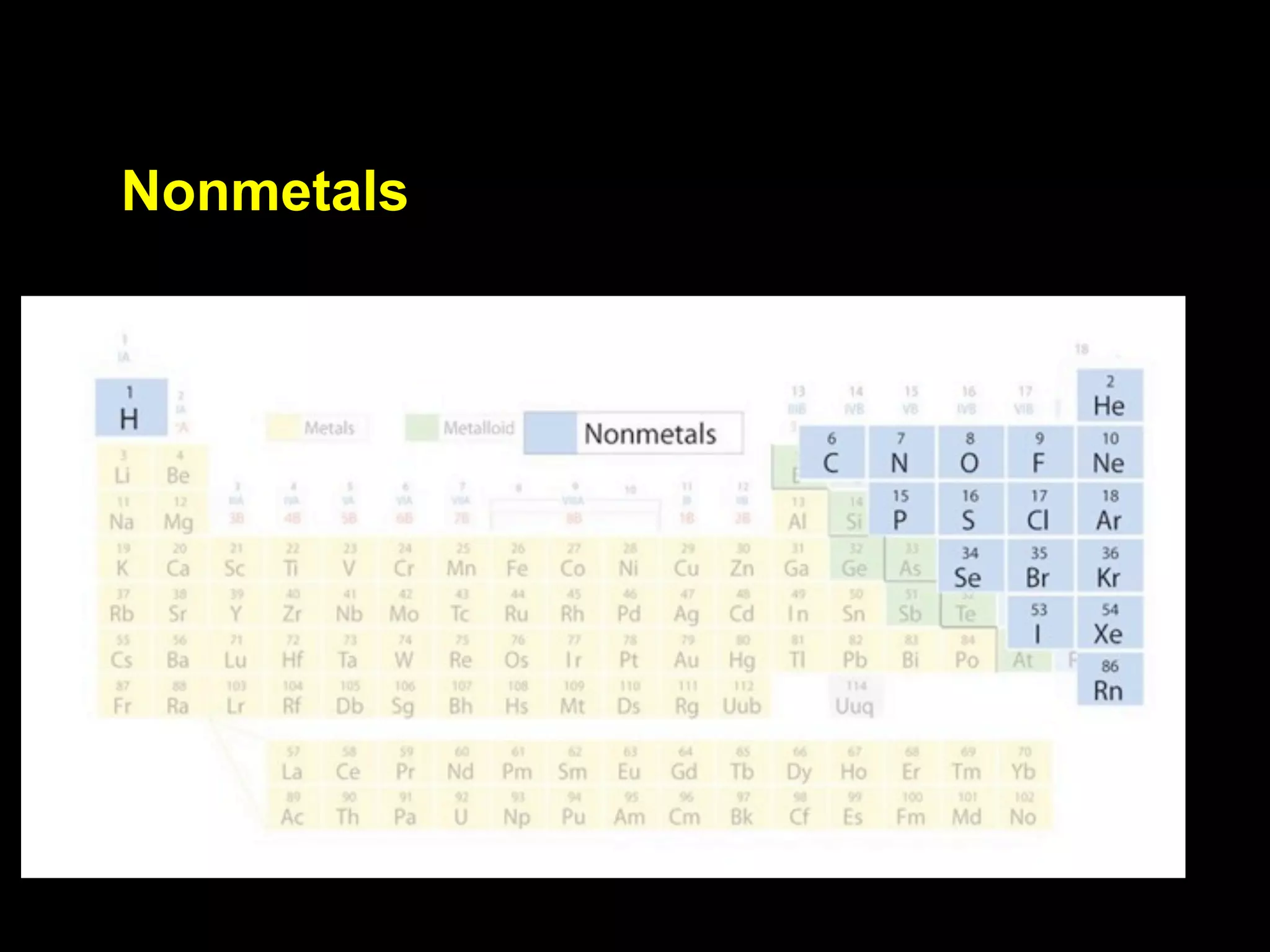
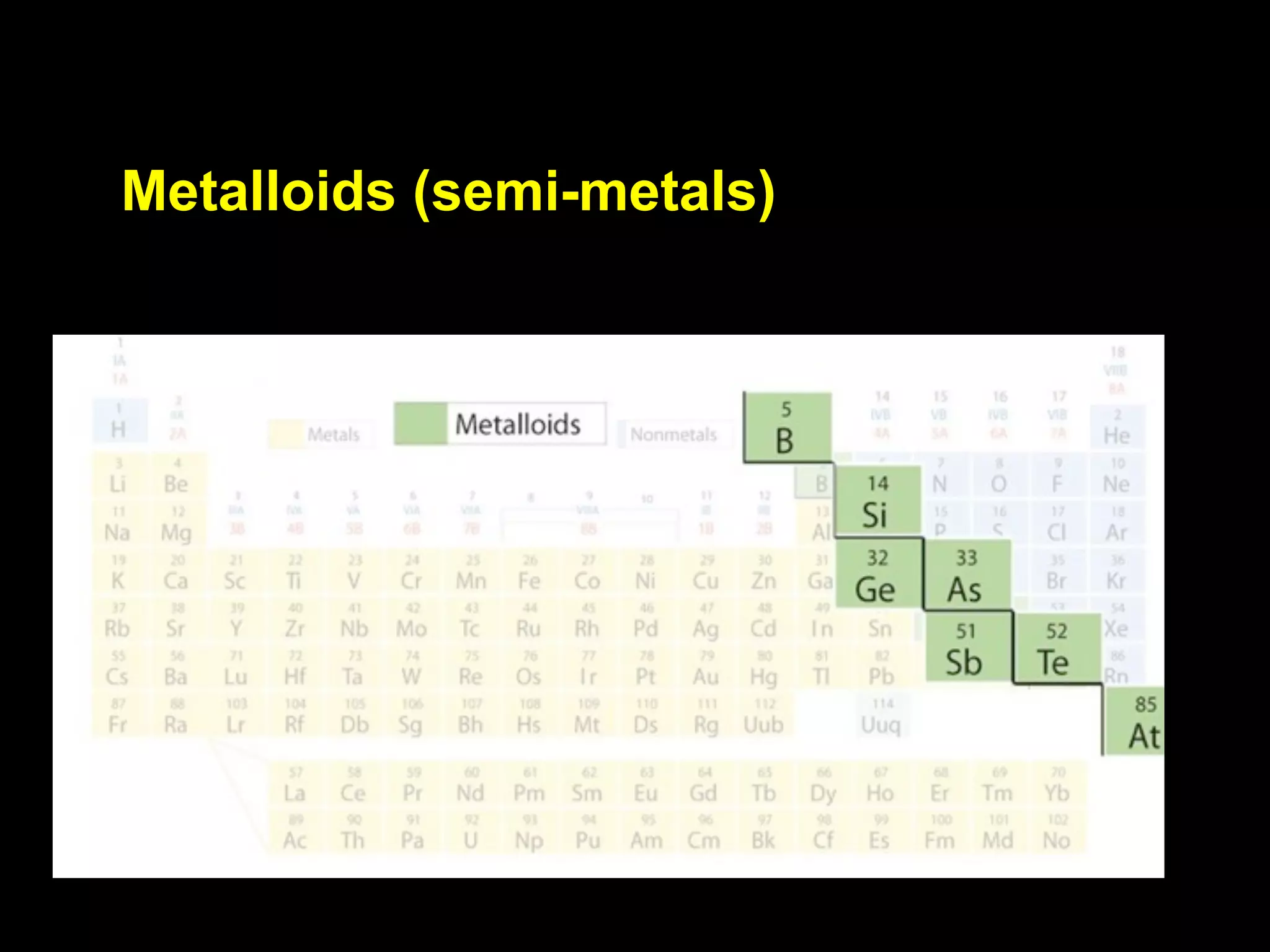
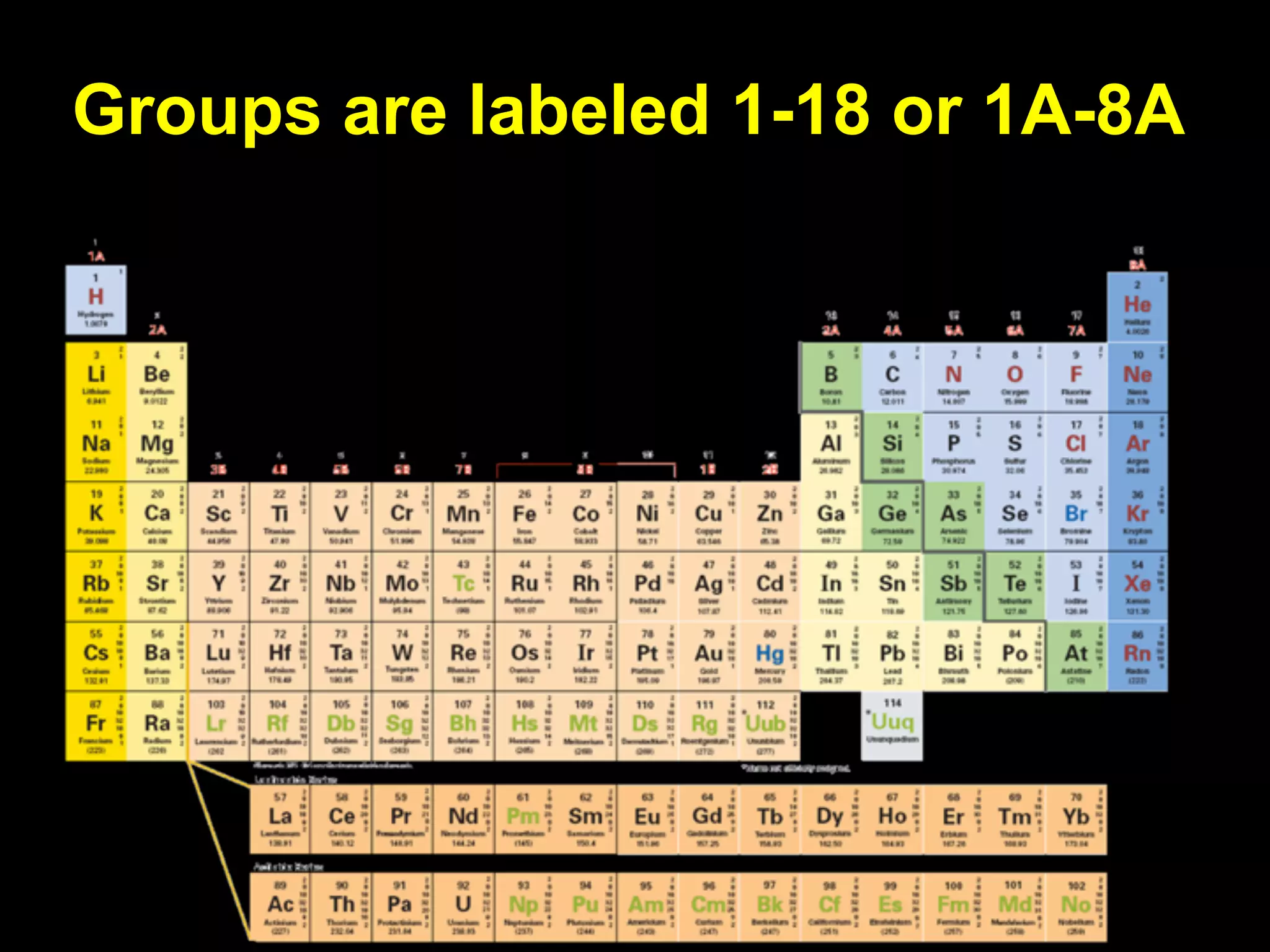
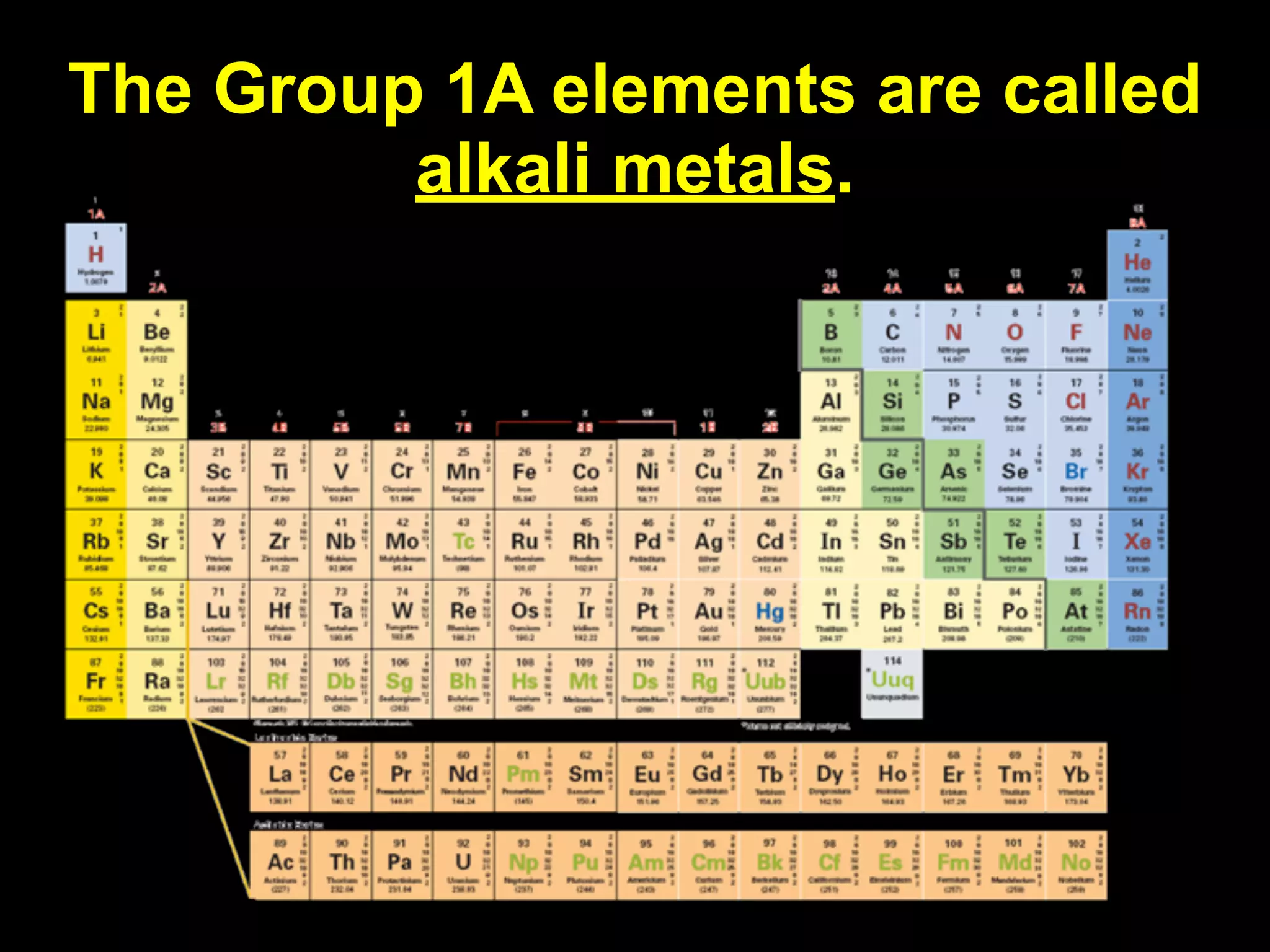
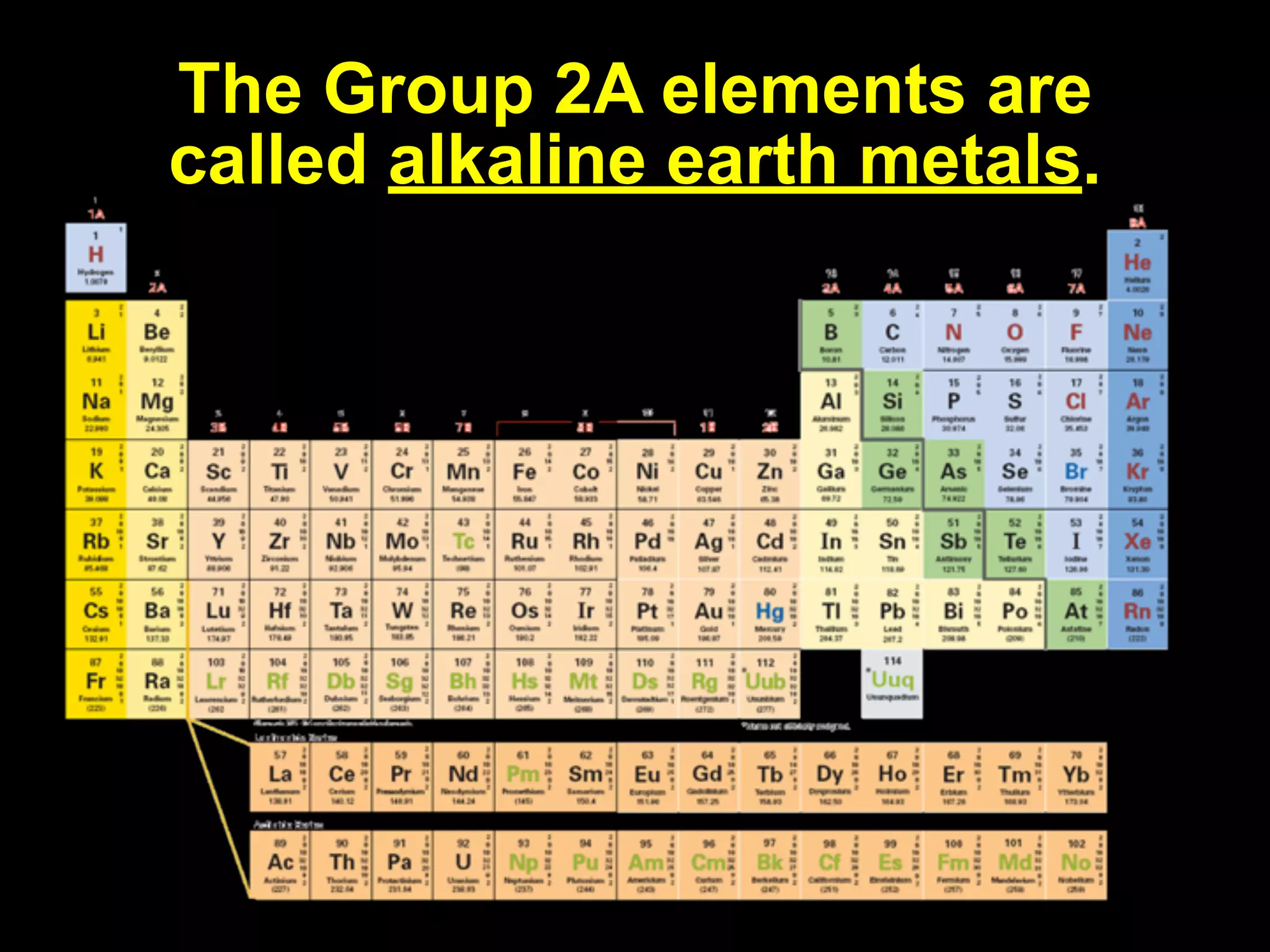
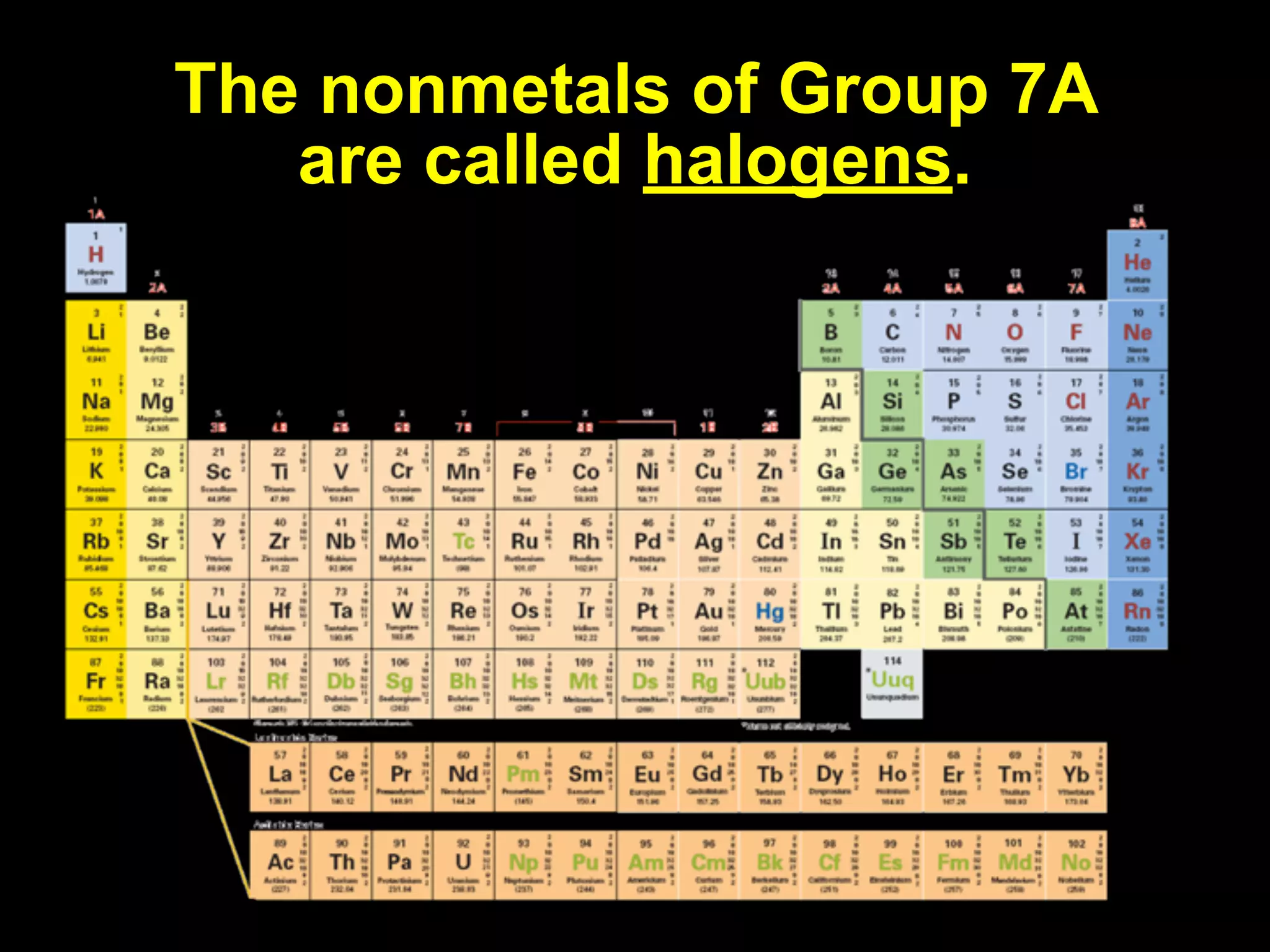
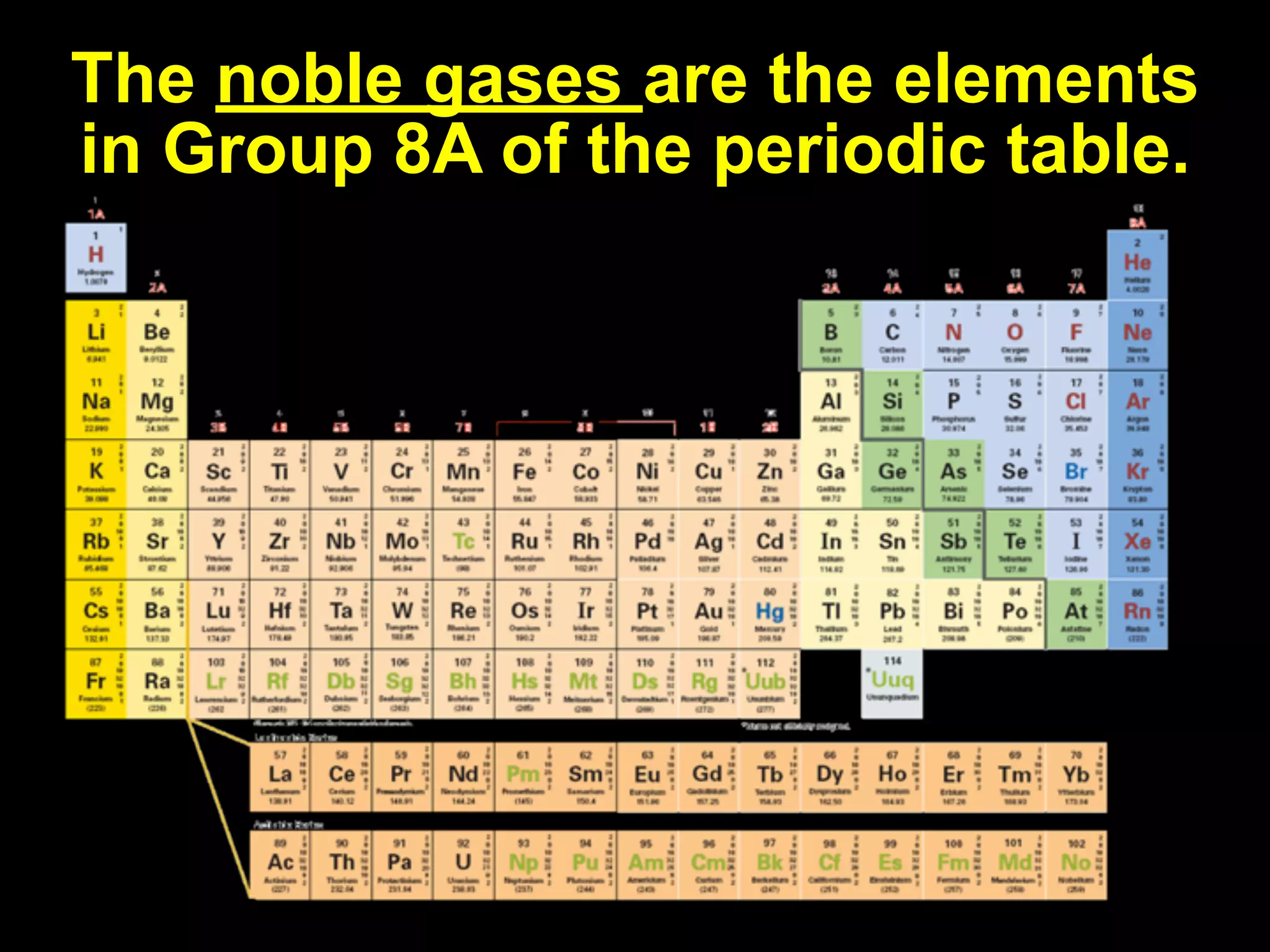
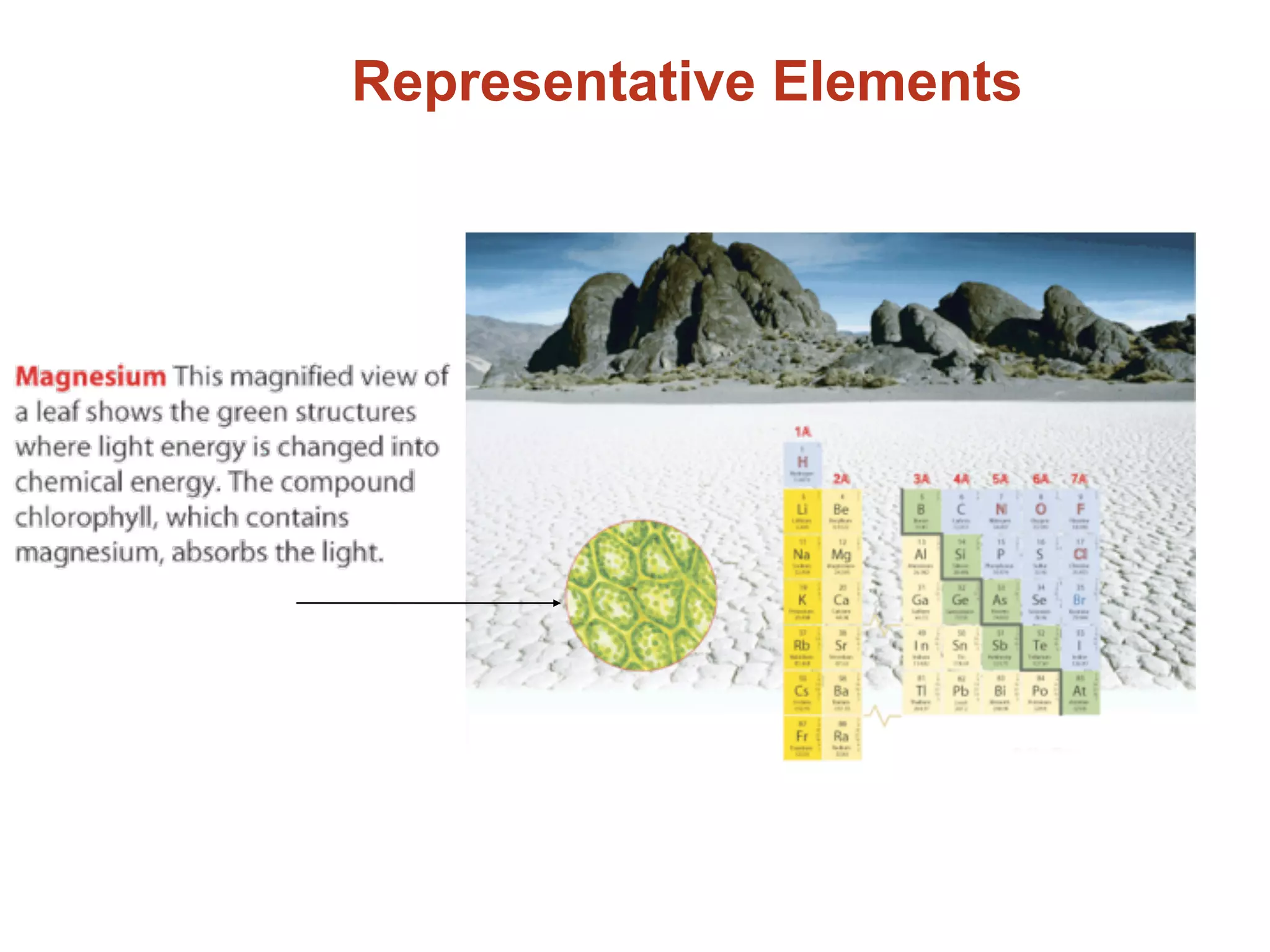
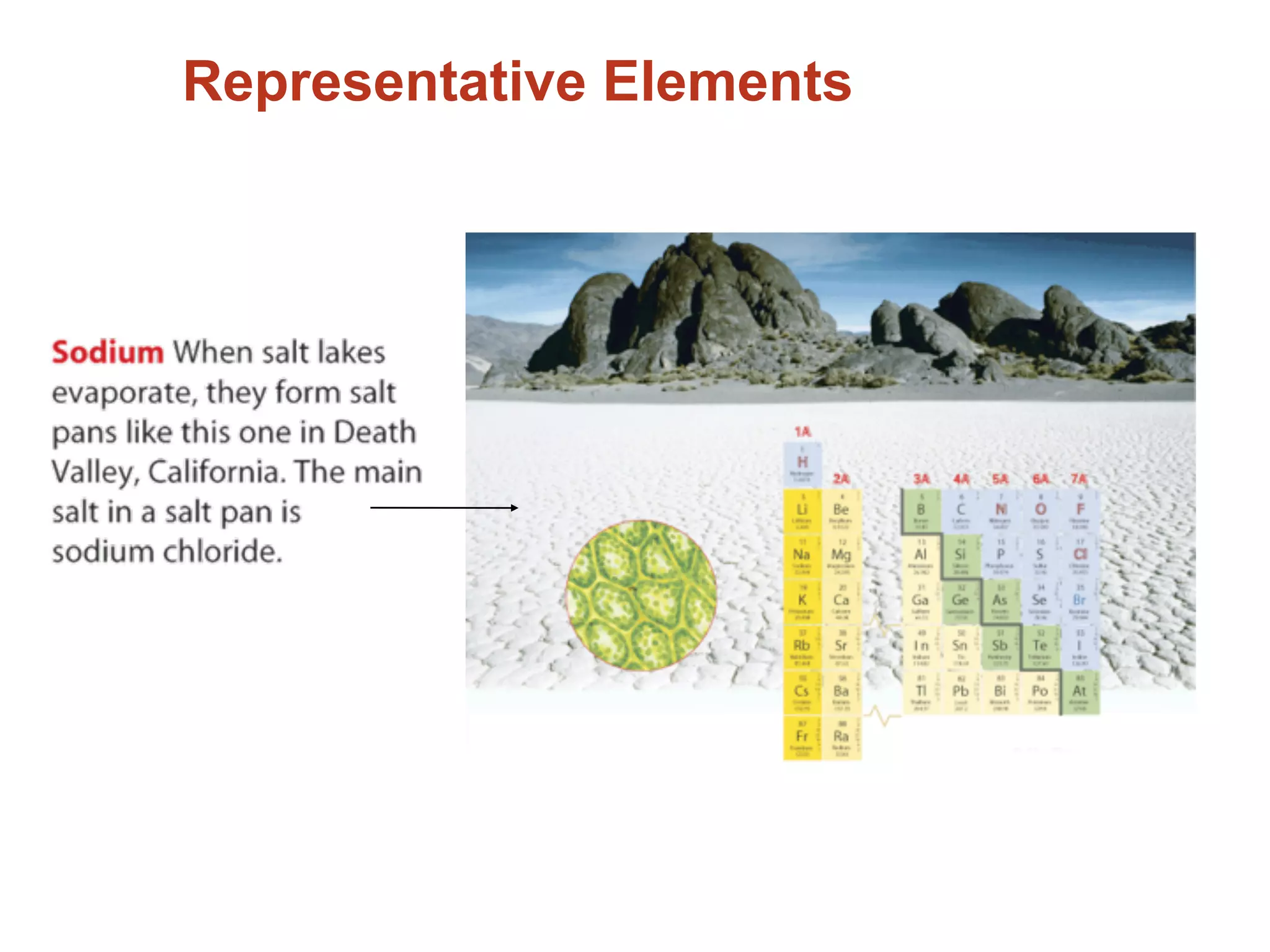
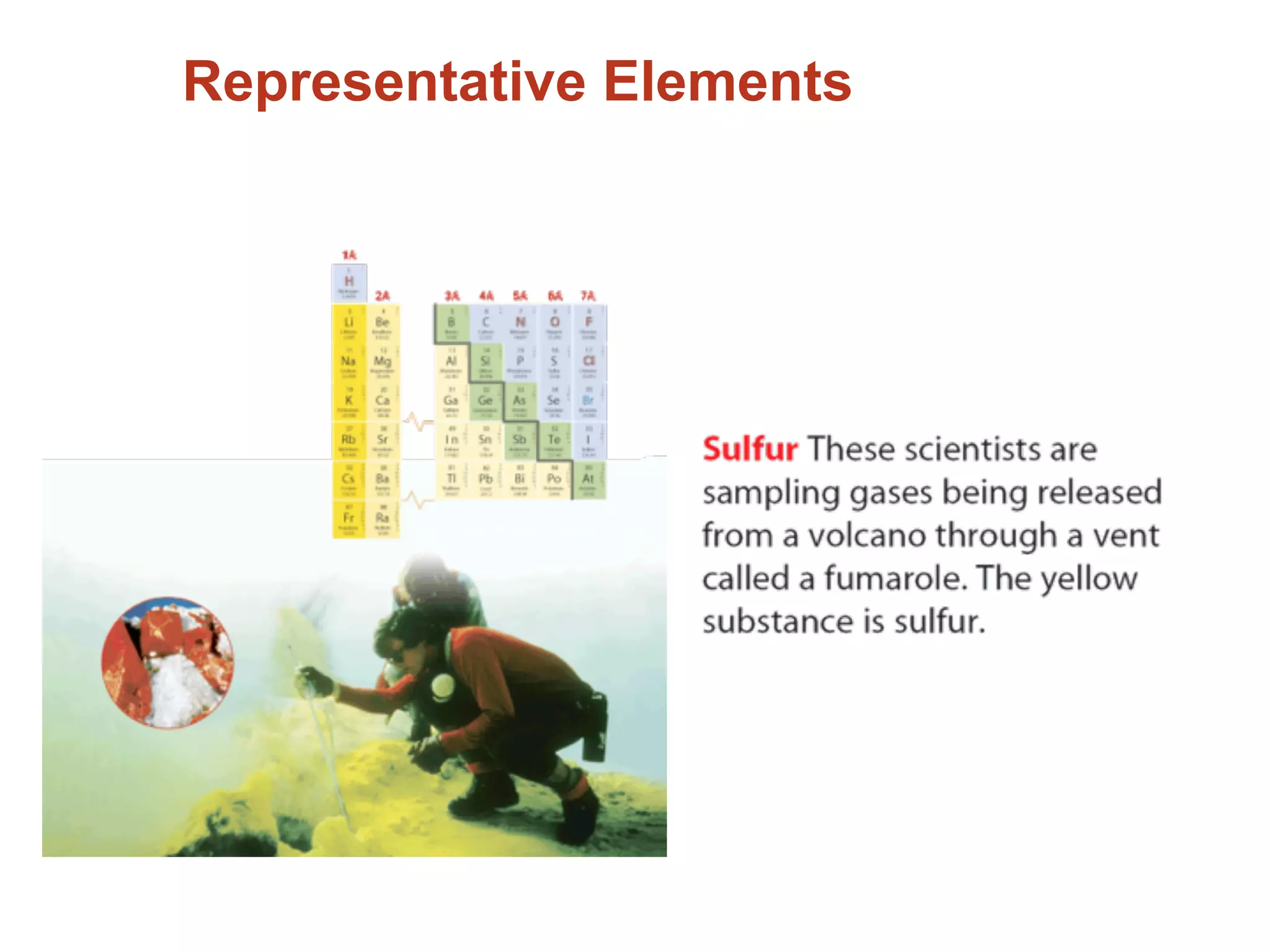
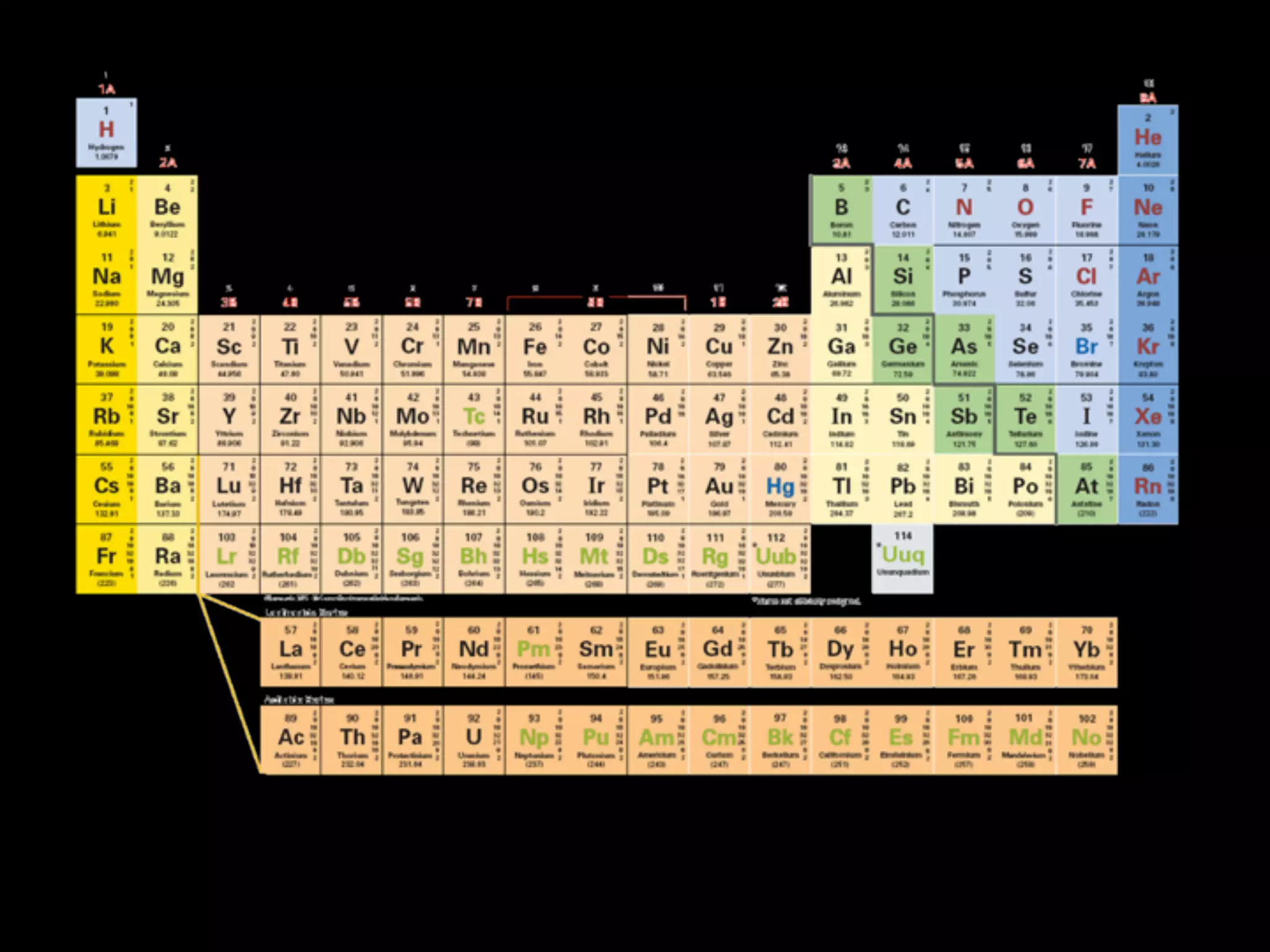
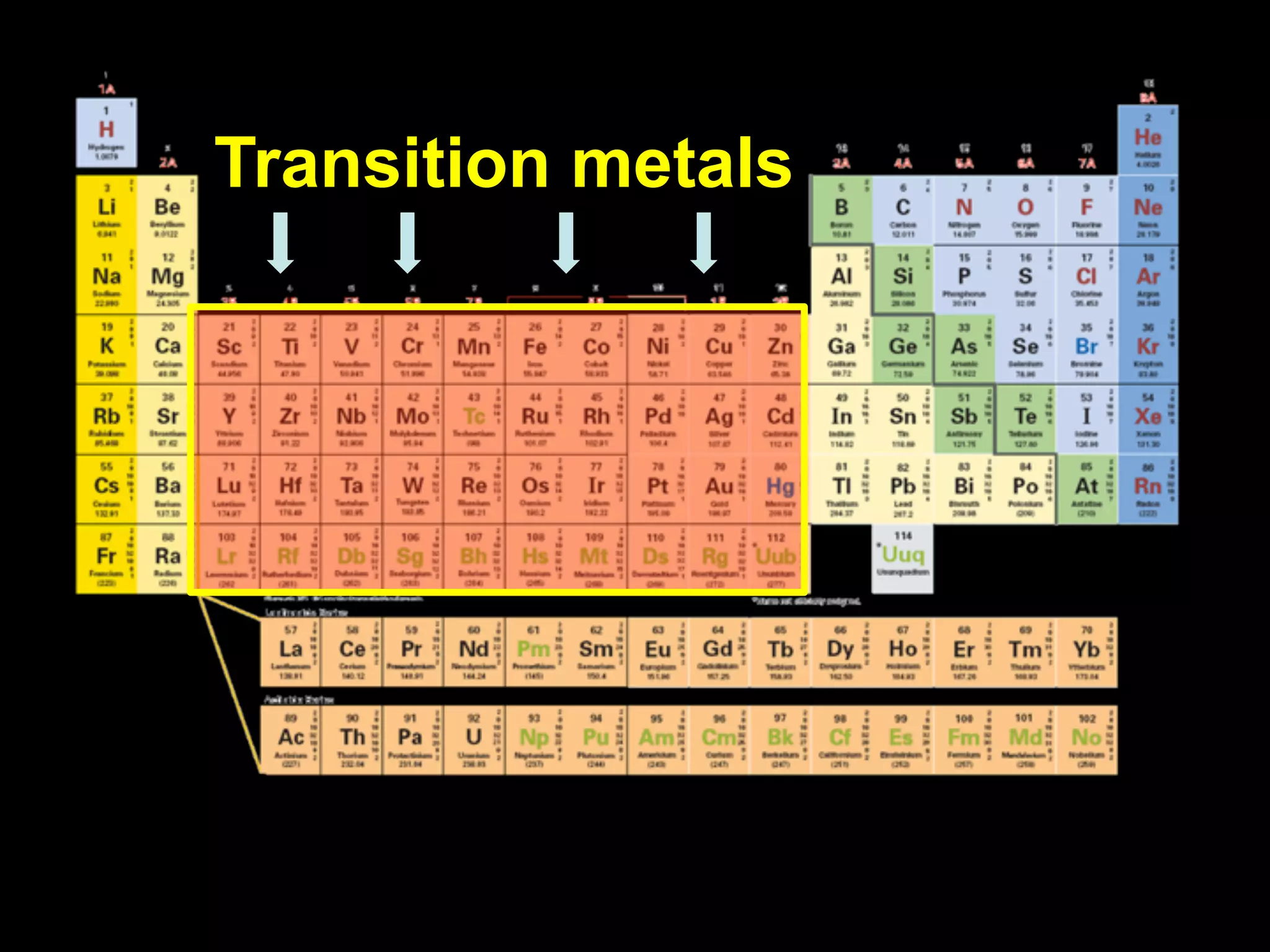
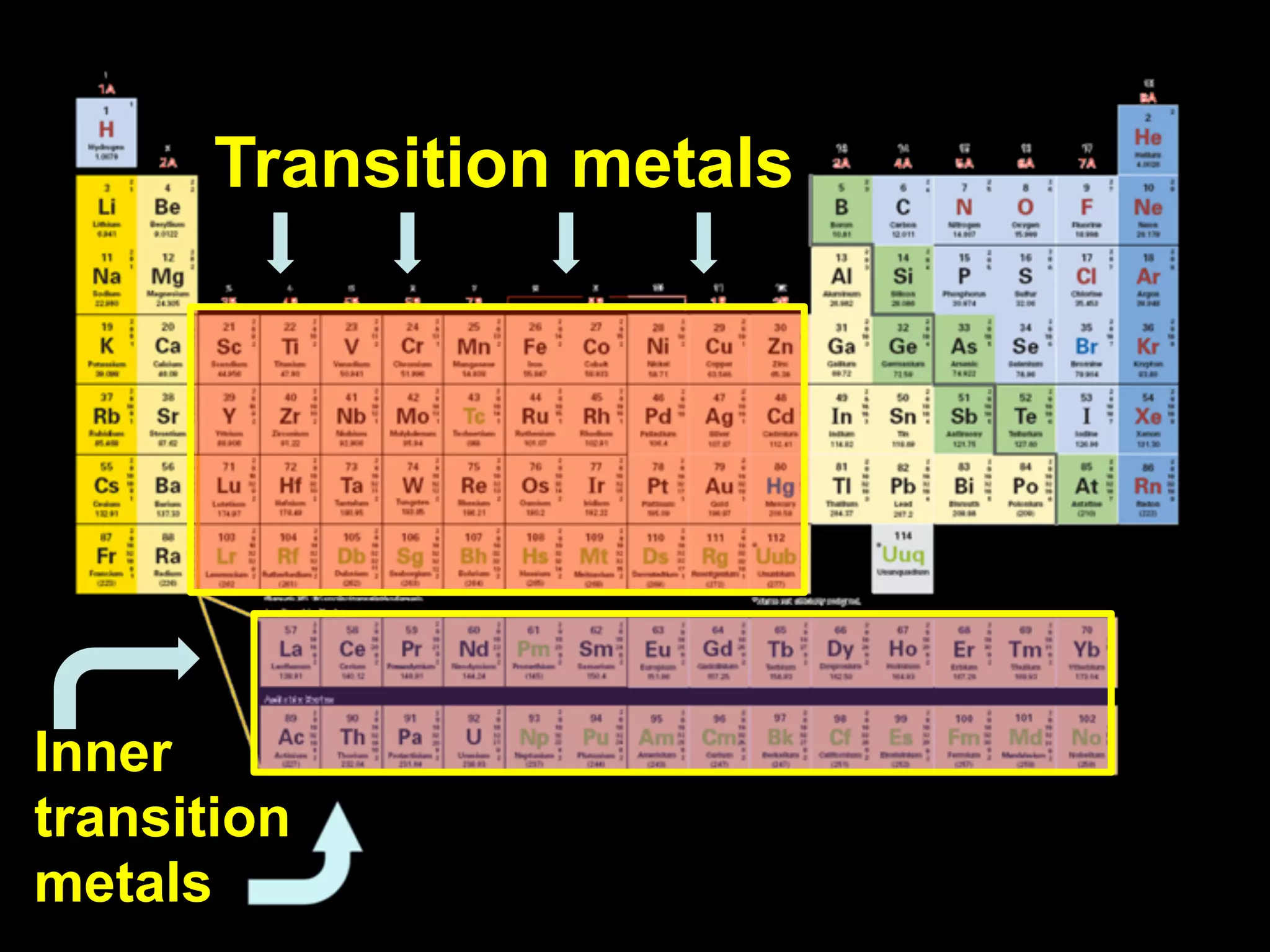
The document provides information about the periodic table and its development. It discusses how chemists group elements based on their properties, and how Mendeleev arranged the first periodic table by atomic mass, allowing him to predict properties of undiscovered elements. The modern periodic table arranges elements in order of atomic number, and elements within the same period have recurring physical and chemical properties. Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are distinguished in the periodic table.