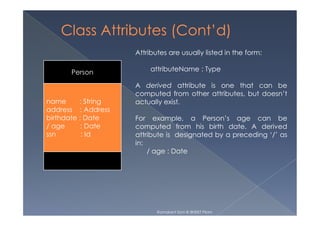
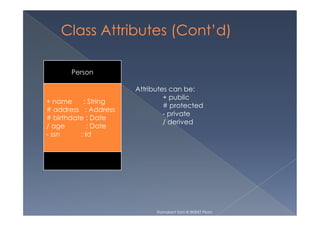
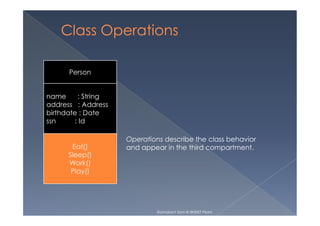
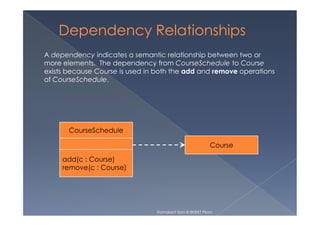
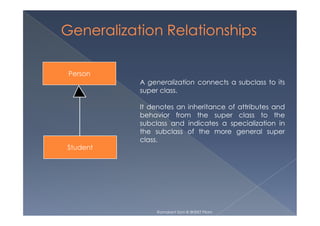
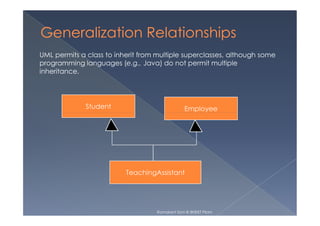
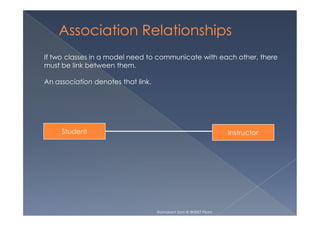
This document provides an overview of class diagrams in UML. It describes the key components of a class including the name, attributes, and operations. It explains how classes can be connected through relationships like generalizations, associations, and dependencies. The document uses examples like Person, Student, and CourseSchedule classes to illustrate attributes, operations, and relationships between classes.