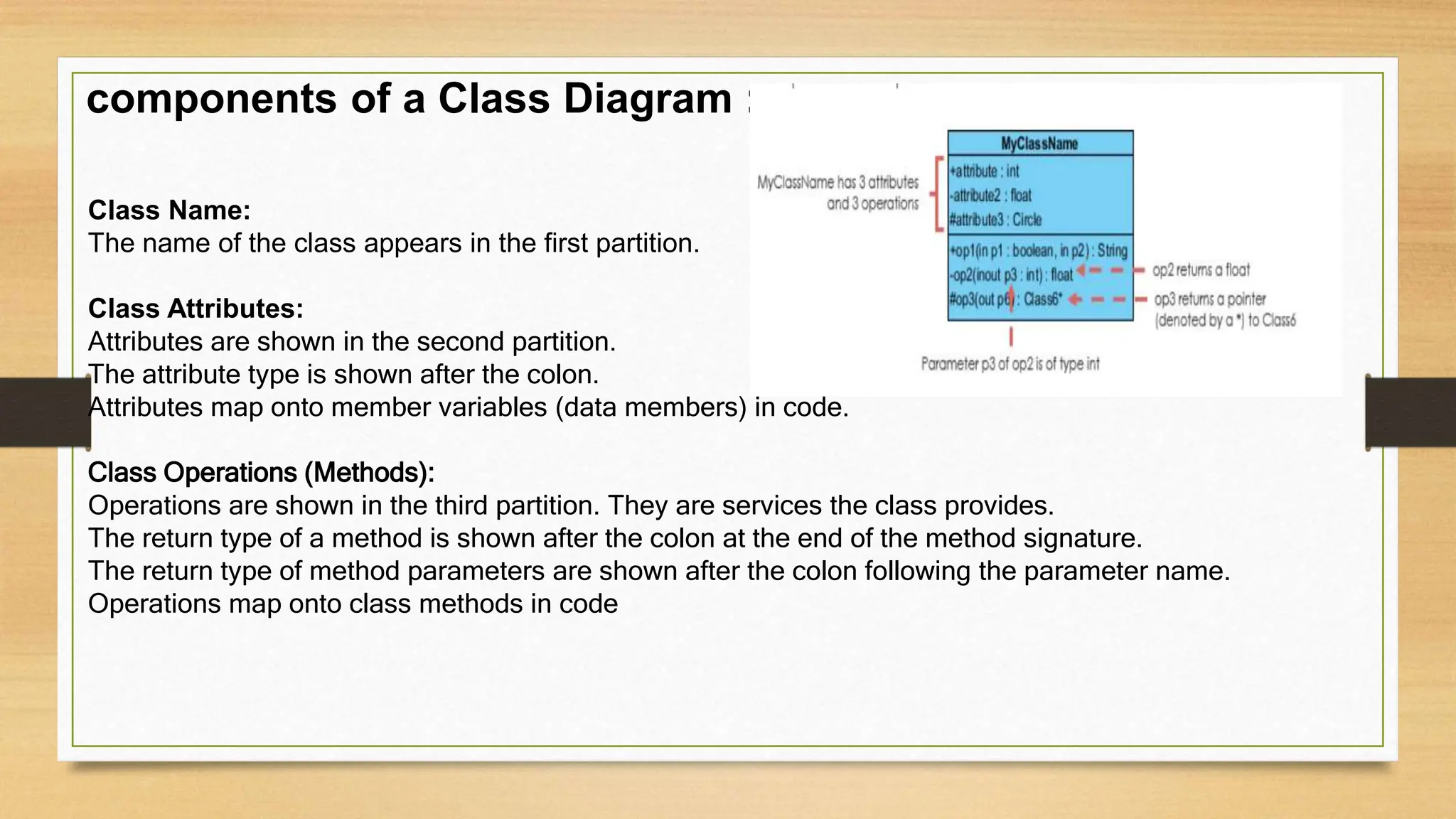
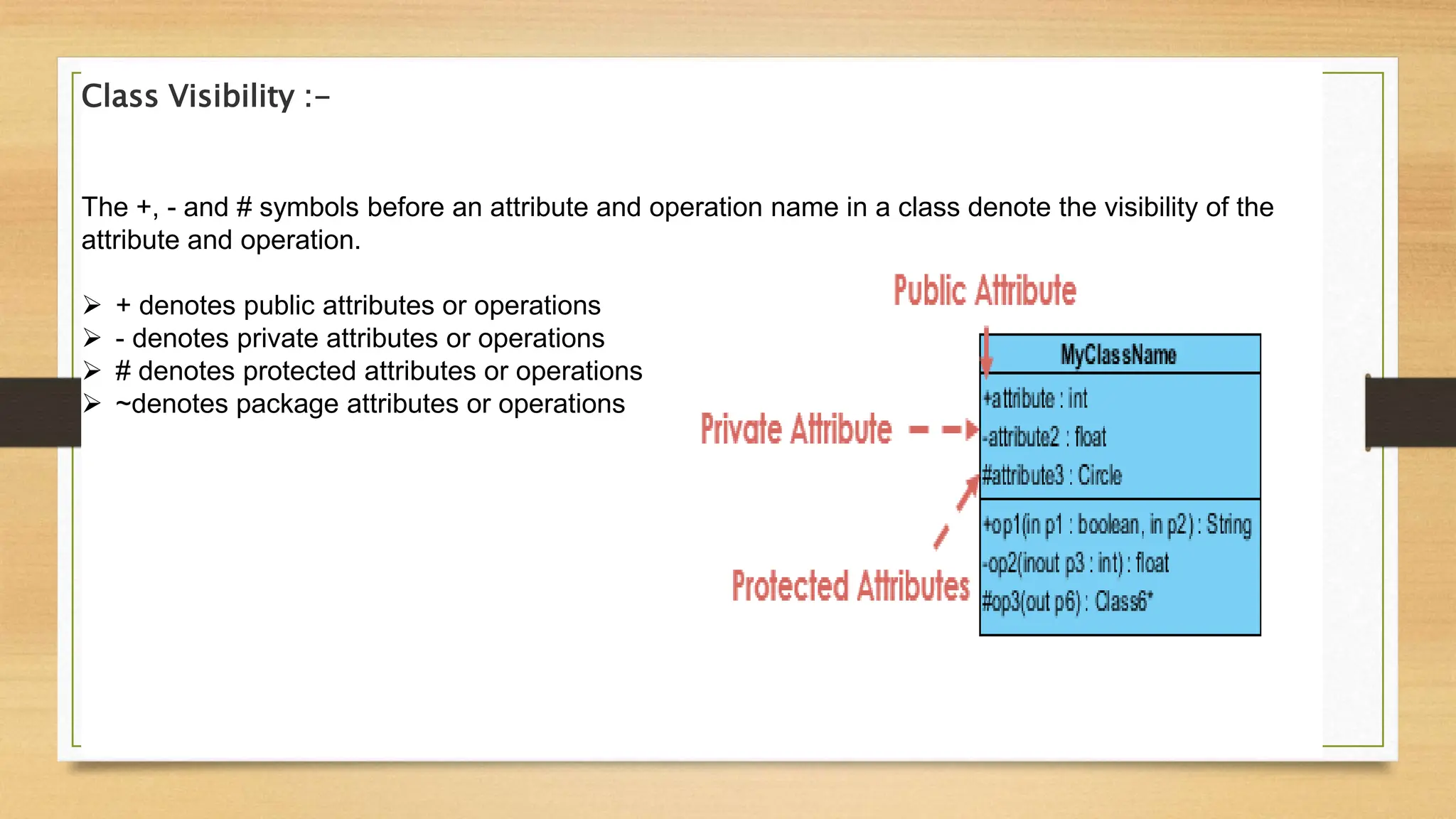
The document defines and explains the key components of a UML class diagram, including classes, attributes, operations, relationships between classes like generalization, association, aggregation, and composition. It provides examples to illustrate these concepts, such as a class diagram for an order system that shows classes like Order and Product connected by associations.