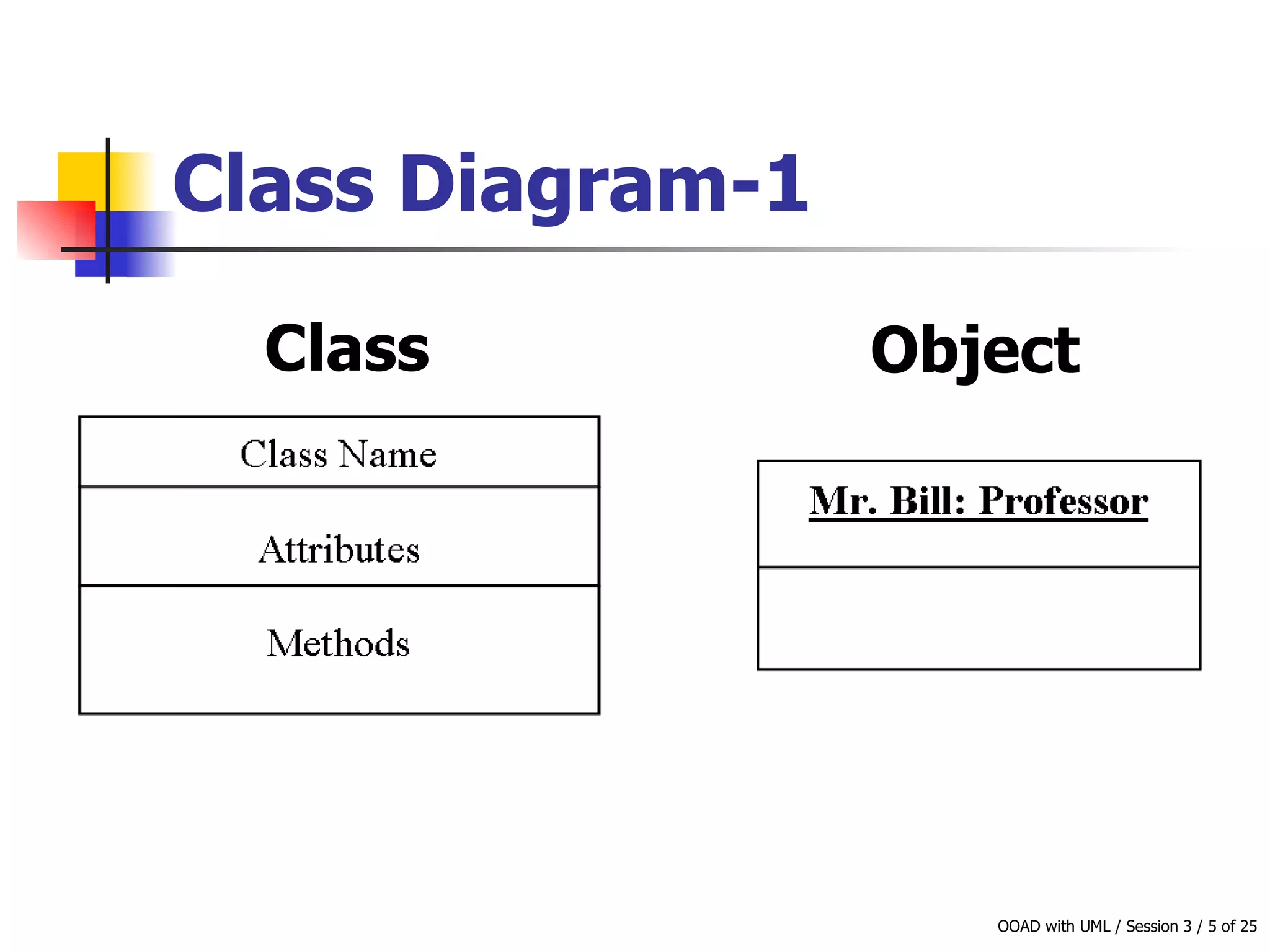
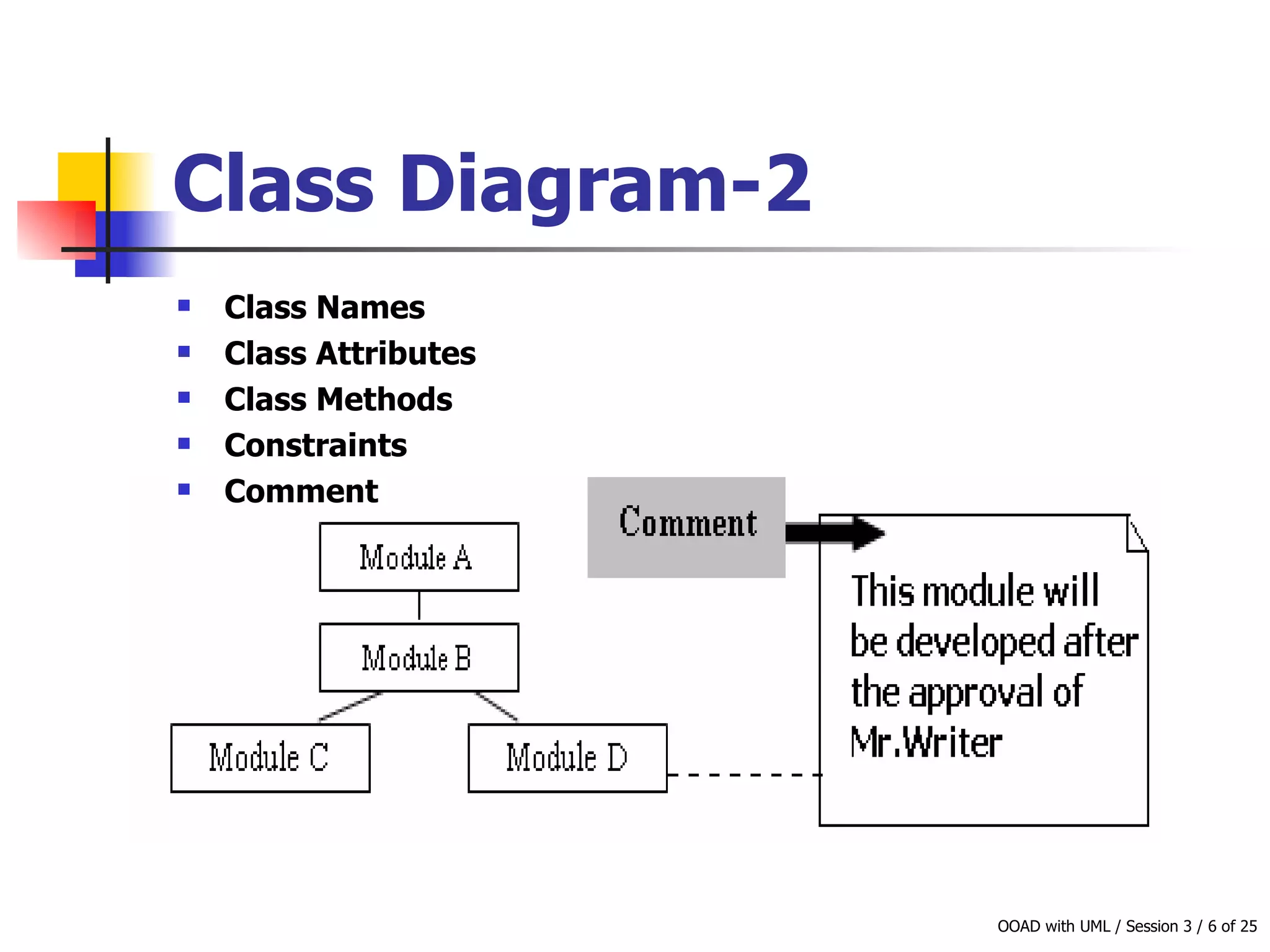
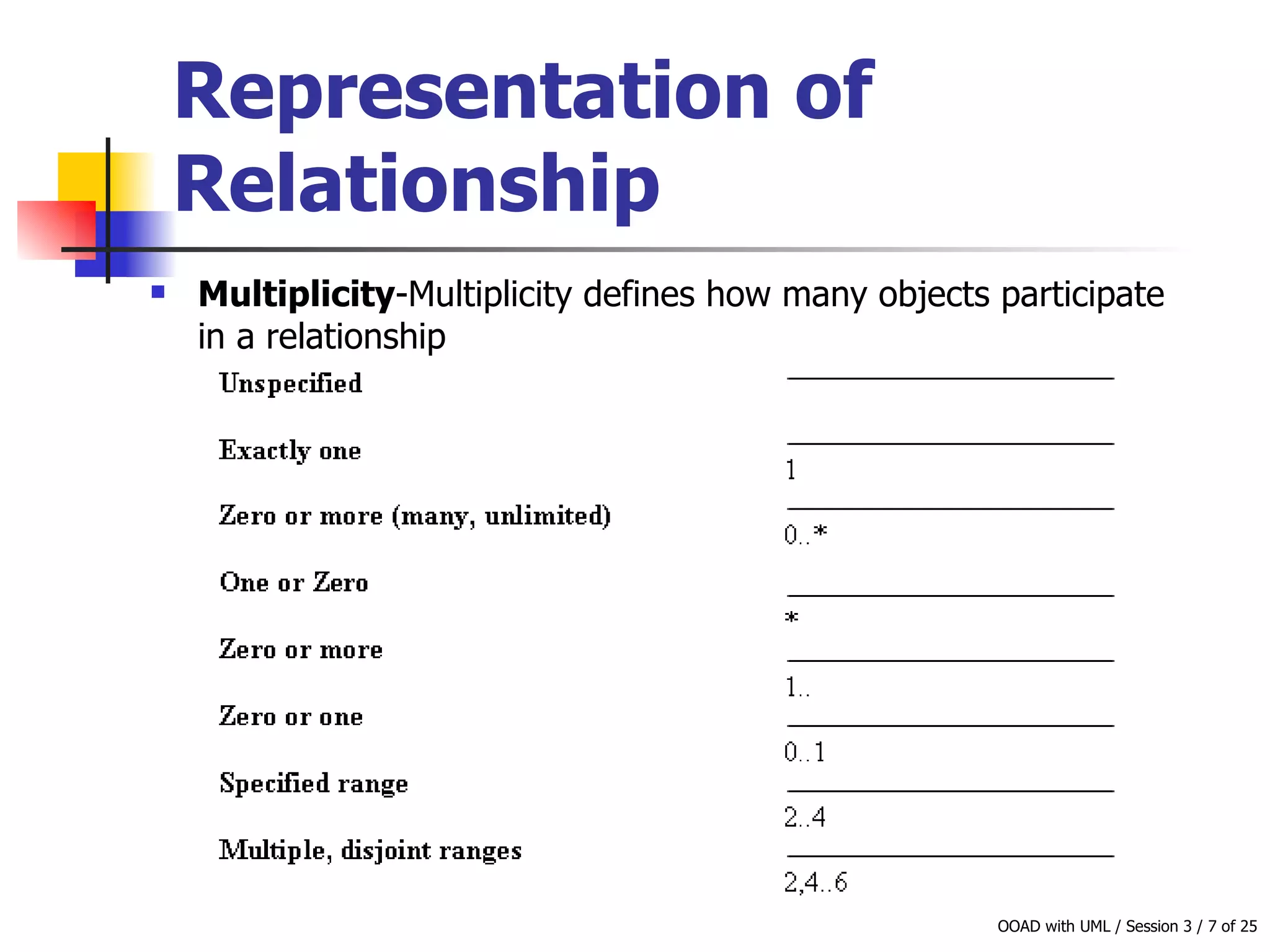
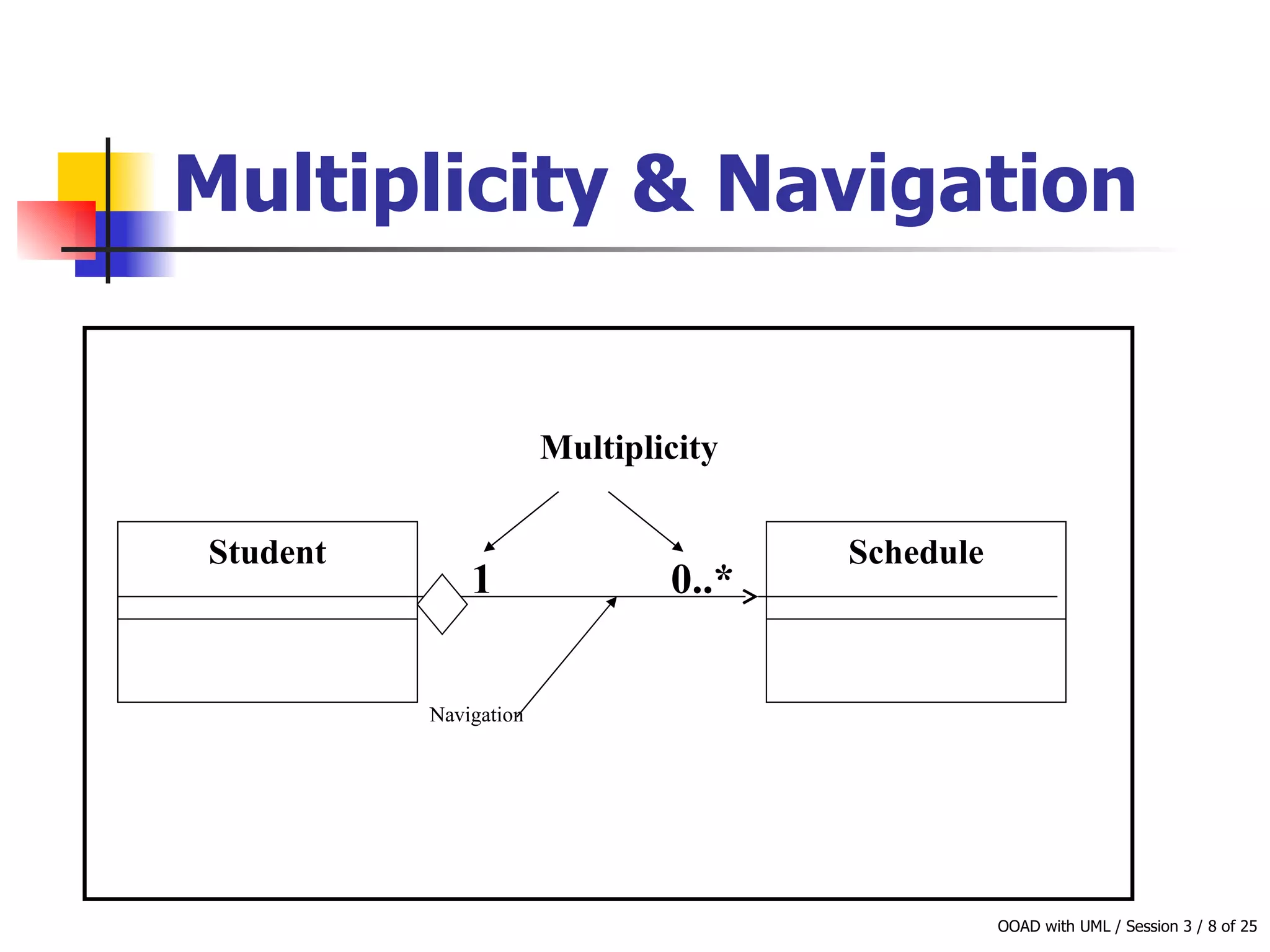
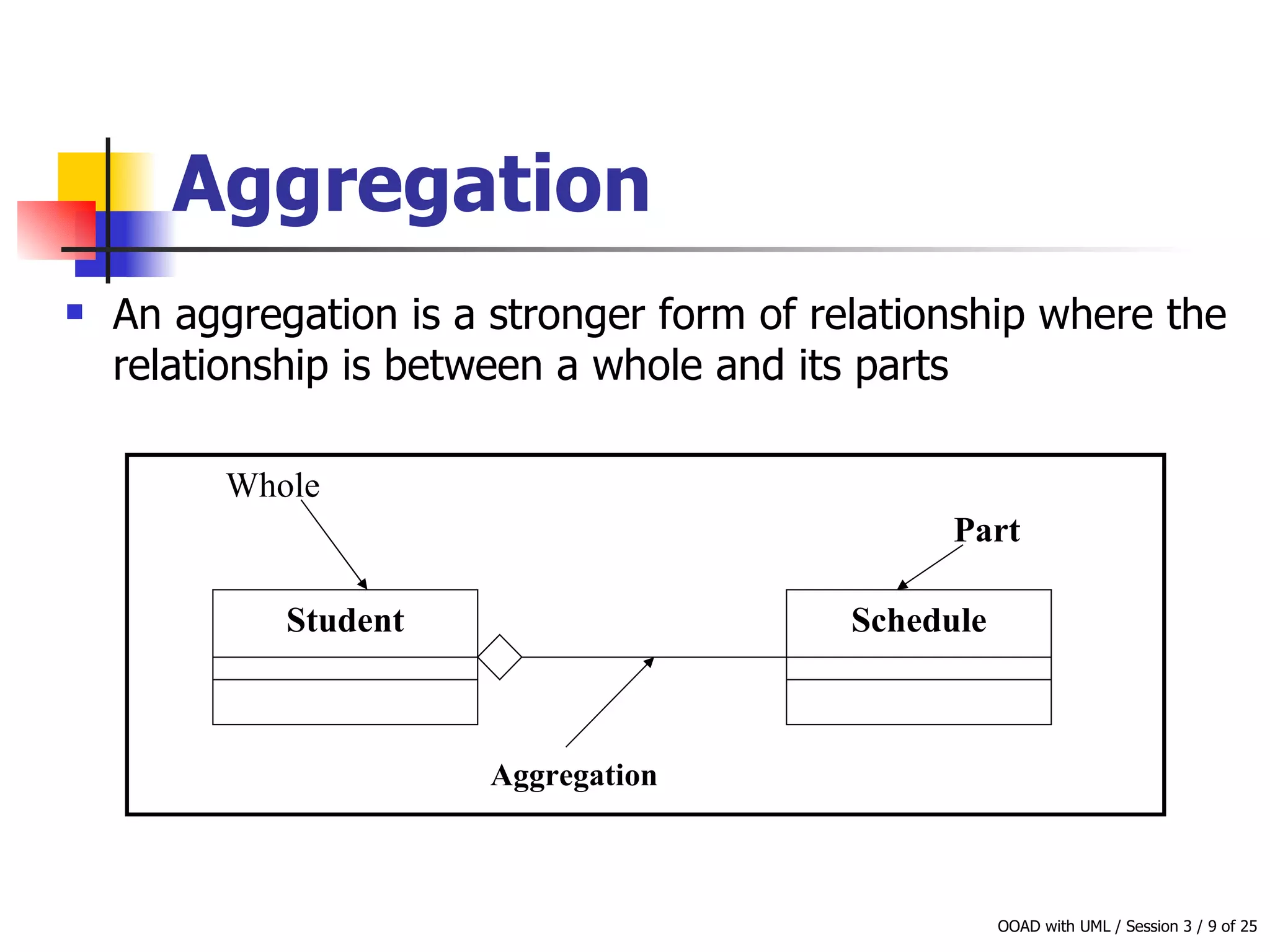
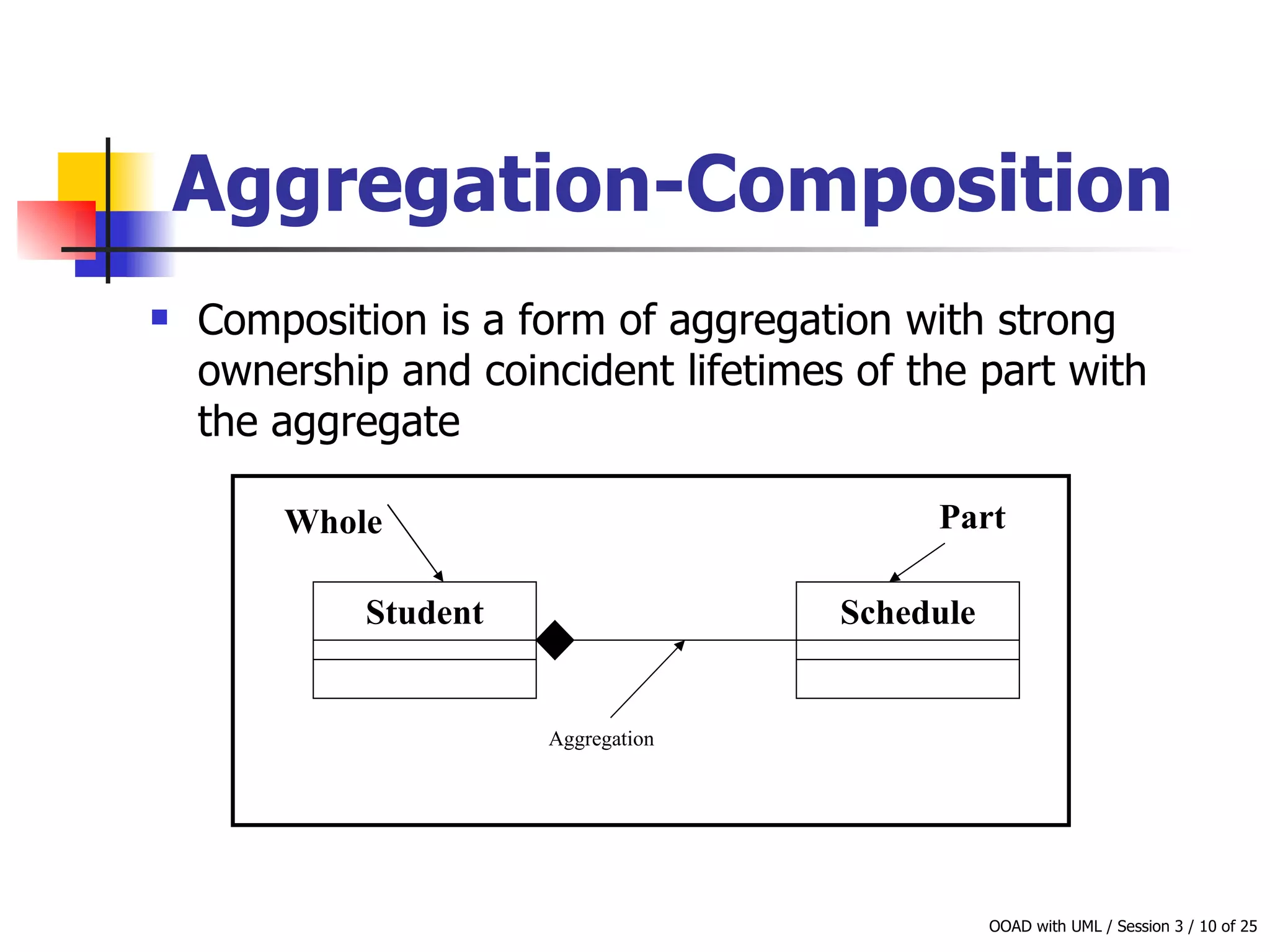
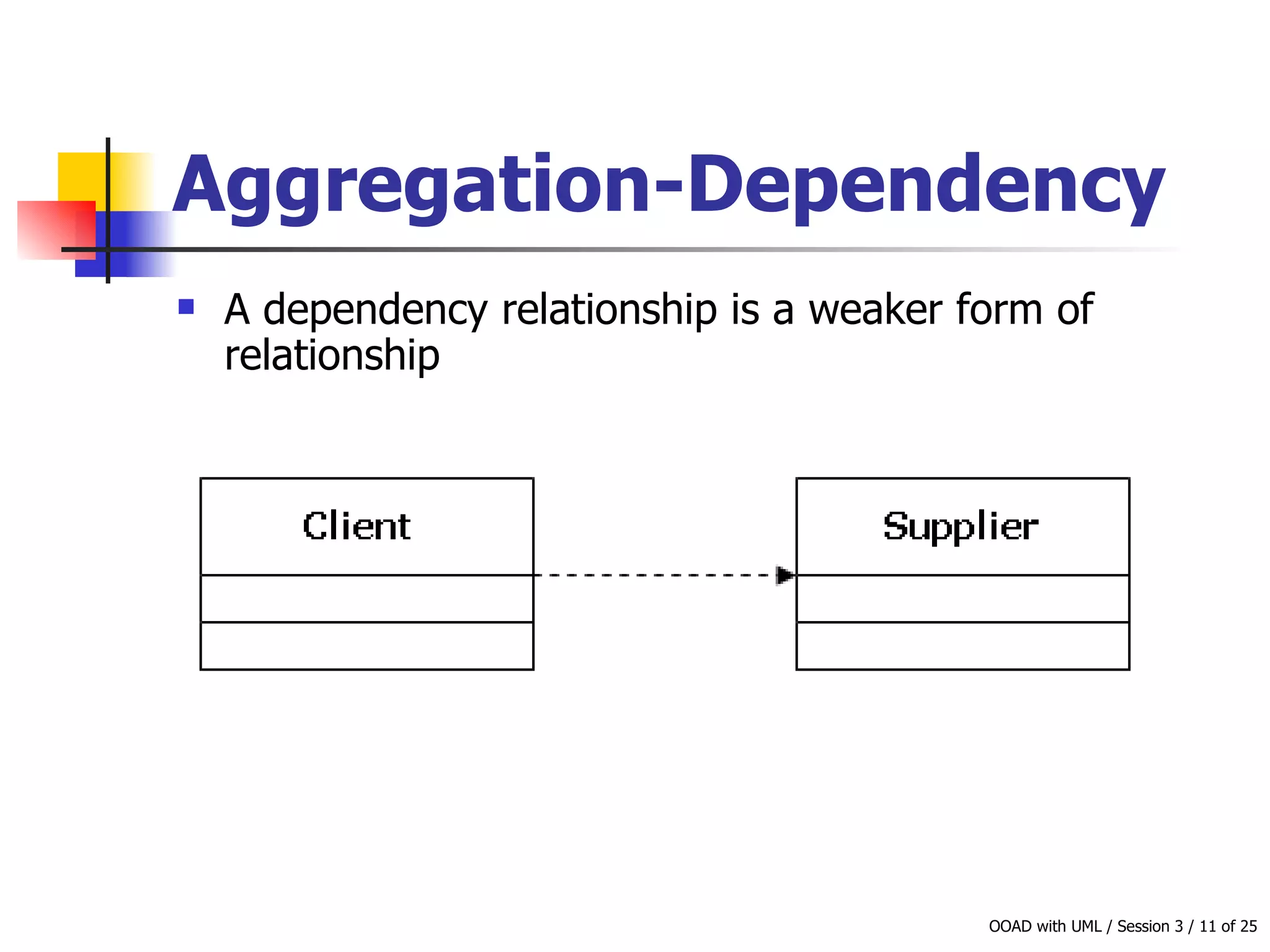
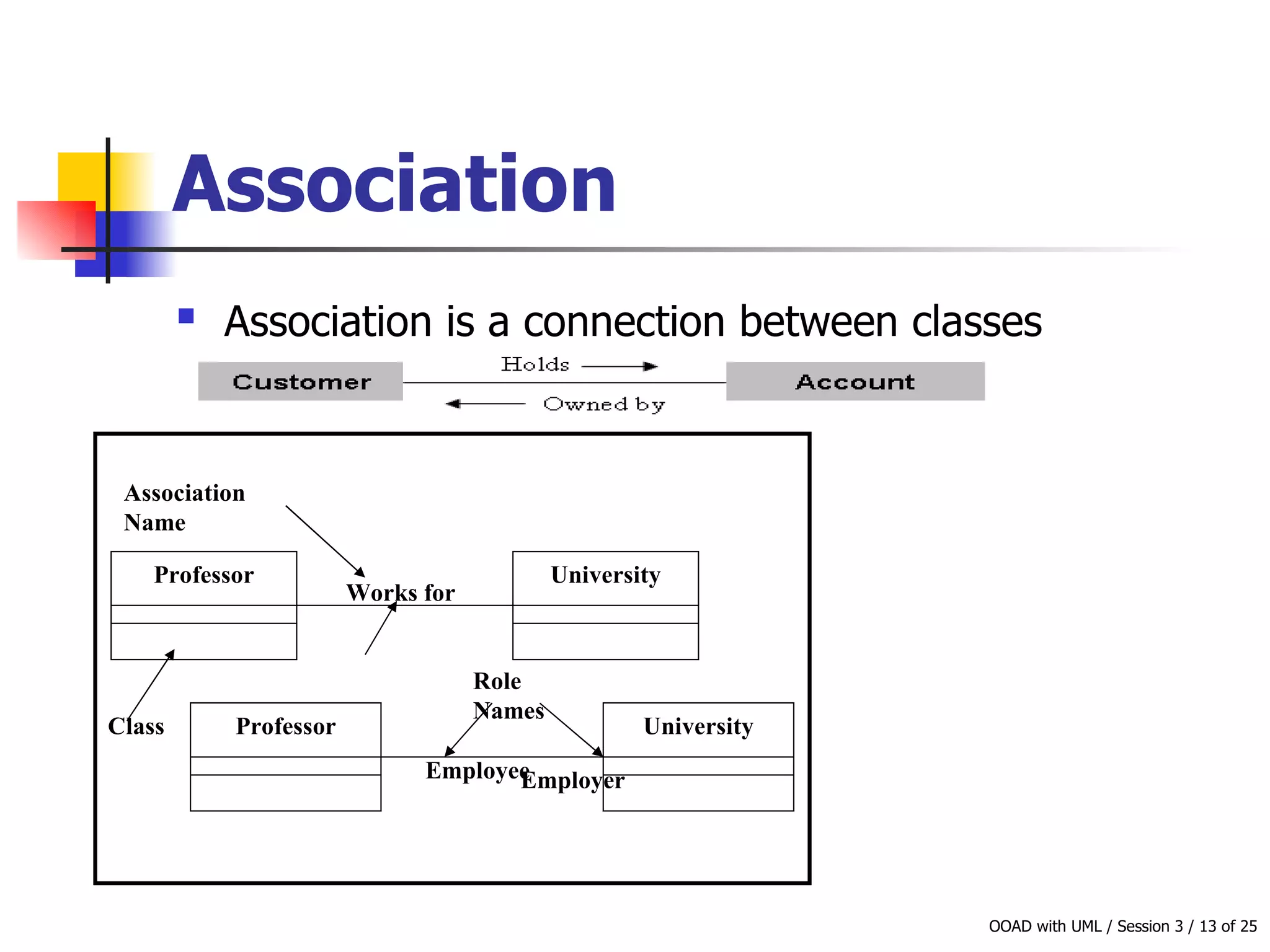
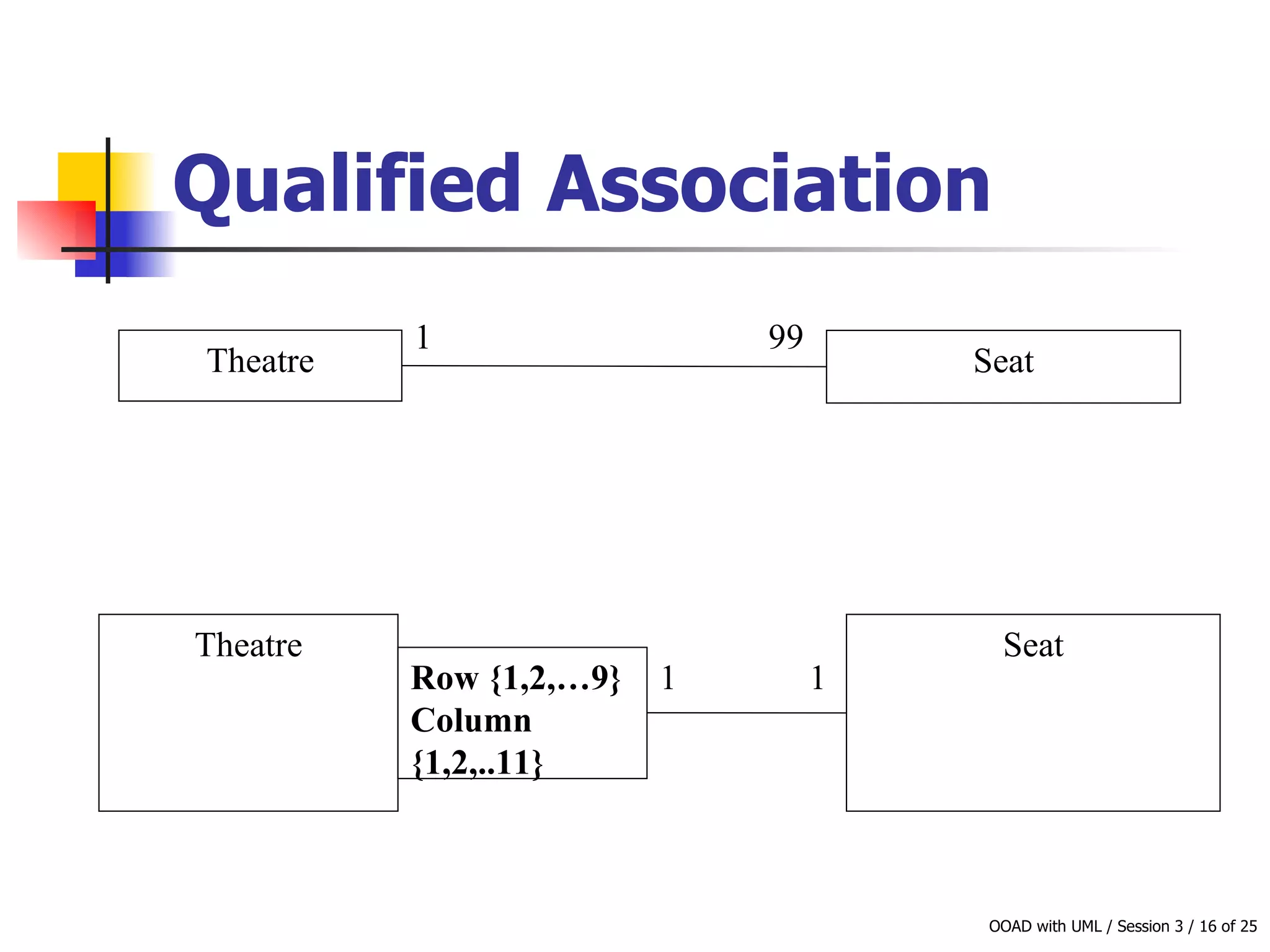
This document discusses object-oriented modeling concepts including classes, objects, class diagrams, relationships between classes like association and aggregation, and how to identify classes during analysis. A class represents a group of objects with common properties and behaviors while an object represents an entity. Class diagrams are used to represent classes, attributes, methods, and relationships. Key relationships include association, aggregation, composition, generalization and dependency. The object model depicts the structural relationships and functional behavior of classes in a system.