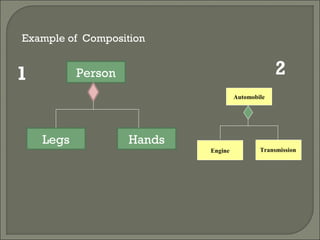
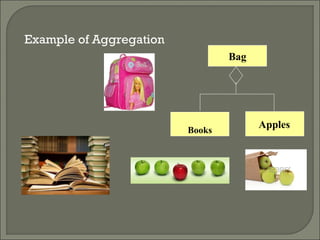
The document discusses class diagrams and their components. A class diagram visually represents the structure of a system by showing classes, their attributes, operations or methods, and the relationships between classes. It includes boxes to represent classes with three parts - name, attributes, and operations. It also discusses the different types of relationships between classes including generalization, association, aggregation and composition.