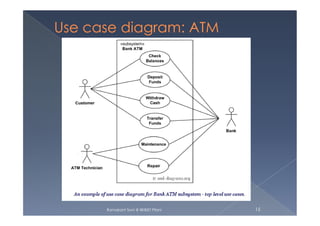
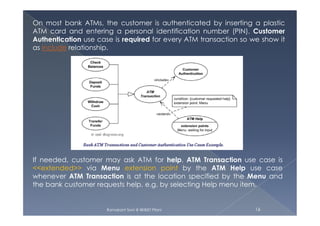
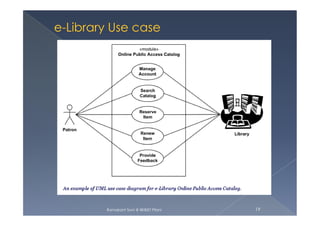
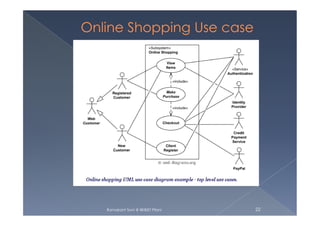
The document discusses use case modeling and provides several examples. It describes key concepts like actors, use cases, relationships between use cases, and multiplicity. It then summarizes 4 examples - an airport check-in system, bank ATM, online library catalog, and credit card processing. The examples illustrate how use cases model systems and interactions between actors and the system.














![References:
[1] http://www.uml-diagrams.org/
Ramakant Soni @ BKBIET Pilani 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture3-usecasediagram-part2-150426161613-conversion-gate01/85/Use-Case-diagram-UML-diagram-2-31-320.jpg)