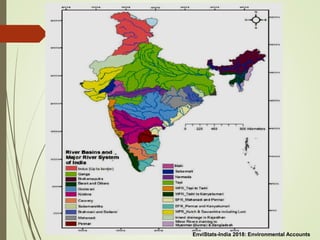
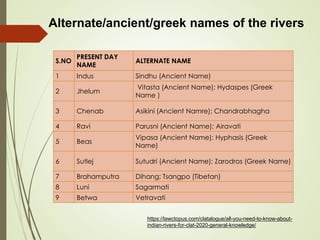
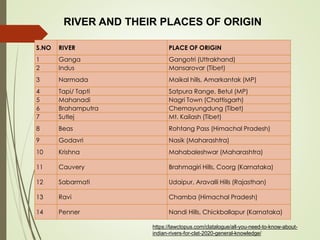
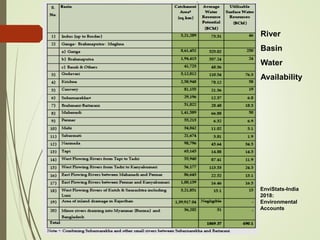
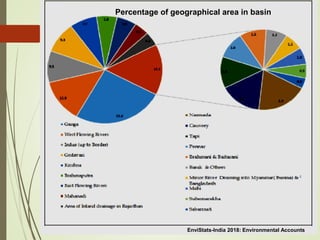
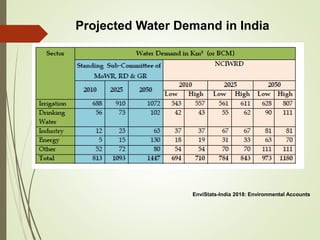
The document discusses various aspects of water resources in India. It notes that while India receives adequate average rainfall, it is unevenly distributed both seasonally and geographically. Nearly three-quarters of rainfall occurs in 120 days of the monsoon season. It also discusses India's surface and groundwater resources as well as the major issues around water scarcity, floods, droughts, and pollution facing the country. Sustainable management of water resources is important for India's development.