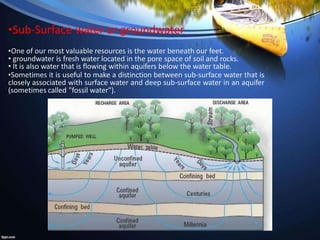
The document discusses various topics related to water resources including fresh water sources, uses of water, water scarcity issues, floods, droughts, conflicts over water, dams, and their environmental impacts. Specifically, it notes that fresh water sources include surface water and groundwater, the main uses of water are agricultural, industrial, household and more. It also discusses how water demand is exceeding supply in many areas, and how overutilization of water worsens scarcity issues.