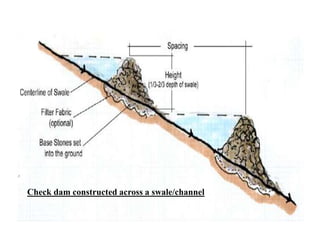
The document details check dams, small structures built across waterways to reduce water flow velocity and trap sediments, thus preventing erosion. It describes various types of check dams, their construction materials, design considerations, advantages, and limitations. Check dams are particularly effective in areas less than 10 acres and are cost-effective but have specific conditions for use and maintenance requirements.