The document discusses key concepts related to laser emission and operation, including:
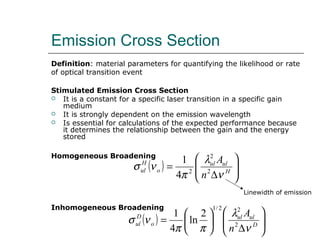
1. Stimulated emission cross section is a constant that determines the relationship between gain and stored energy in a laser medium. It depends on emission wavelength.
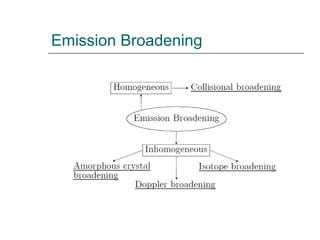
2. Homogeneous and inhomogeneous broadening contribute to the linewidth of laser emission.
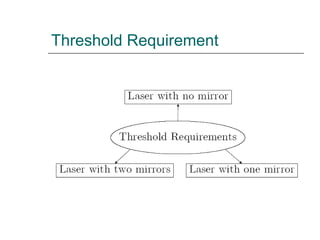
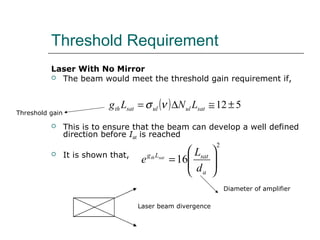
3. Threshold requirements refer to the gain needed for a laser beam to reach saturation intensity after passing through an amplifier multiple times with mirrors.
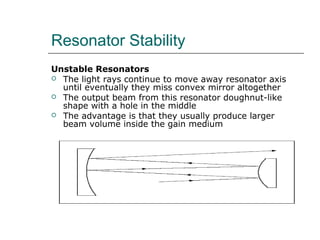
4. Resonator stability depends on mirror curvature, with stable resonators keeping light near the axis and unstable resonators producing doughnut-shaped output beams.
5. Pumping techniques include direct, optical, and particle pumping to excite the












![Cavity Modes
Longitudinal Laser Cavity Modes
This expression is valid for almost all gas lasers, as well as
for solid-state and dye lasers in which the mirrors are
placed immediately at the ends of the gain medium. If a
laser has a space of length d - L between the gain medium
and the mirrors, and if that cavity space has a different
value for the index of refraction nc than the index nL of the
laser gain medium, then a specific laser mode frequency
associated with a mode number m can be expressed as,
ö
ù
1
[ ] ÷ ÷ø
æ
ç çè
úû
é
êë
- +
=
n d L n L
m c
c L
2
n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture122013-140828061613-phpapp01/85/Lecture-12-2013_-18-320.jpg)