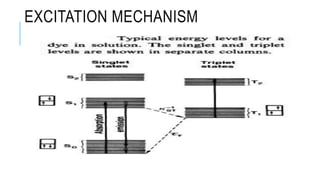
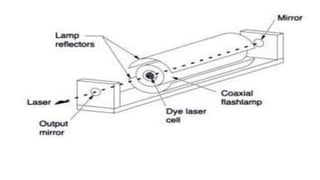
Dye lasers use organic dyes dissolved in liquid solvents as the lasing medium, which allows them to produce tunable laser outputs across a wide range of wavelengths from 320nm to 1200nm. They operate by pumping dye molecules into excited electronic states using another light source, such as from an argon-ion or flashlamp, after which stimulated emission produces the laser beam. Dye lasers are commonly used in research applications requiring tunable laser sources, such as spectroscopy, atomic physics, photochemistry, and pollution monitoring.