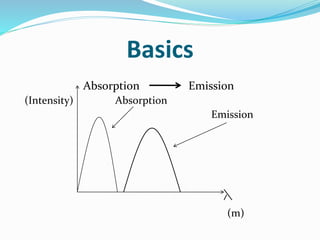
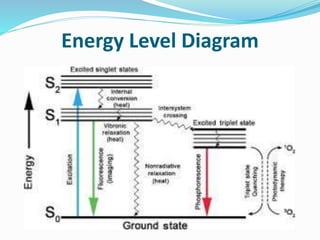
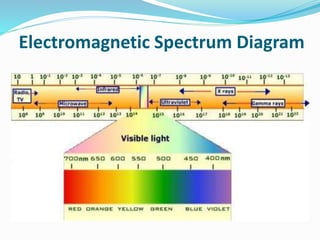
Dye lasers use an organic dye dissolved in a liquid as the active lasing medium and can produce a wide range of wavelengths. They work on the principle of population inversion using a pumping source like a flash lamp or other laser to excite the dye molecules. The major components are the active dye medium, pumping source, and resonator mirrors, with one mirror sometimes replaced by a diffraction grating to allow tuning of the output wavelength. Dye lasers offer tunability but have limitations in lifetime and output power.