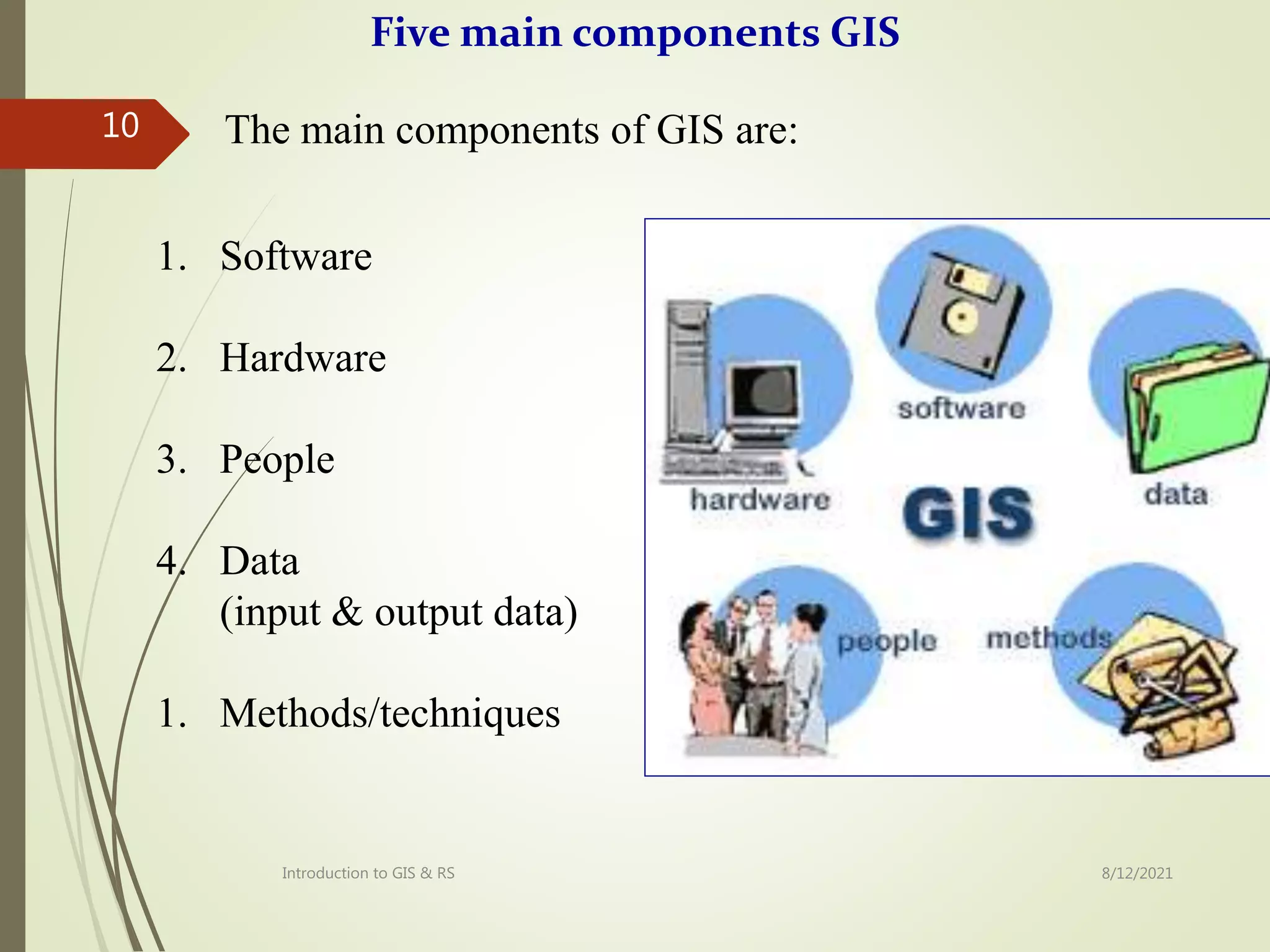
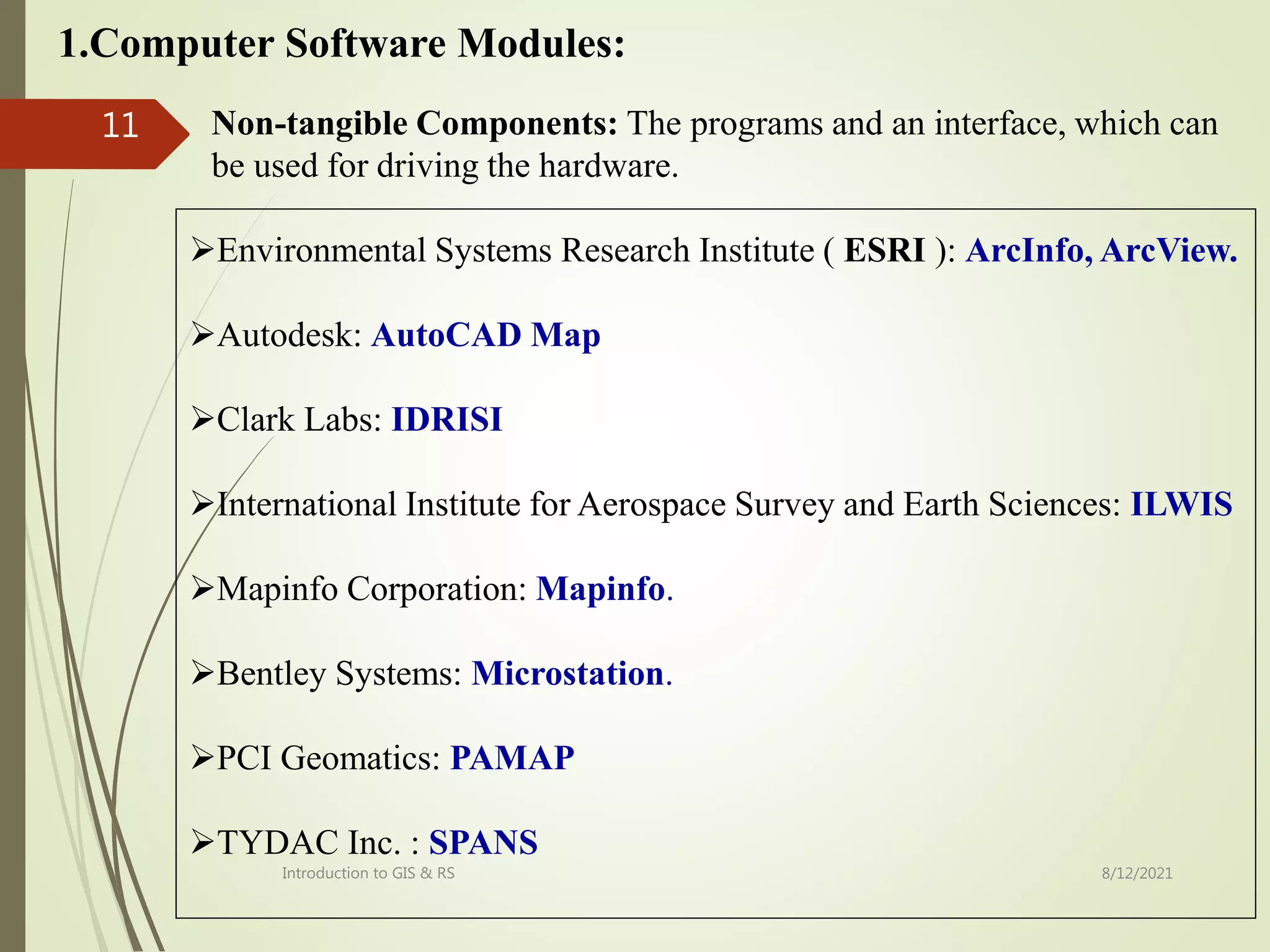
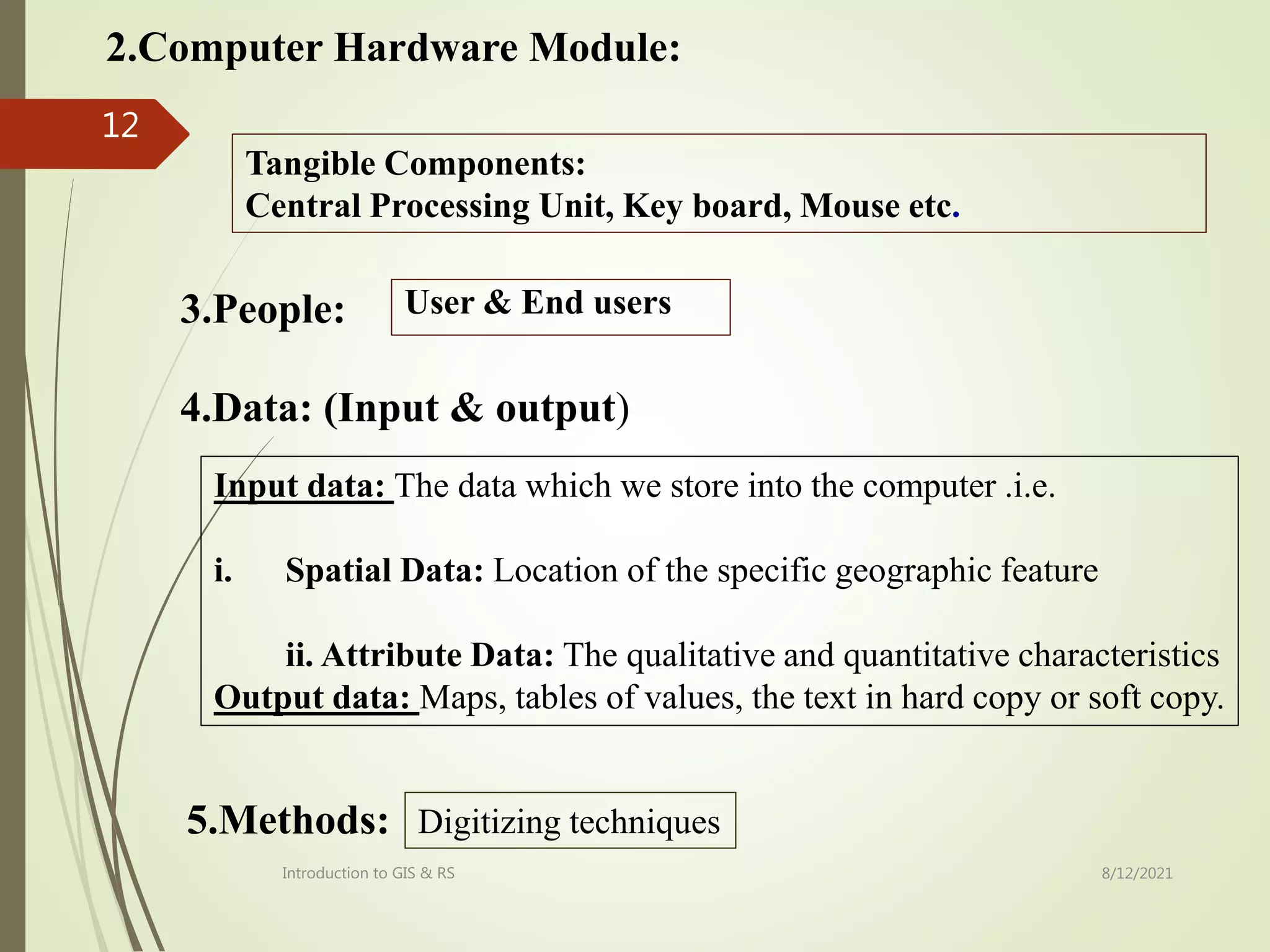
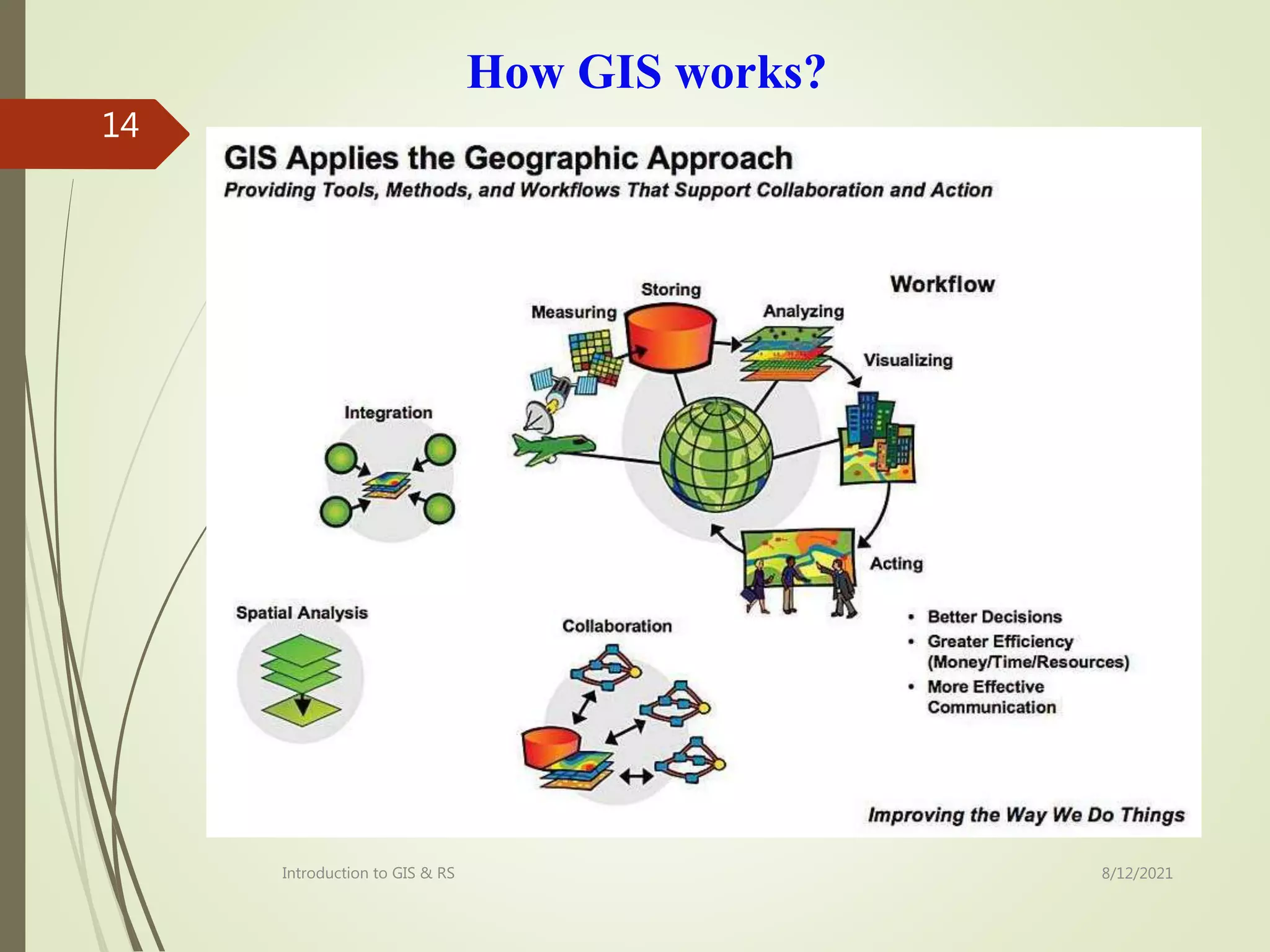
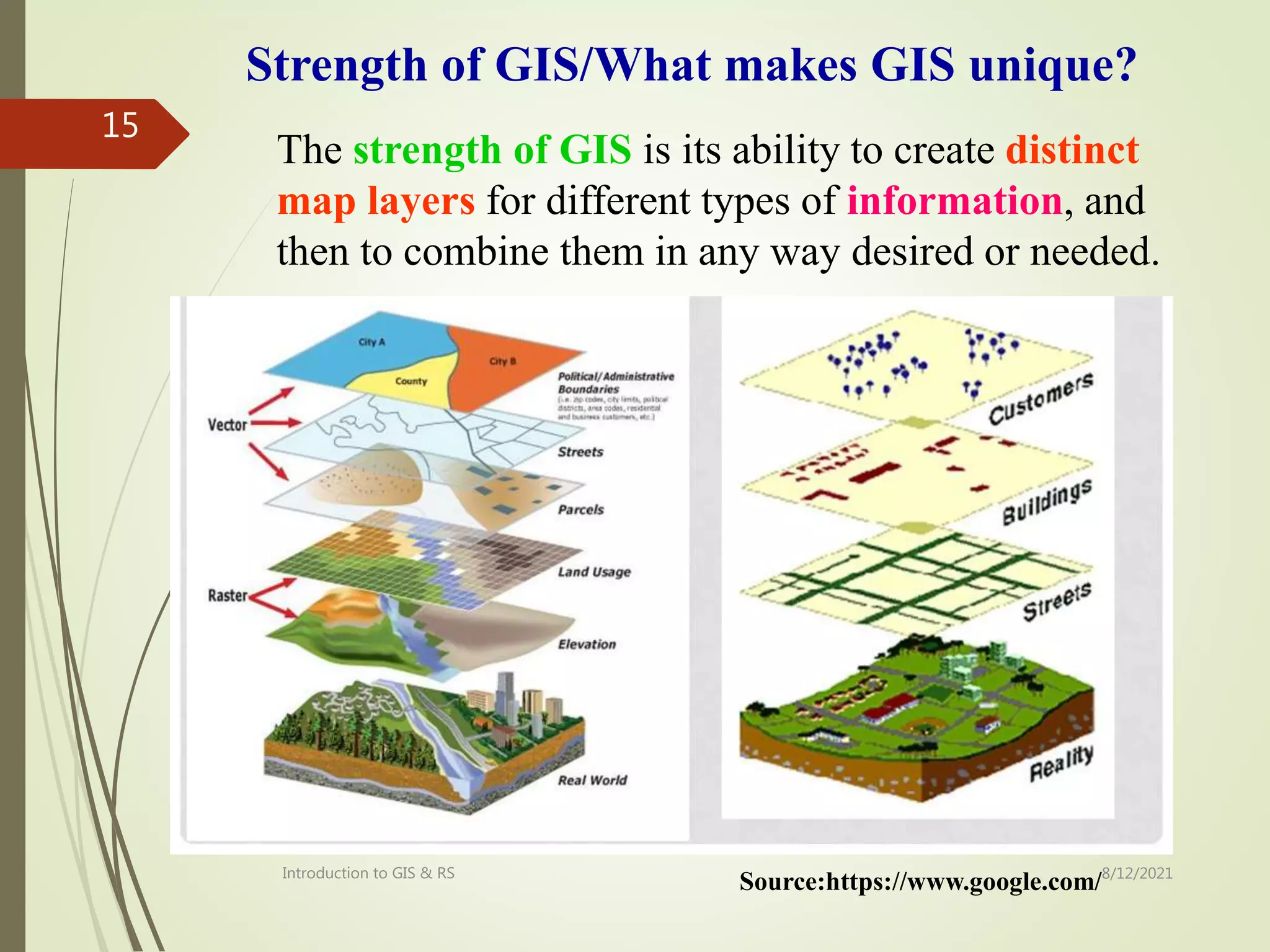
The document provides an introduction to remote sensing including:
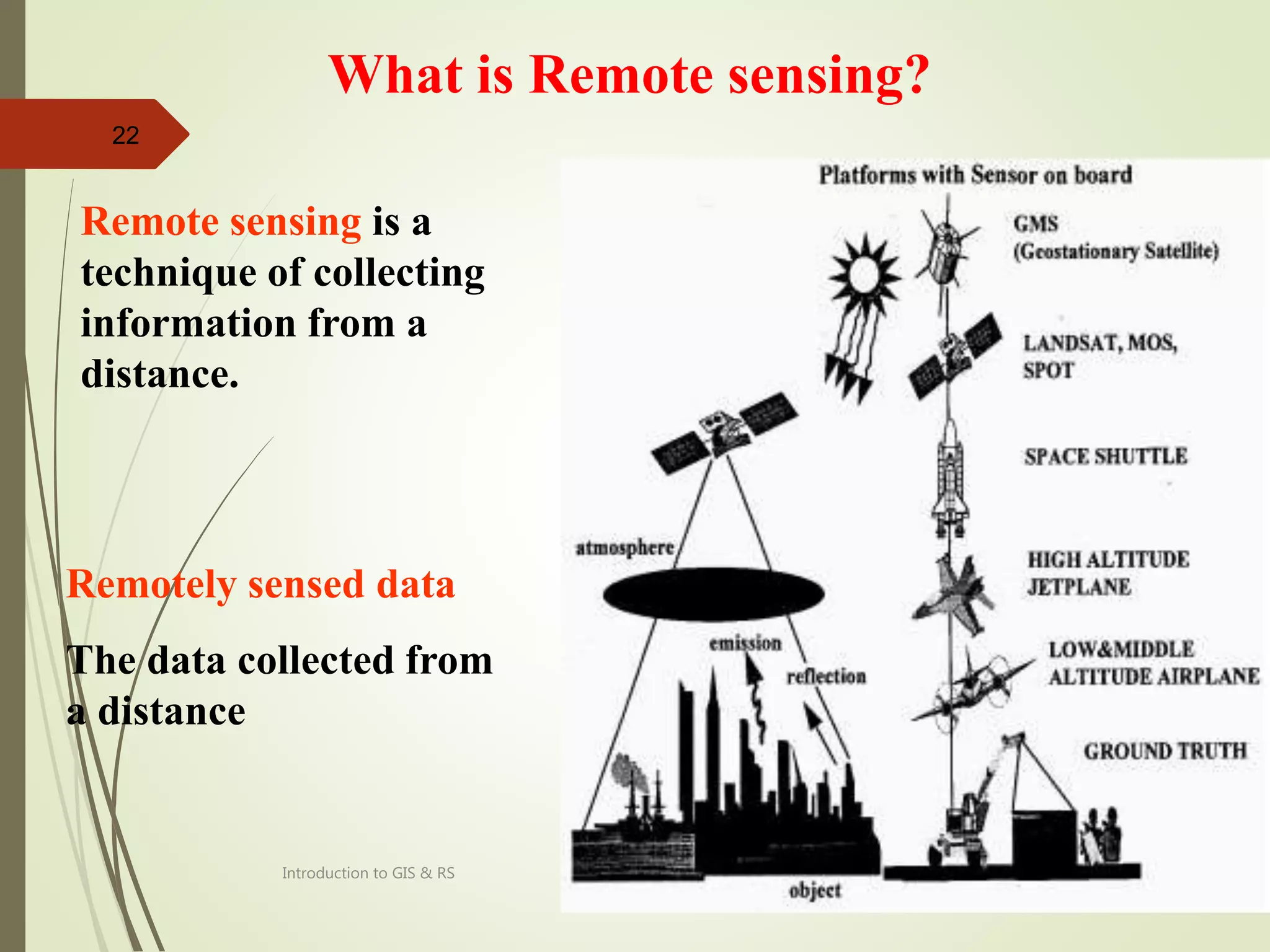
- A definition of remote sensing as collecting information about objects or areas from a distance without physical contact.
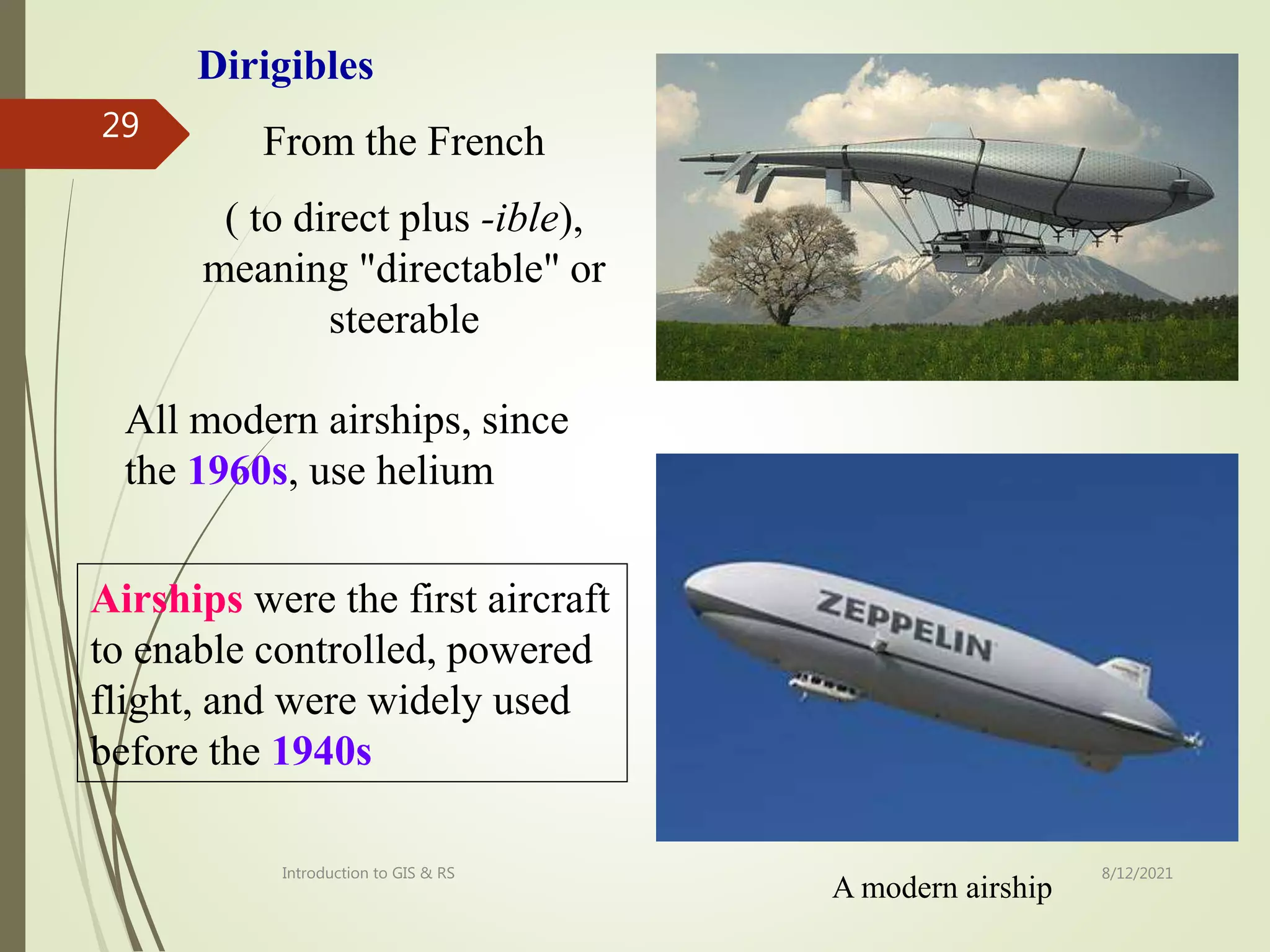
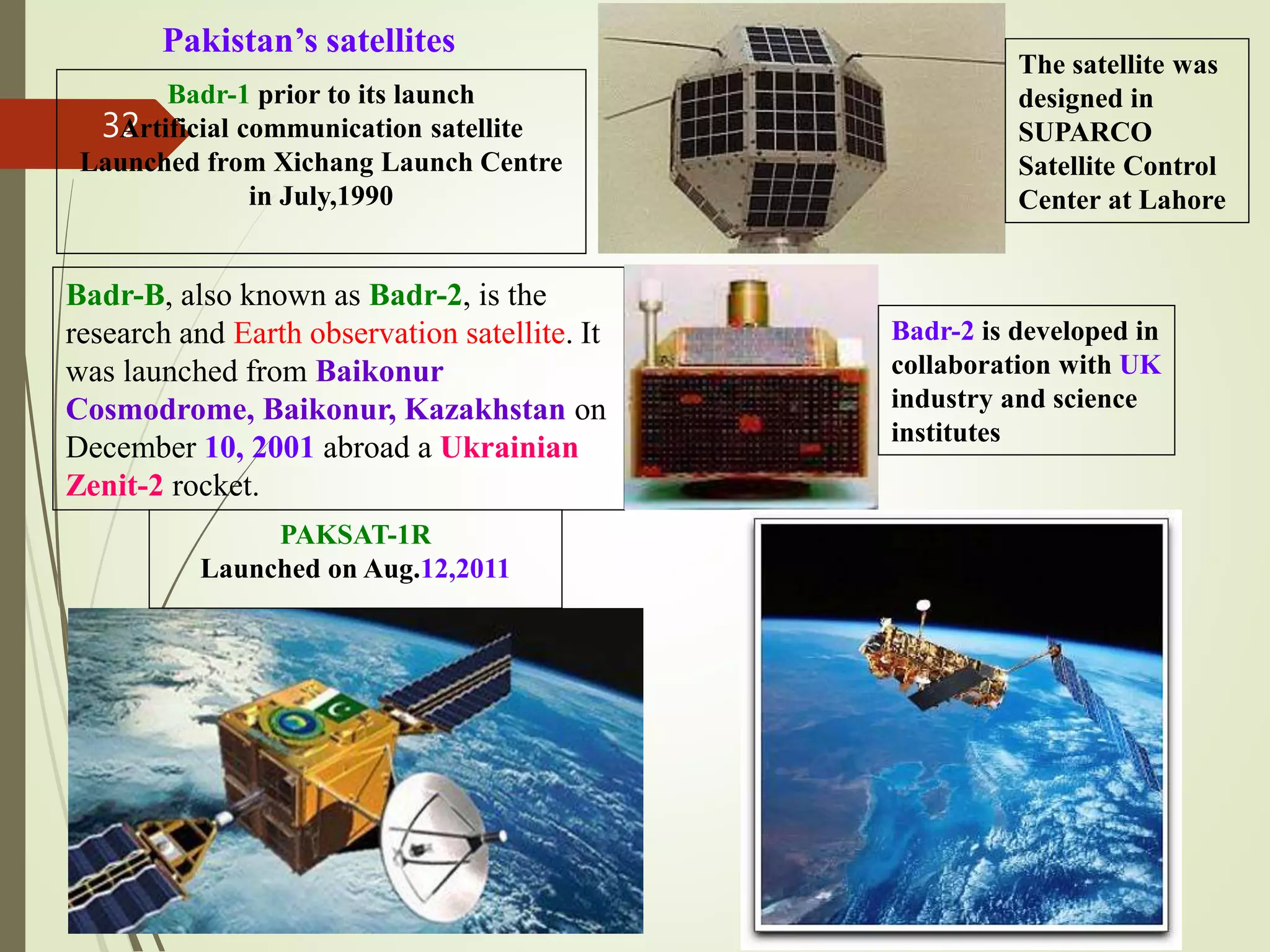
- An overview of the history of remote sensing from early aerial photography using balloons and airplanes to modern satellite imagery.
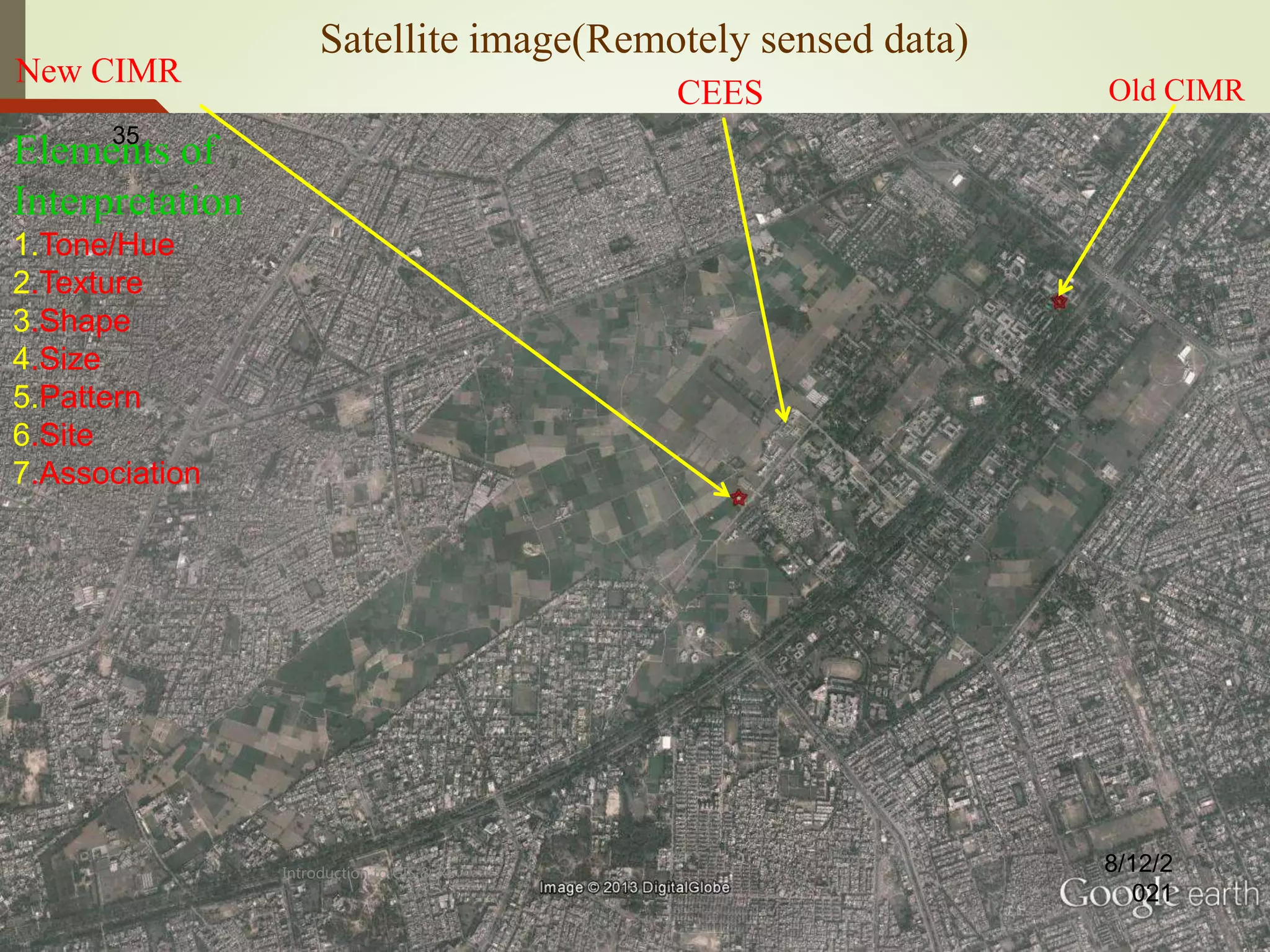
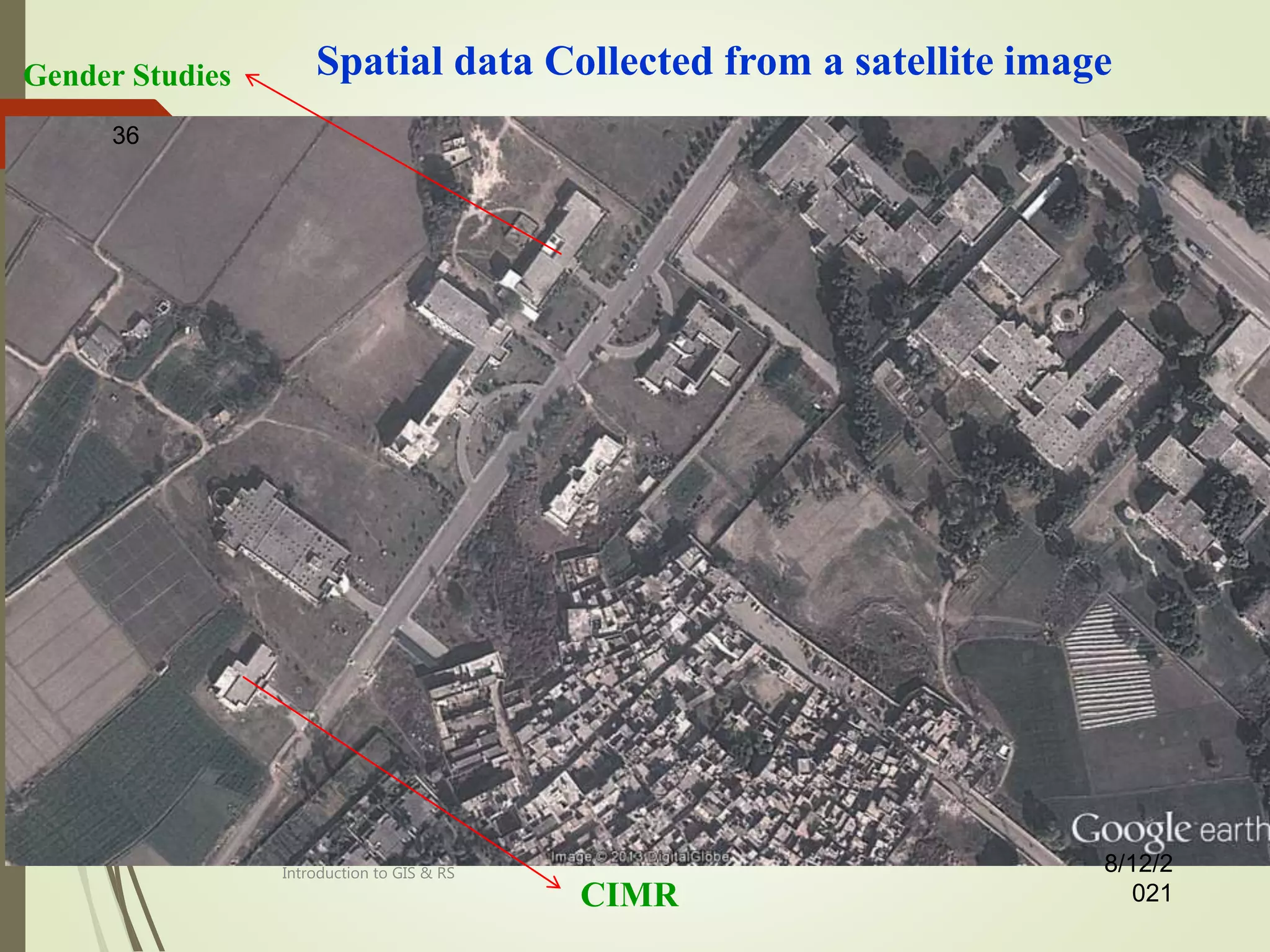
- An explanation that remote sensing is a spatial data acquisition technique that collects remotely sensed data from various platforms and sources.