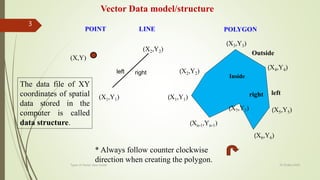
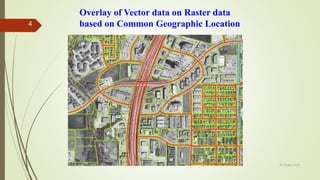
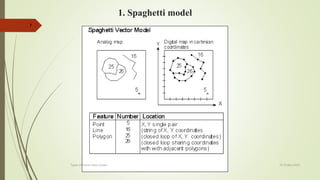
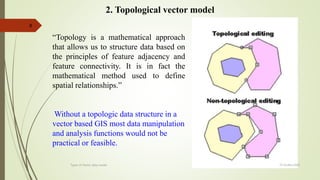
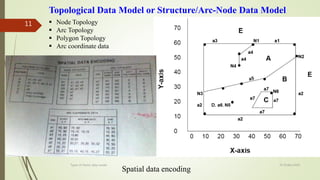
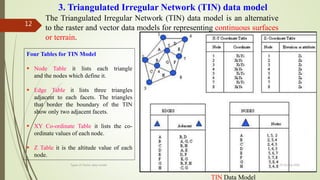
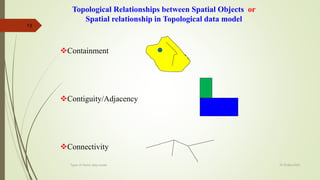
This document discusses different types of vector data models, including the spaghetti model, topological vector model, and TIN (Triangular Irregular Network) model. It provides details on topological vector models, which use an arc-node structure to represent spatial relationships between data entities. The topological model allows for analysis of features' adjacency and connectivity. The document also summarizes the TIN model, which represents continuous surfaces using triangles formed by nodes with x,y,z coordinates.