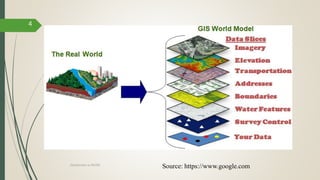
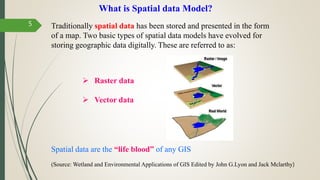
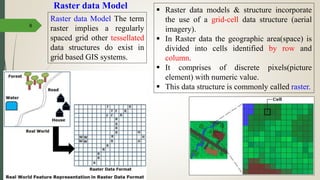
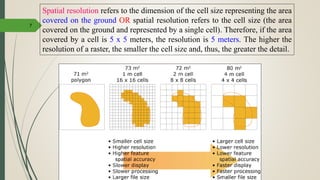
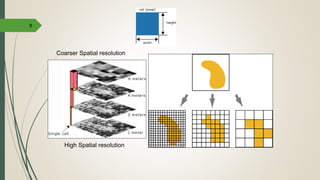
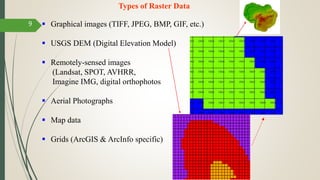
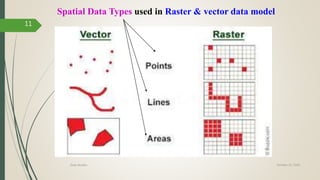
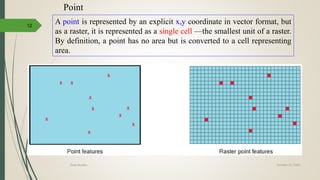
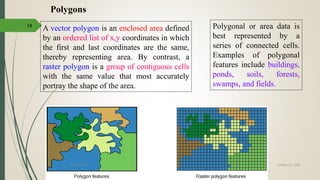
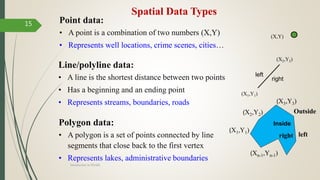
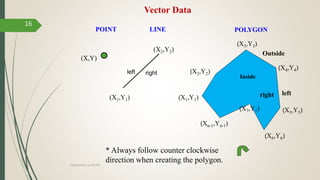
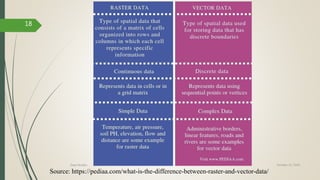
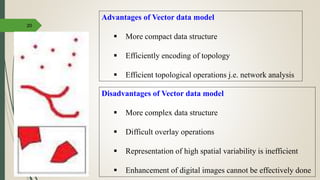
This document discusses raster and vector data models used in GIS. Raster data models use a grid structure of cells organized by rows and columns, with each cell containing a numeric value. Vector data models represent spatial features as points, lines, and polygons using x,y coordinates. The key spatial data types—points, lines, and polygons—are explained for both raster and vector formats. Advantages and disadvantages of each model are provided. The document is a lecture on GIS data models presented by Rehana Jamal to students at Arid Agriculture University.