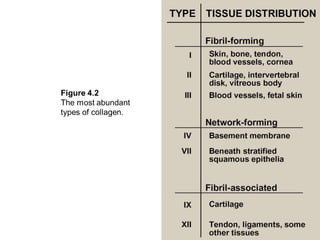
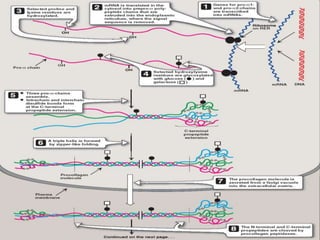
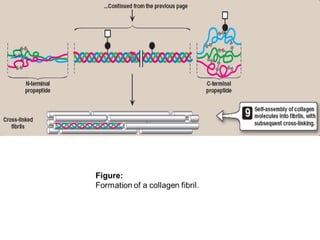
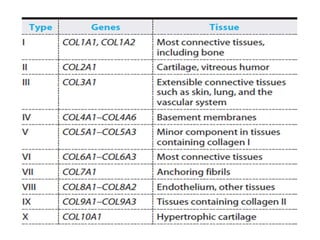
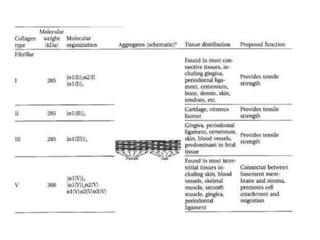
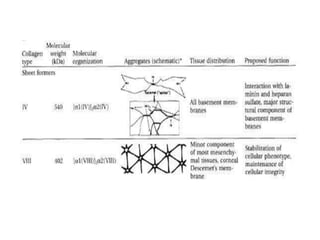
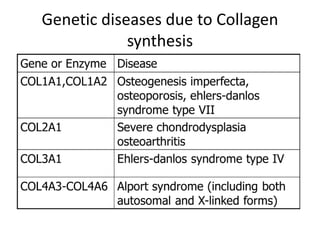
This document discusses collagen fibers. It begins by introducing collagen as the main structural protein in connective tissues, making up 25-35% of body protein. Collagen forms elongated fibrils found in tissues like skin, tendons, and bones. It then describes the triple helix structure of collagen and types I-III that form fibrils and networks. Type I collagen comprises many supporting tissues, while type II is found in cartilage. The document also notes medical uses of collagen in skin grafts and cosmetics, as well as genetic diseases associated with collagen deficiencies.