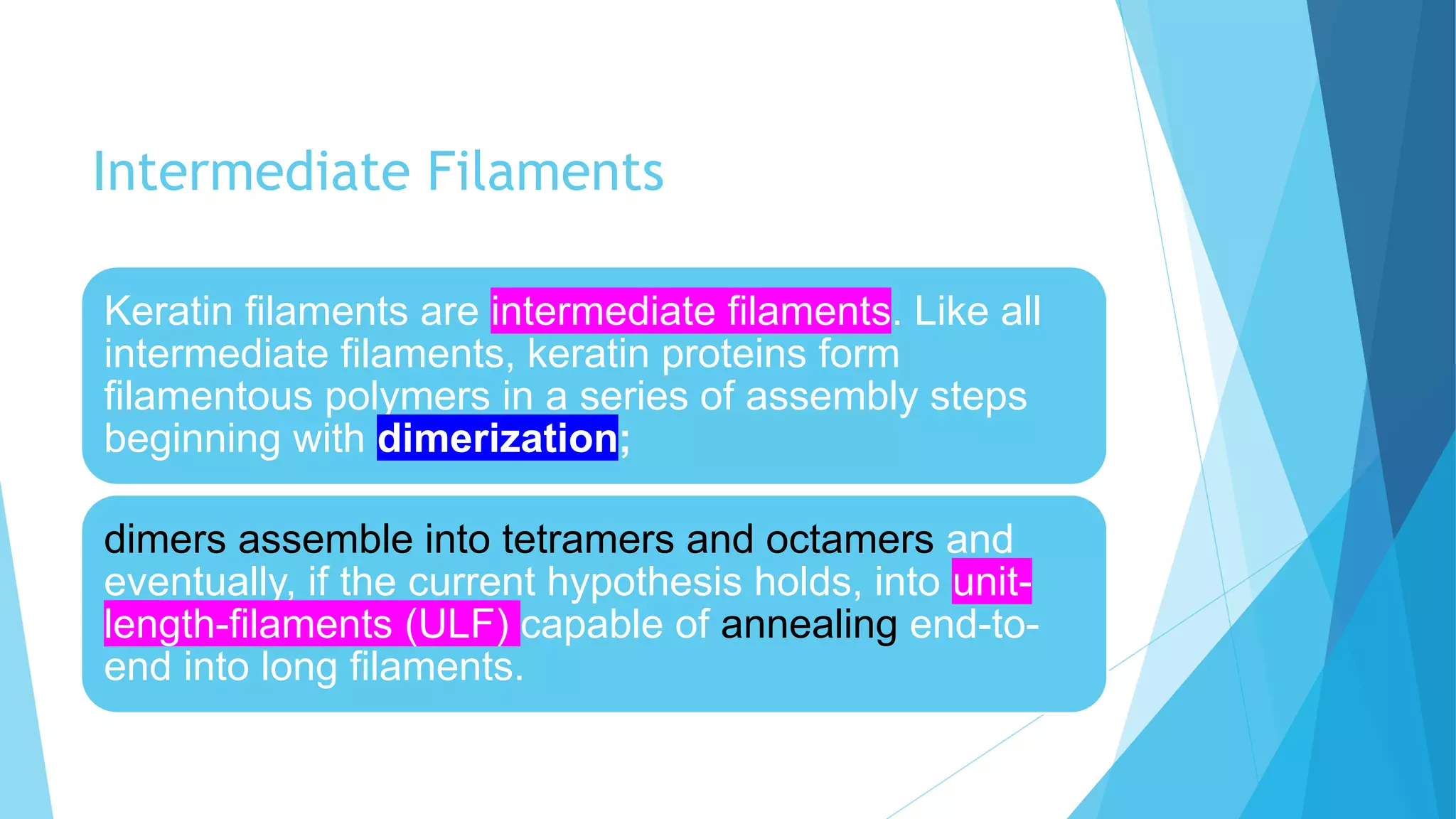
Fibrous proteins are a group of proteins associated with rod or wire shapes. They are usually inert structural or storage proteins that are generally water insoluble. Examples include keratin, collagen, and elastin. In the early 1950s, the basic structures of fibrous proteins were determined to be long protein chains composed of amino acid strings that fold into limited structures like alpha helices and beta sheets. Fibrous proteins often have biological roles as structural components and are found in tissues like bone, cartilage, hair and skin.