Complex analysis deals with complex-valued functions of complex variables. Some key concepts covered in the document include:
- Complex functions can be expressed in either Cartesian (z = x + iy) or polar (z = reiθ) form.
- For a complex function f(z) to be differentiable, it must satisfy the Cauchy-Riemann conditions.
- Analytic functions are differentiable at every point in their domain. For example, ez is analytic everywhere while z̅ is analytic nowhere.
- Branch cuts arise for multi-valued functions like √z, with the line between θ = 2π and θ = 4π representing one branch cut.

![NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1
The value of the function at A is 𝑓(𝑧) = √𝑟𝑒𝑖 𝜃1⁄2. After a complete revolution,
𝑓(𝑧) = √𝑟𝑒
𝑖(𝜃1+2𝜋⁄2
= −√𝑟𝑒𝑖 𝜃1⁄2
So it does not return to the same value. So the function is multivalued and √𝑟𝑒
𝑖𝜃1⁄2 is a
value on one of the branches and between 2𝜋 ≤ 𝜃 ≤ 4𝜋, the function assumes another
branch. The line OB is called the branch cut.
Complex integration Cauchy – Goursat Theorem
If 𝑓(𝑧) is analytic in a region R and on it’s boundary 𝐶, then ∮ 𝑓(𝑧)𝑑𝑧 = 0 Also known as
cauchy’s integral theorem.
Cauchy’s Integral formula
𝑓(𝑎) =
1 𝑓(𝑧)
∮ 𝑑𝑧
2𝜋𝑖 𝑧 𝑧−𝑎
𝑓(𝑧) is analytic inside and on the boundary c of a simply connected region R, excepting
at a point a.
Residue theorem
If 𝑓(𝑧) is analytic inside and on a simple closed curve c except for a pole of order m at 𝑧
= 𝑎, inside c, prove that
1 1
2𝜋𝑖
∮ 𝑓(𝑧)𝑑𝑧 = 𝐿𝑖𝑚
𝑧→𝑎 (𝑚 − 1)! 𝑑𝑧𝑚−1
𝑑𝑚−1
[(𝑧 − 𝑎)𝑚𝑓(𝑧)]
𝑐
If there are two different poles of order 𝑚1and 𝑚2
1 1
2𝜋𝑖
∮ 𝑓(𝑧)𝑑𝑧 = 𝐿𝑖𝑚
𝑧→𝑎1 (𝑚1−1)! 𝑑𝑧𝑚1−1
𝑐
𝑑𝑚1−1
[(𝑧 − 𝑎1)𝑚1 𝑓(𝑧)] +
𝐿𝑖𝑚
𝑧→𝑎2 (𝑚2−1)! 𝑑𝑧𝑚2−1
Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 55 of 66
1 𝑑𝑚2−1
[(𝑧 − 𝑎 )𝑚2 𝑓(𝑧)]
2
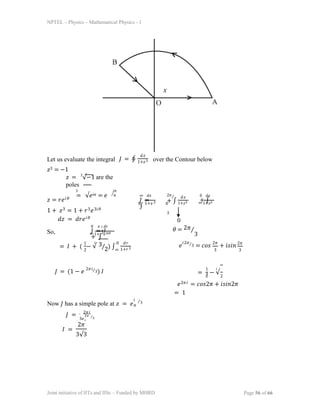
Example
Integrate,
∞ 𝑑𝑥
𝐼 =
∫
0 1+𝑥3
The integrand I is not even so we cannot extend it up to -∞.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec40-231023100403-fdfab015/85/lec40-ppt-2-320.jpg)