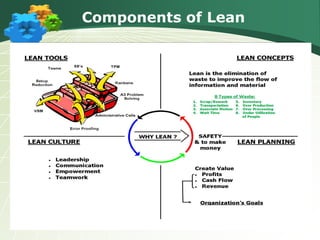
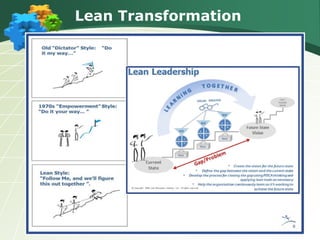
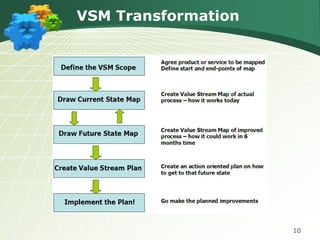
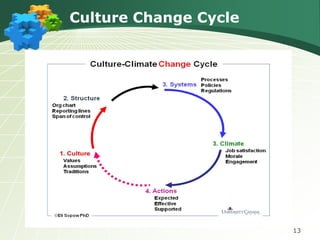
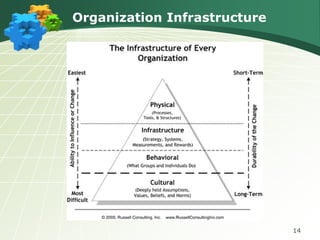
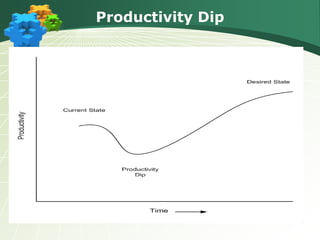
The document discusses the components and goals of organizational change management, emphasizing the need for an organization to prepare for, implement, and sustain significant changes. It outlines the phases of change, challenges faced during transitions, and the cultural transformations required for successful lean implementation. Key strategies for managing resistance to change and achieving organizational-wide acceptance are also highlighted.