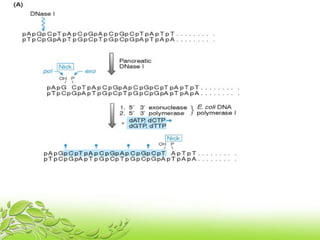
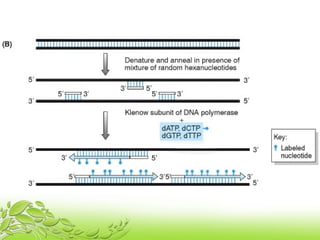
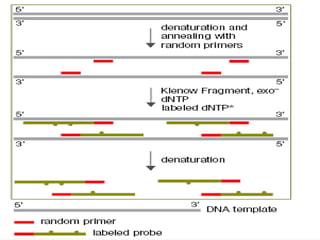
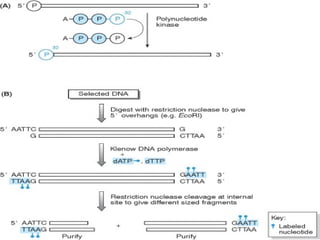
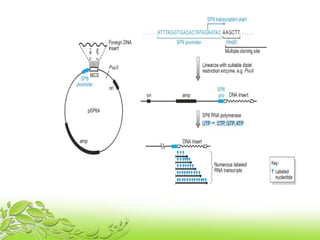
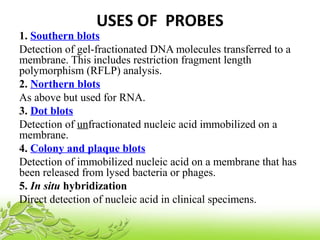
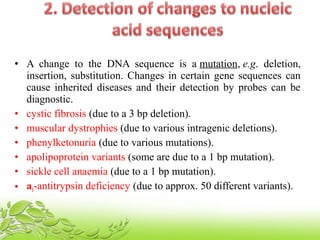
A probe is a short sequence of DNA or RNA that is used to detect complementary DNA or RNA sequences in samples. Probes can be labeled with radioactive isotopes or fluorescent tags to allow for their detection after hybridizing to target sequences. They are commonly used techniques like Southern blots, Northern blots, and in situ hybridization to detect specific nucleic acid sequences and identify microorganisms, viruses, or genetic mutations associated with diseases. Probes provide a sensitive method for detecting nucleic acids and have many applications in medical research and diagnosis.