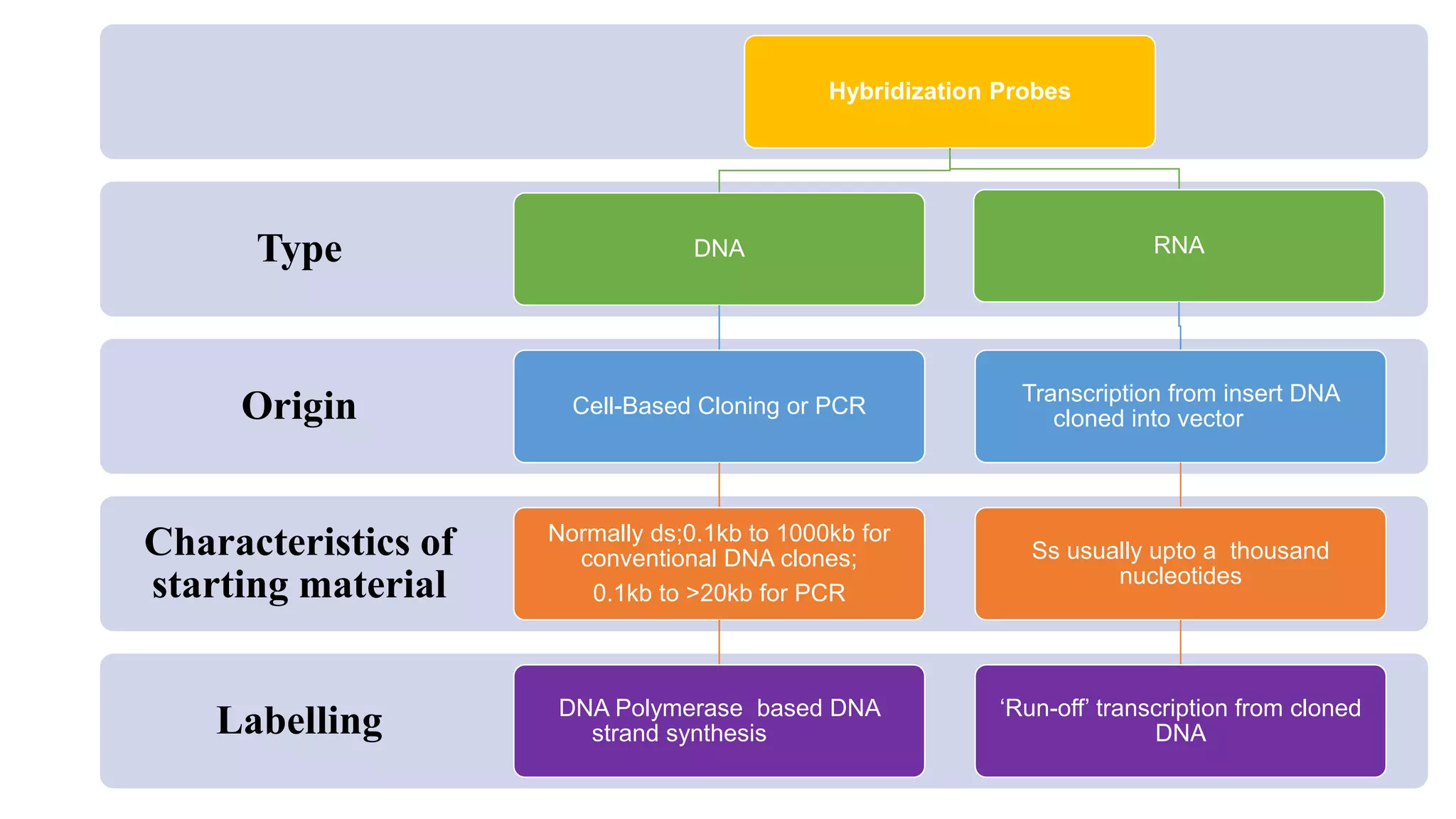
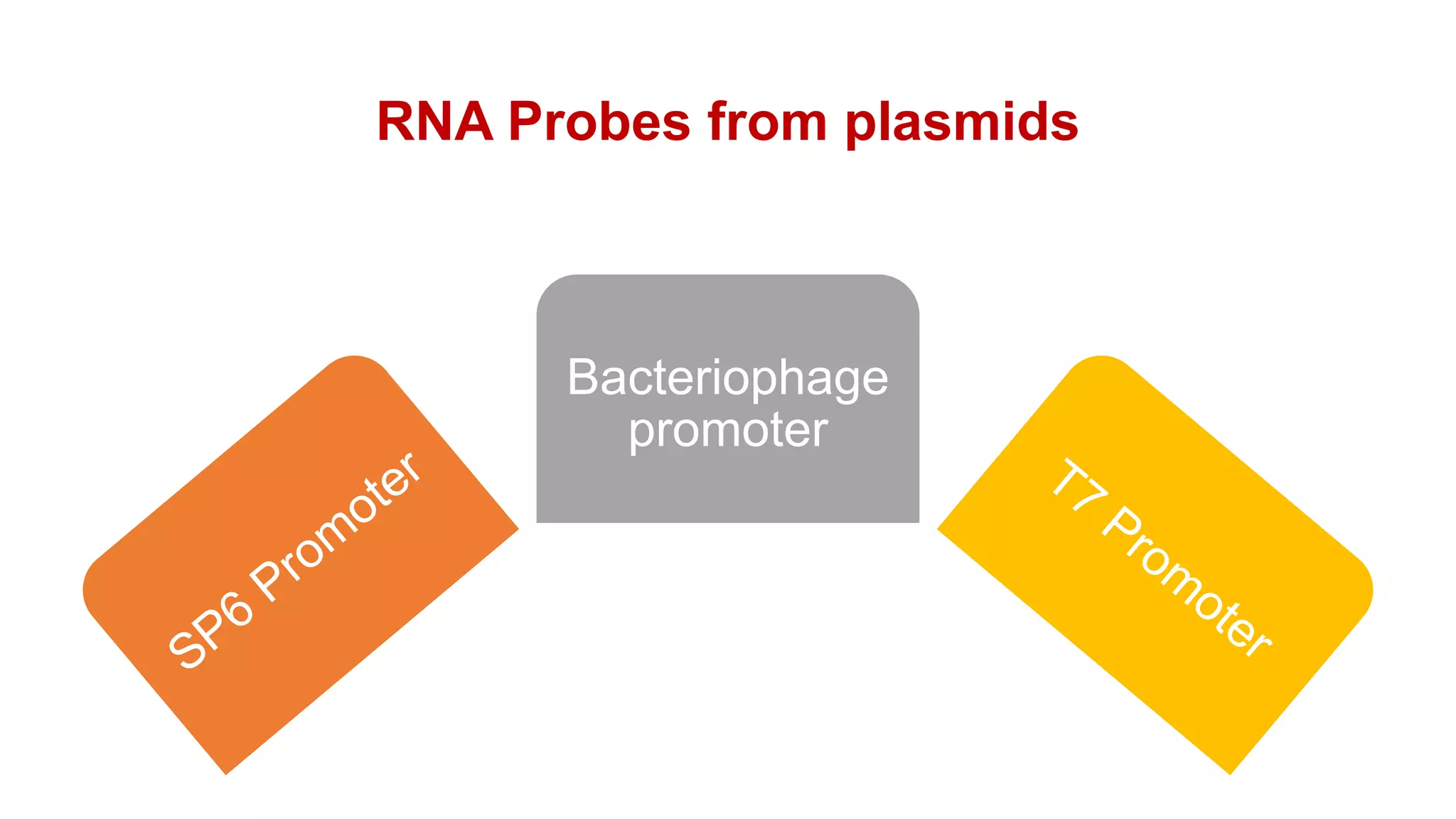
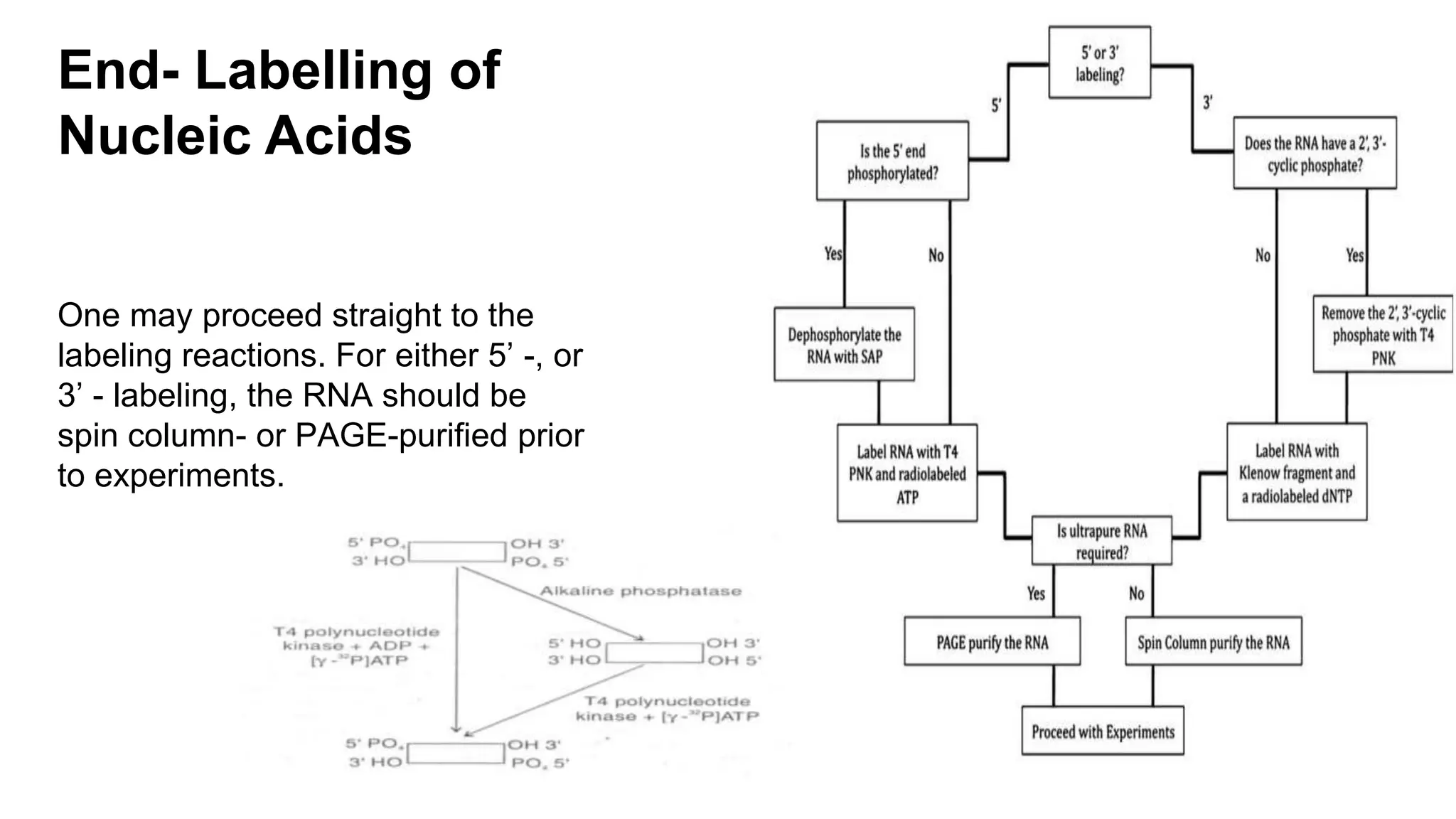
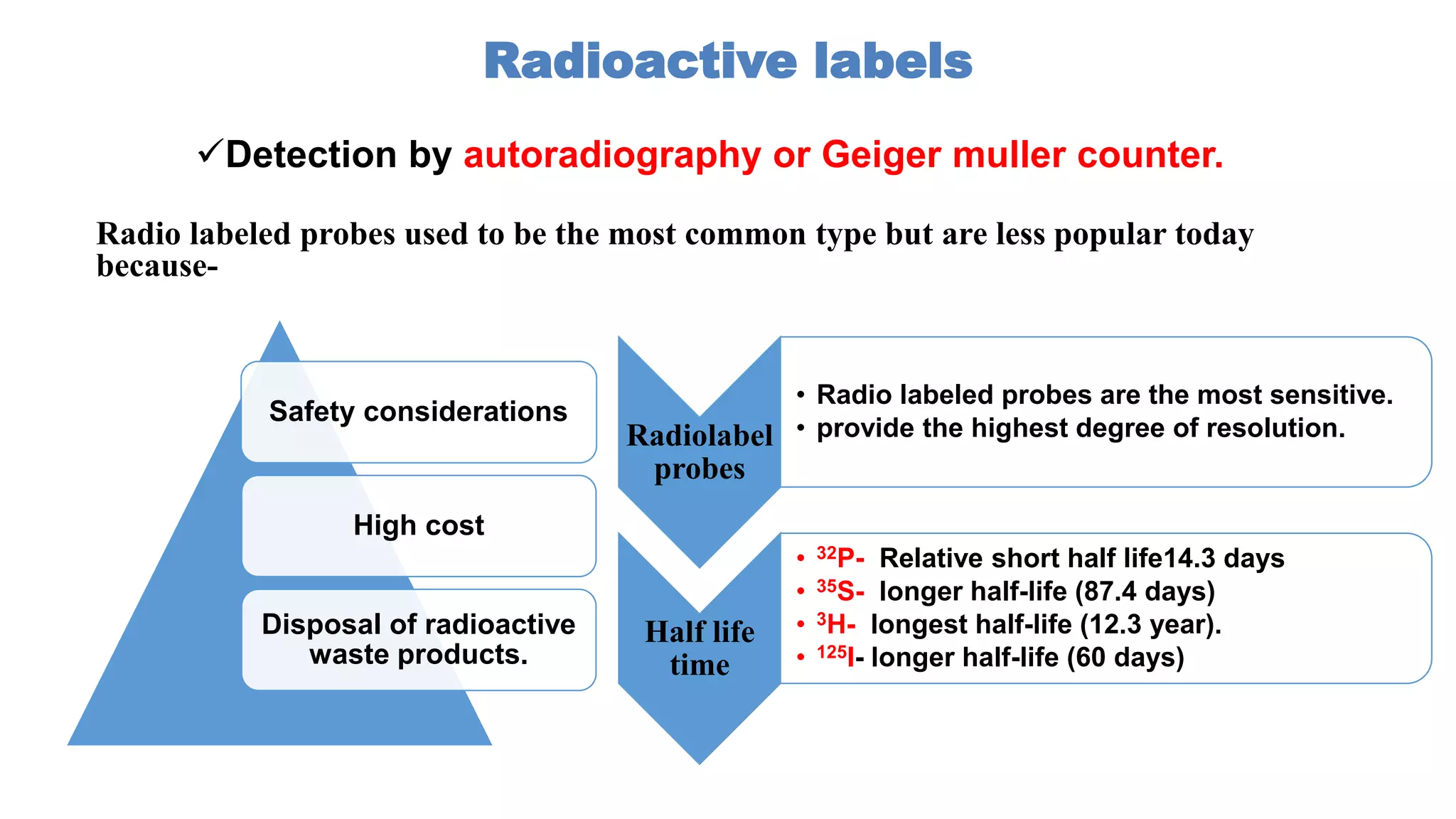
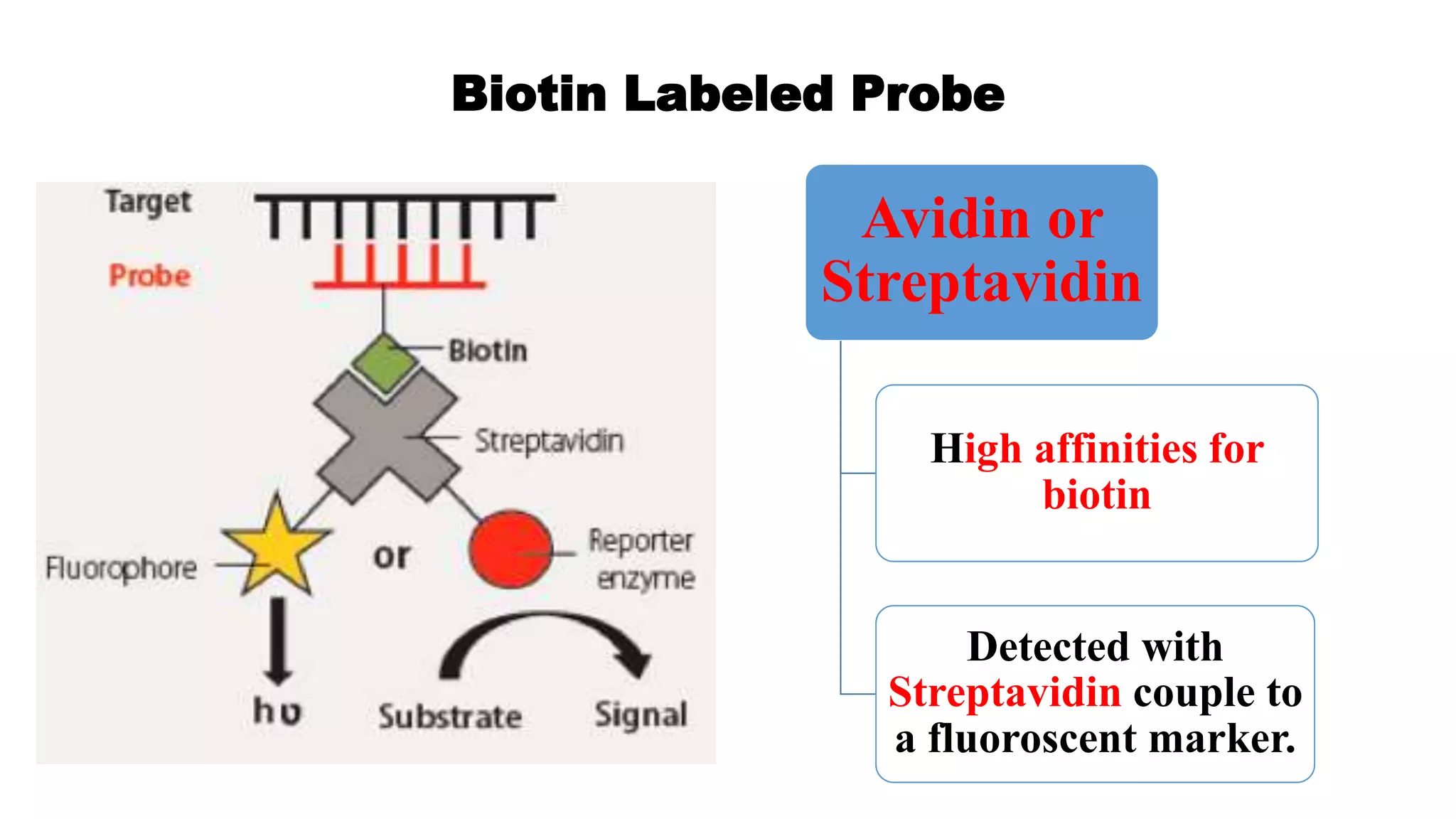
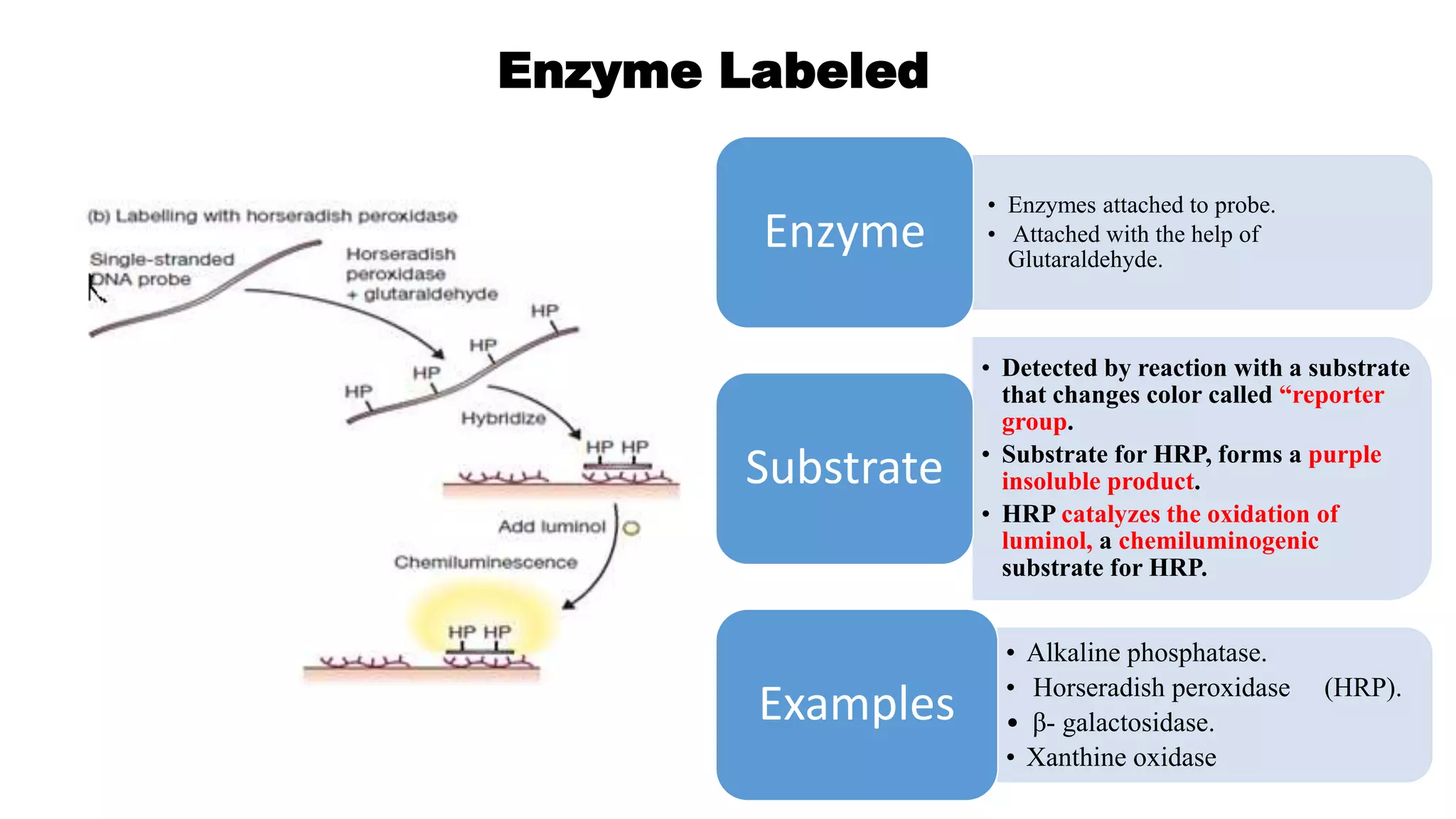
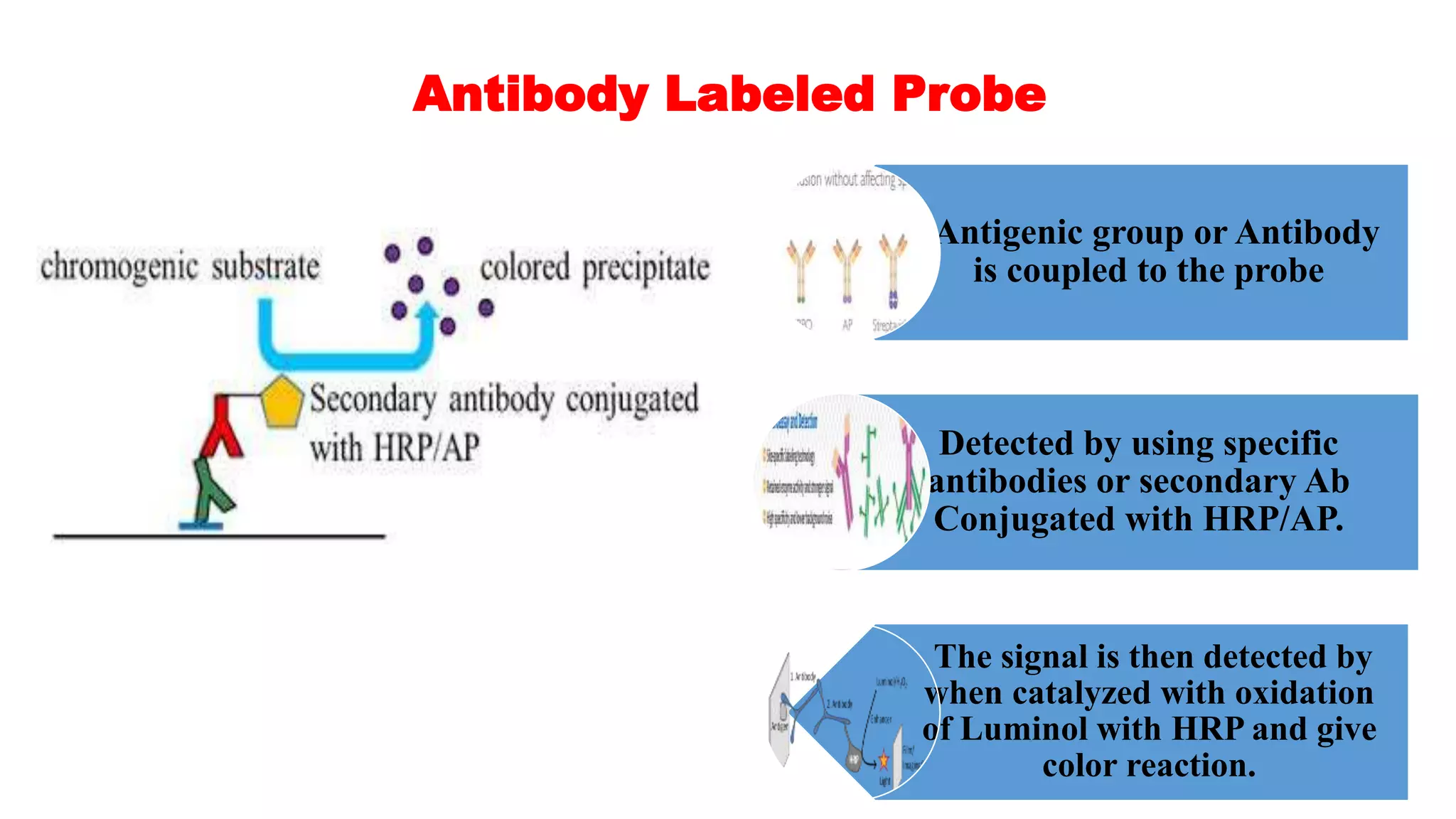
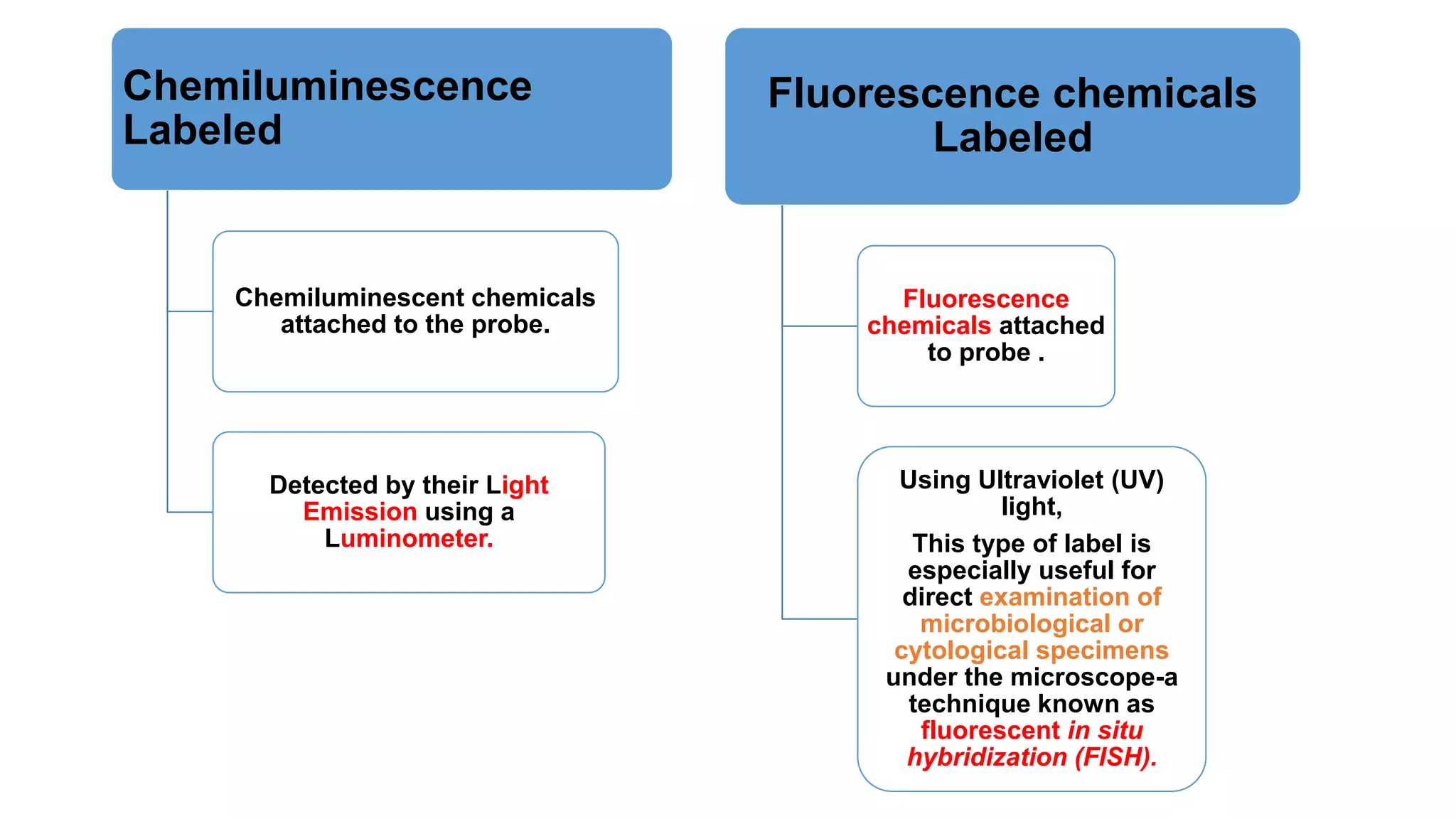
The document discusses molecular RNA probes, detailing their design, labeling methods, and applications in biotechnology. It differentiates between radioactive and non-radioactive labeling techniques, highlighting their advantages and safety considerations. The document also covers RNA probe applications such as northern blotting, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and RNA protection assays.