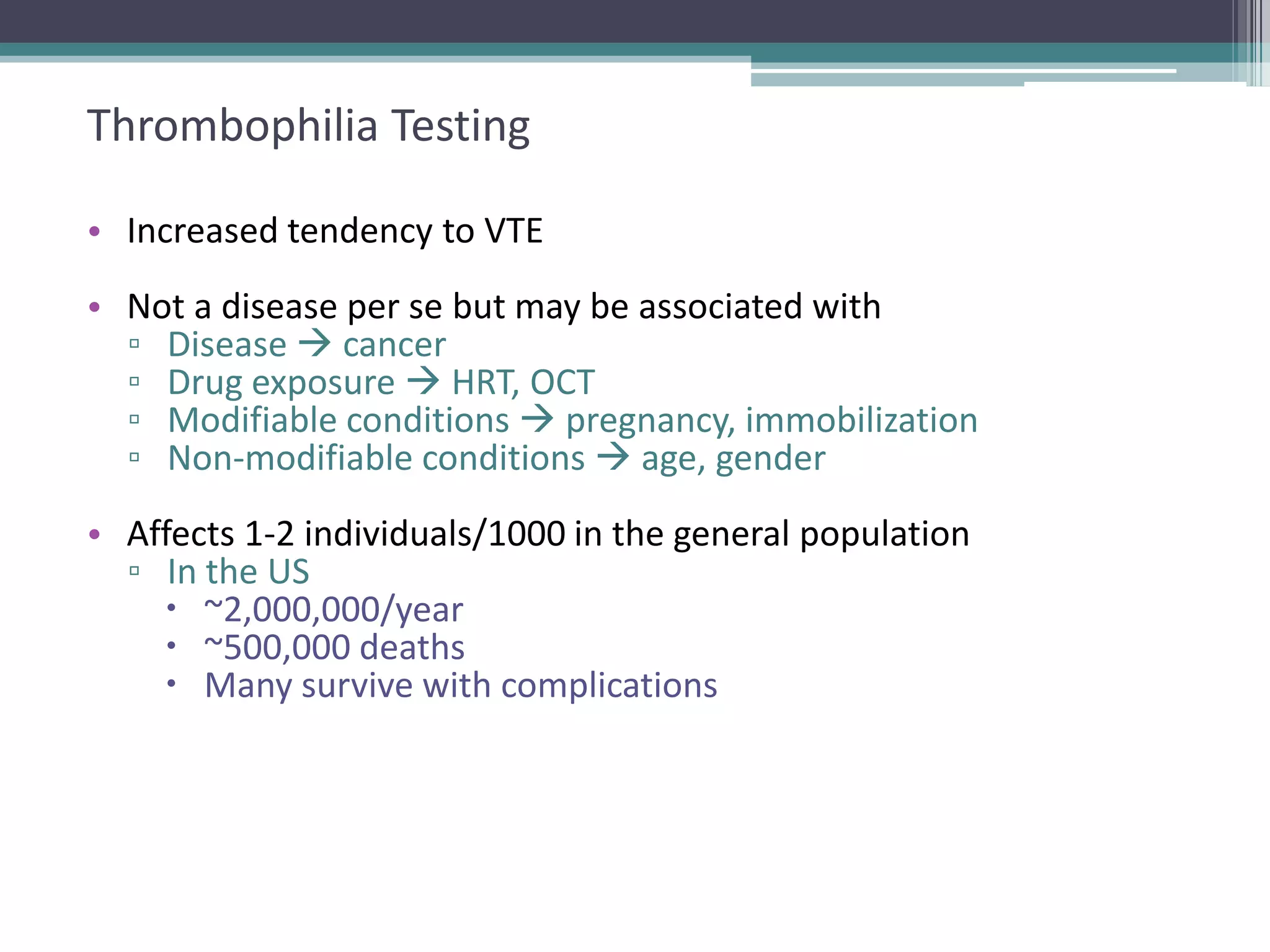
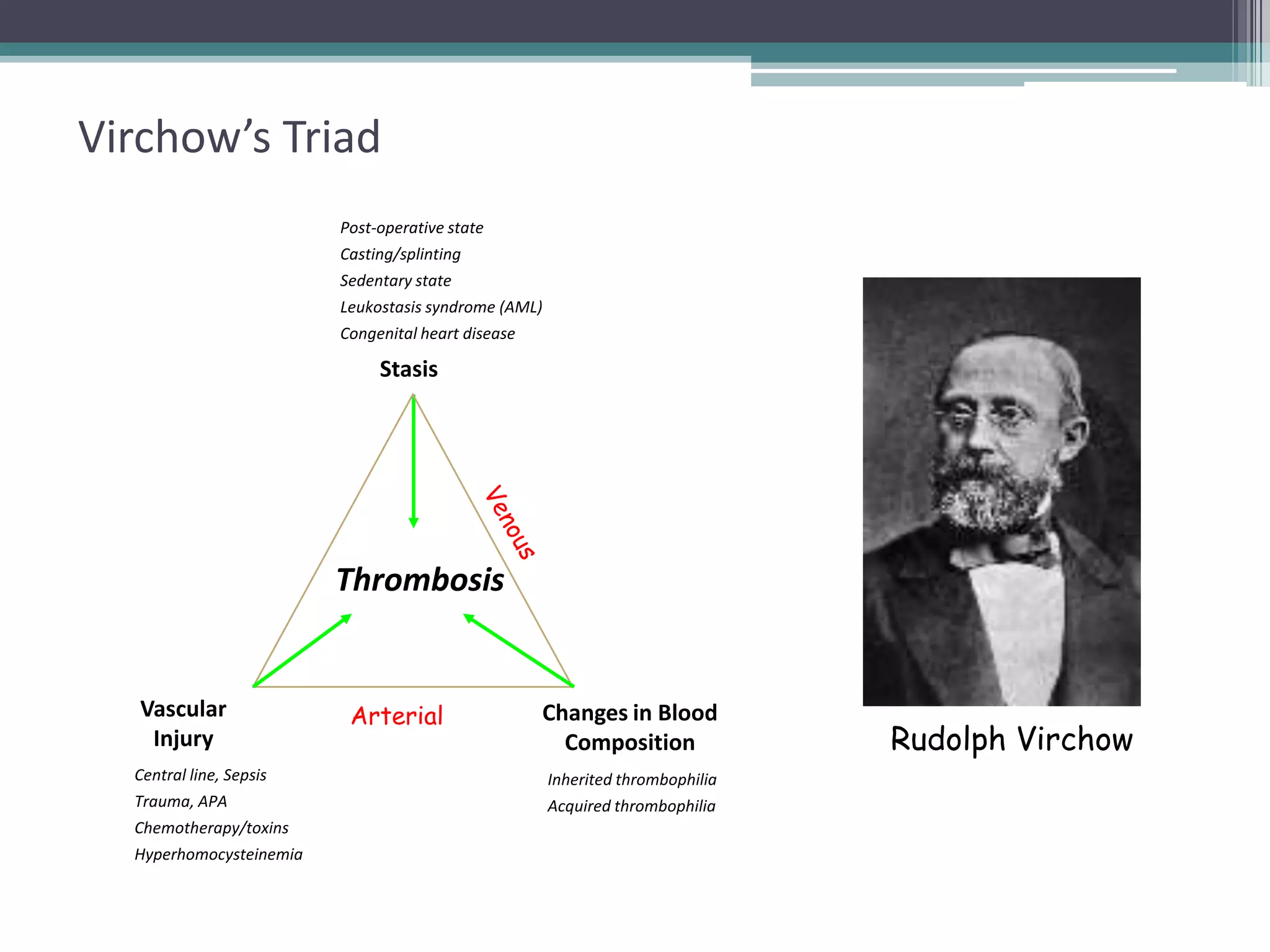
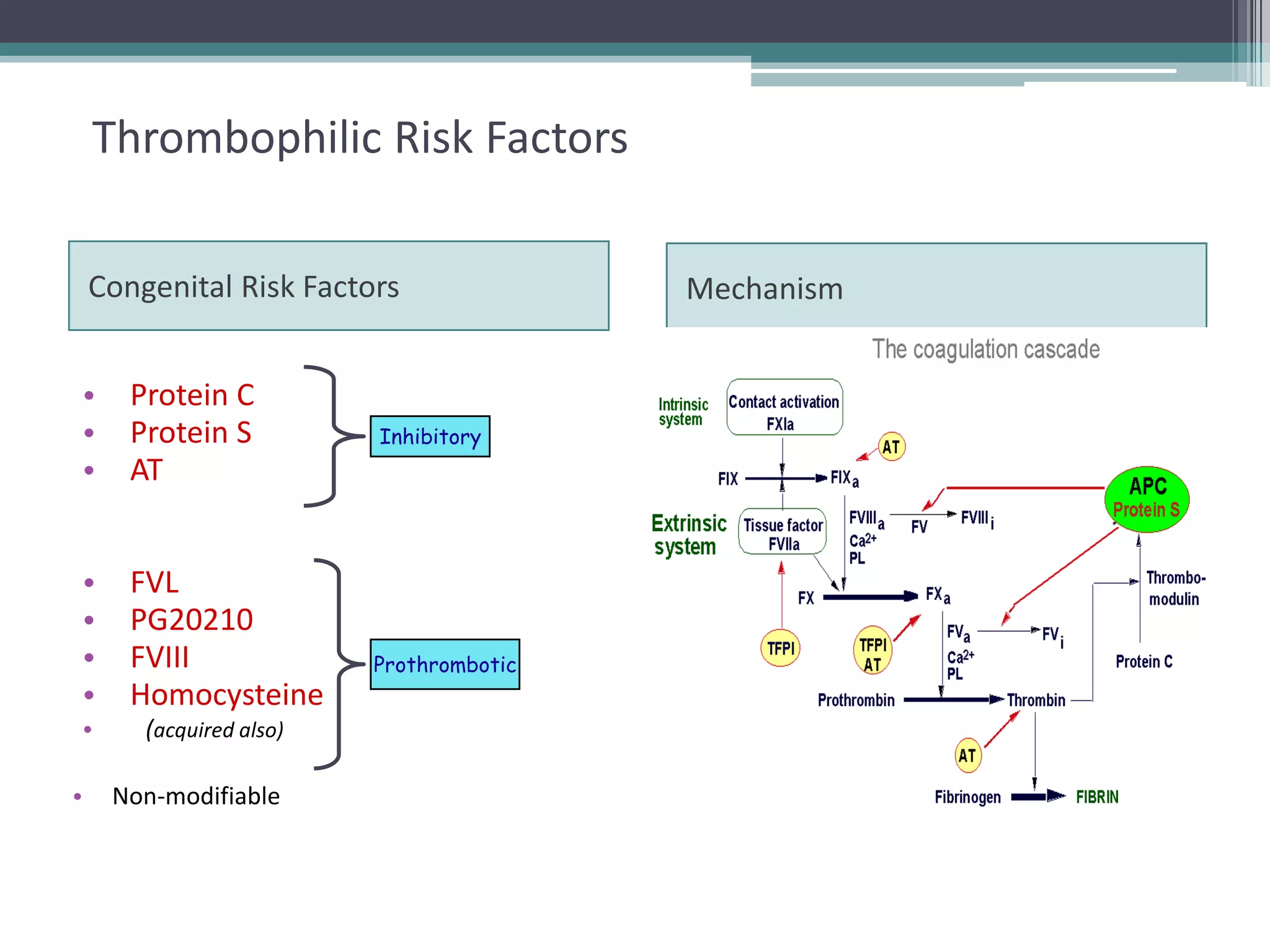
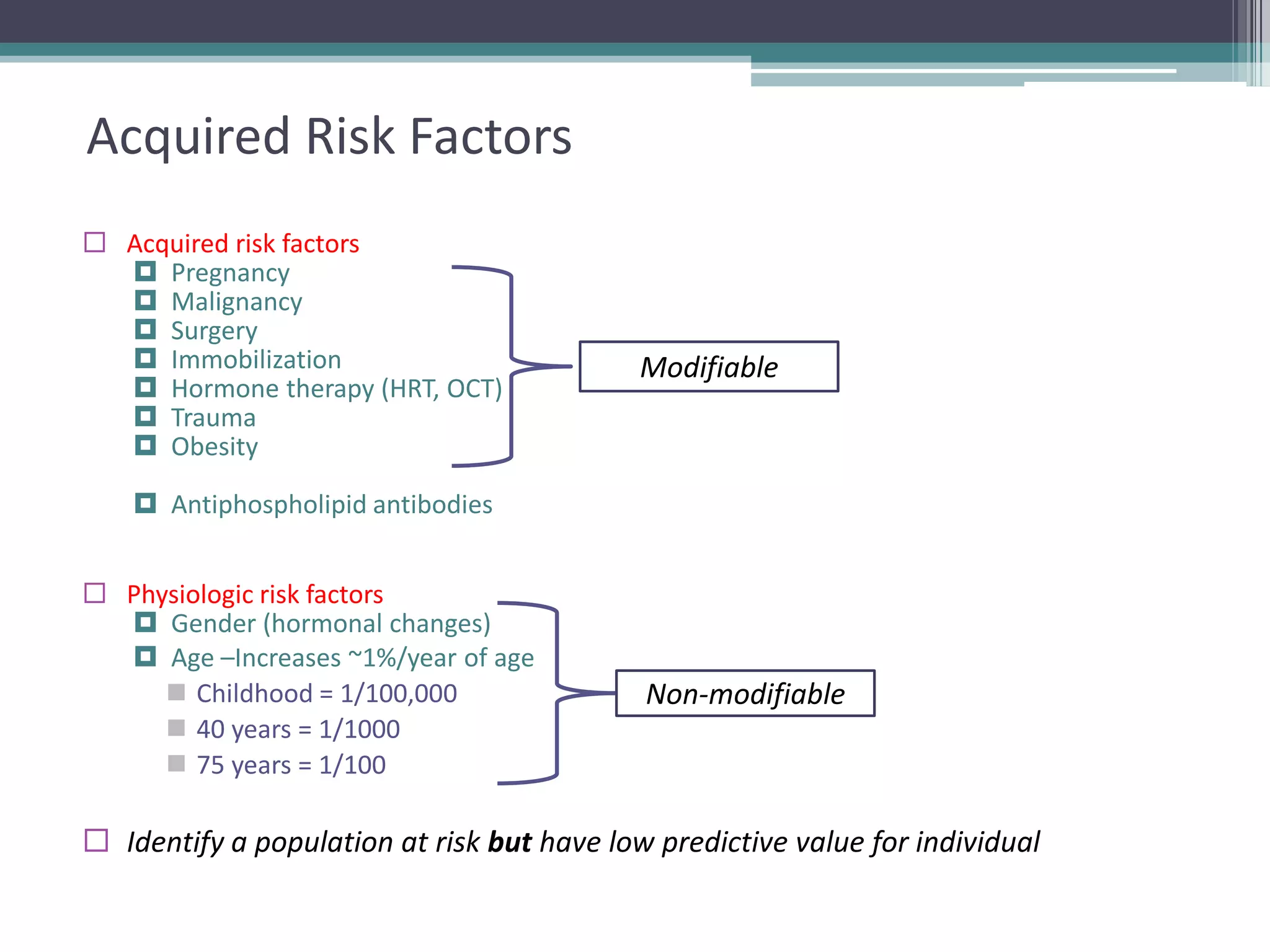
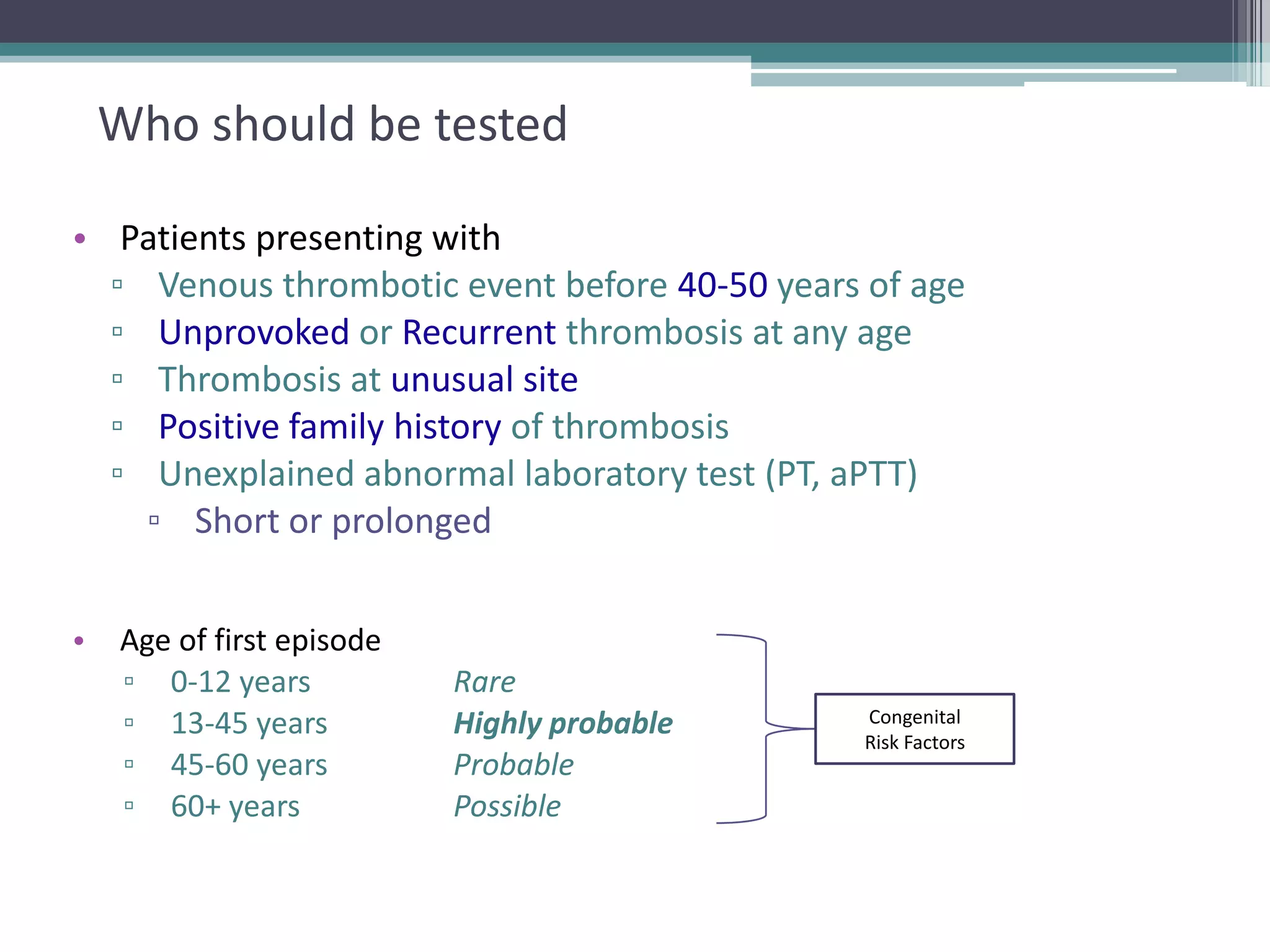
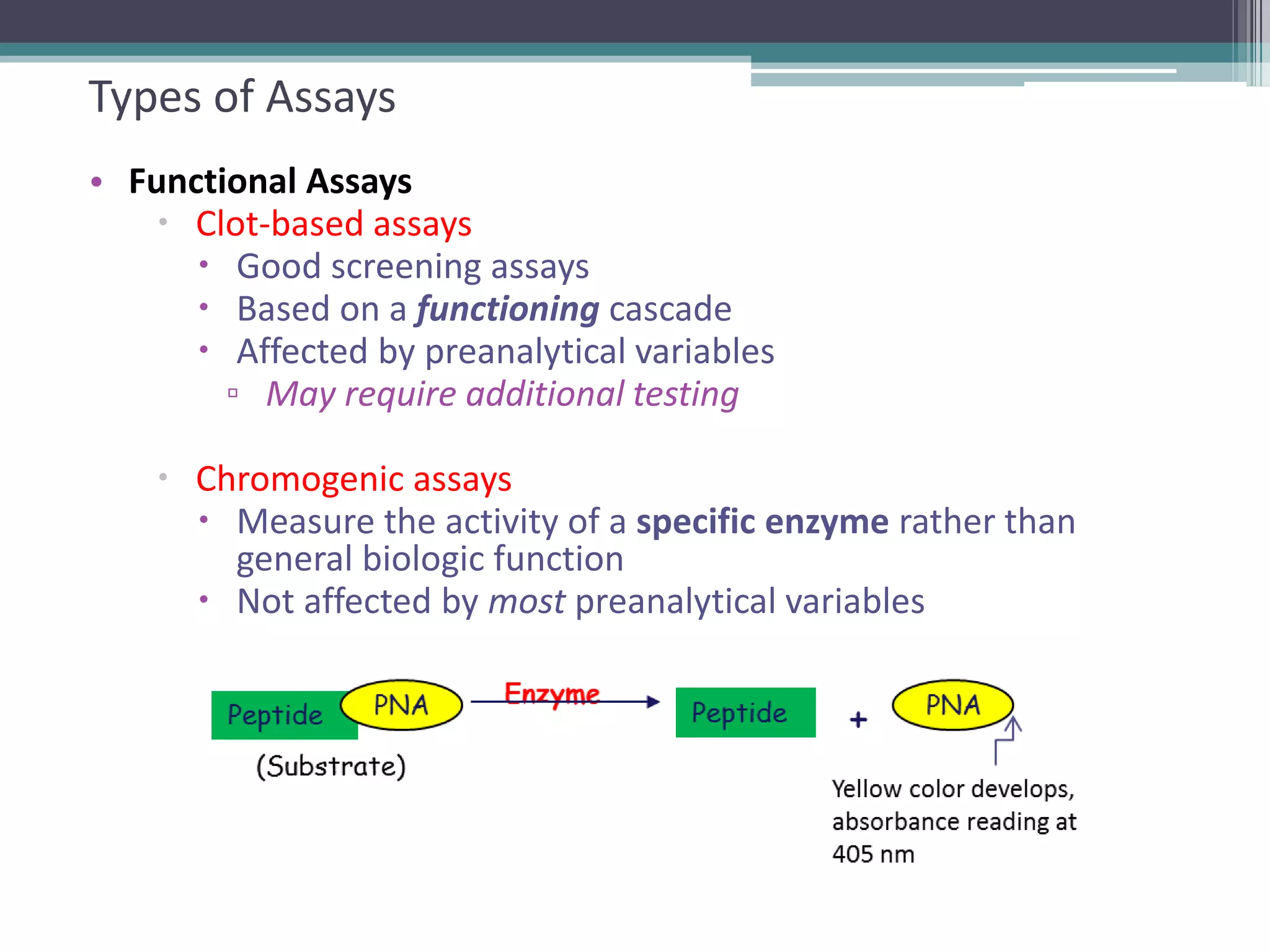
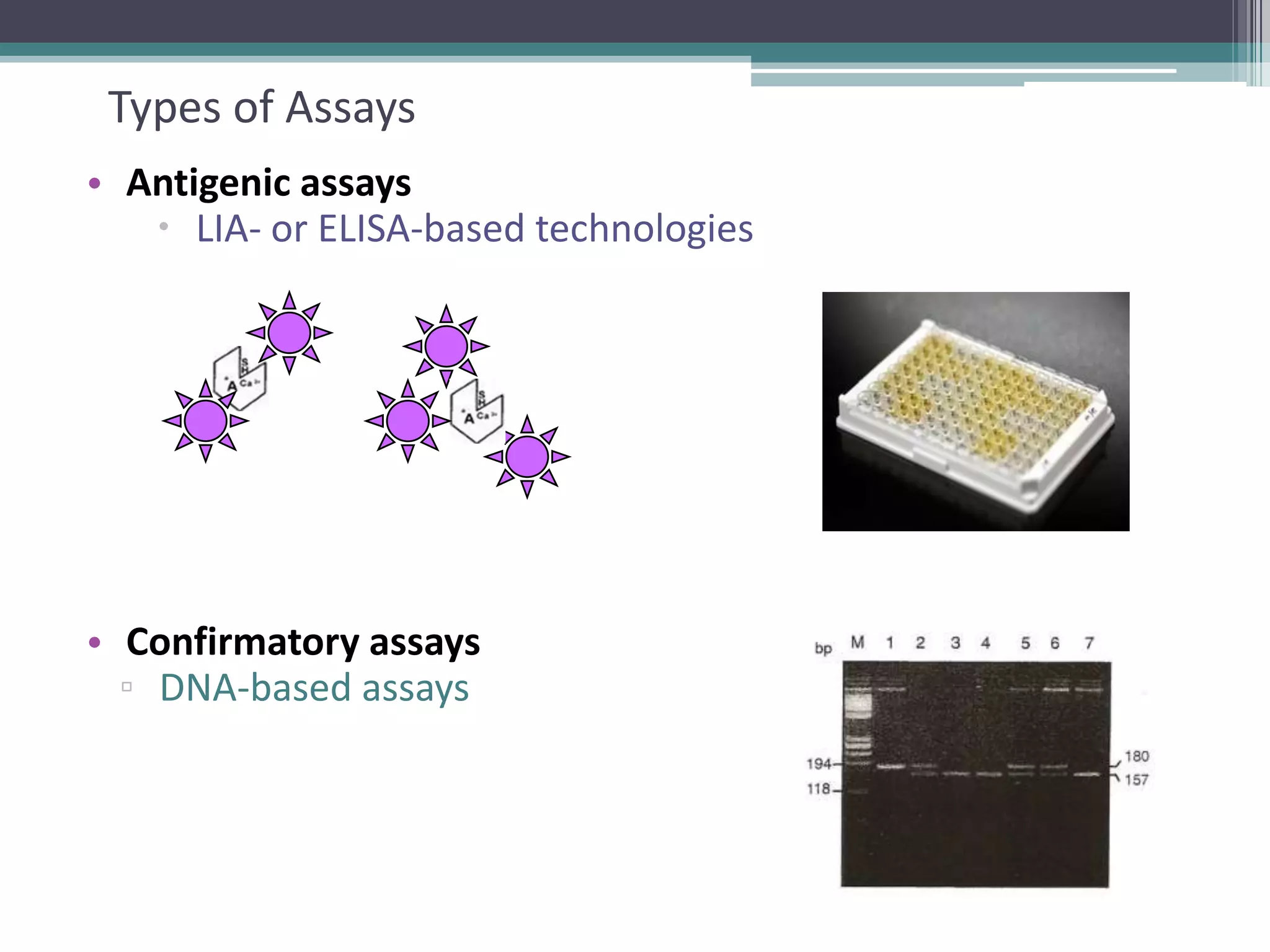
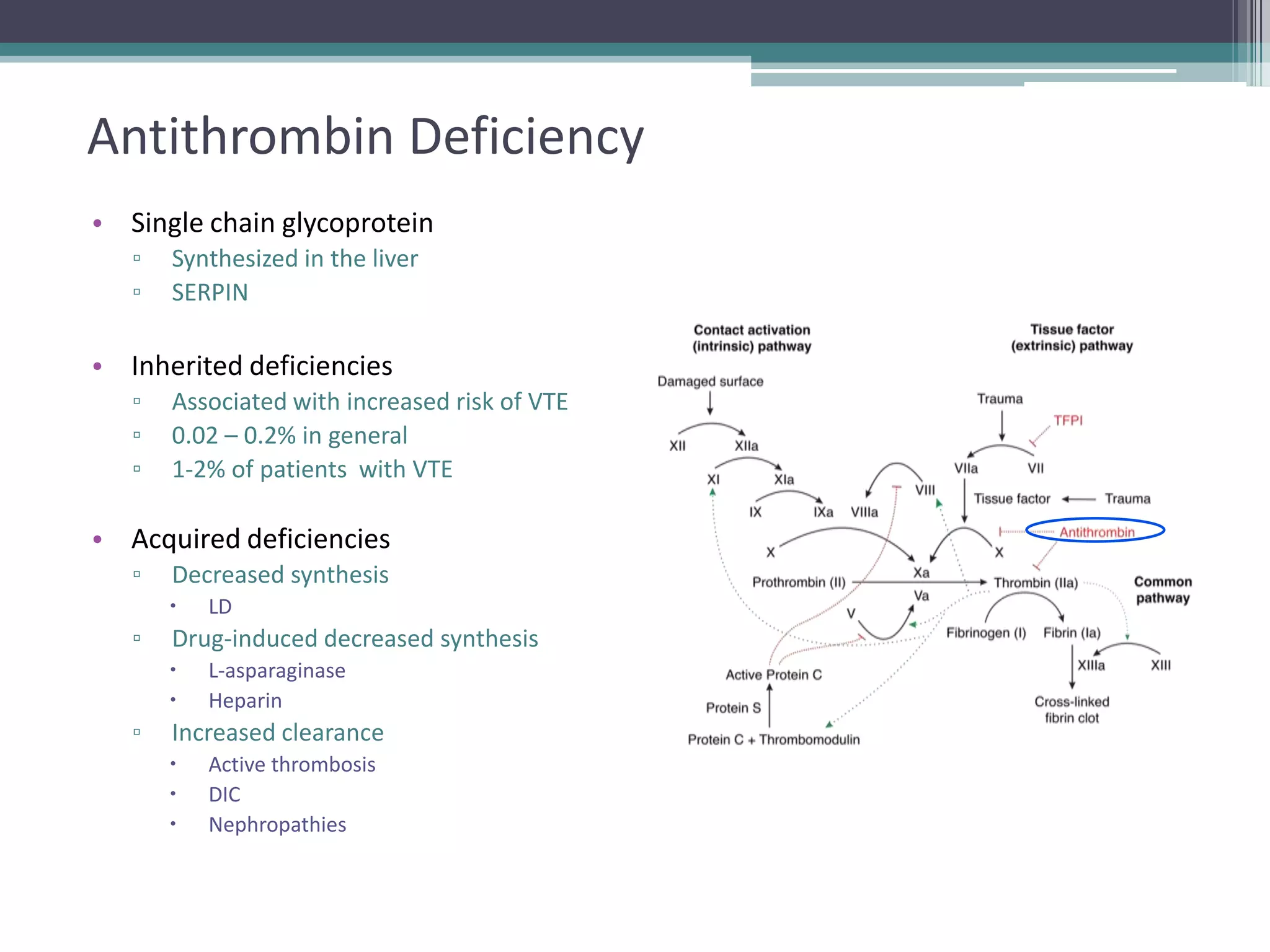
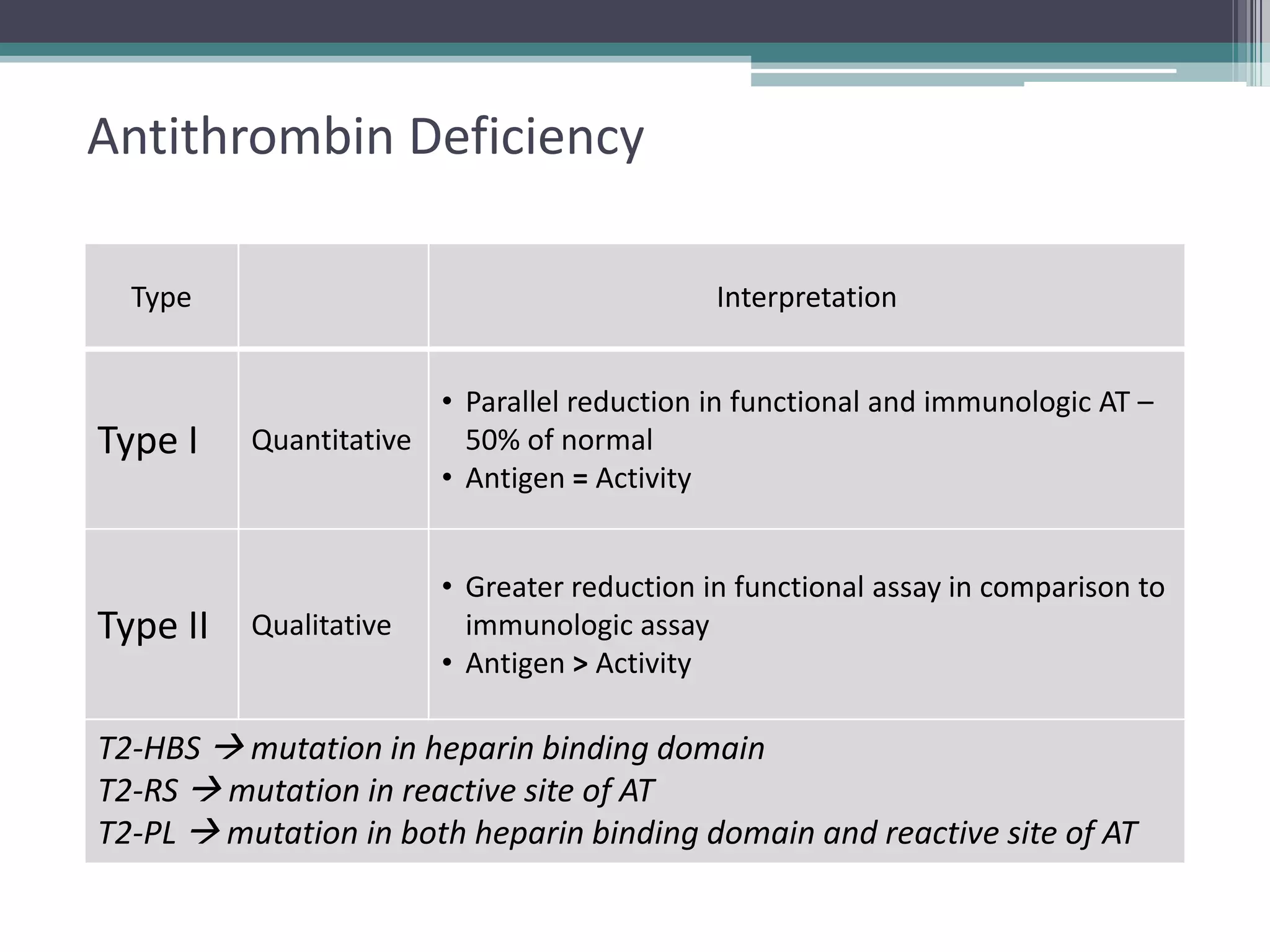
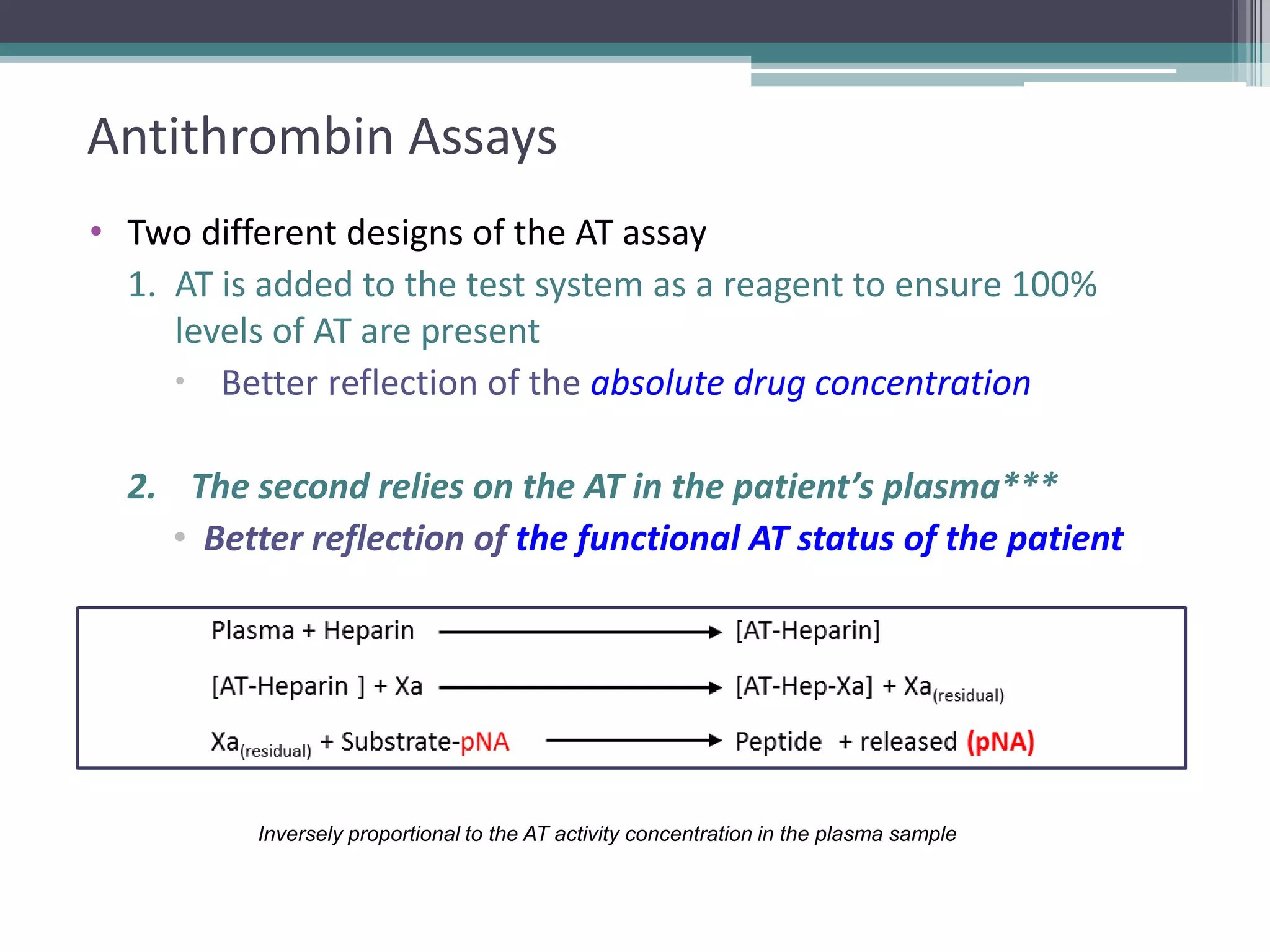
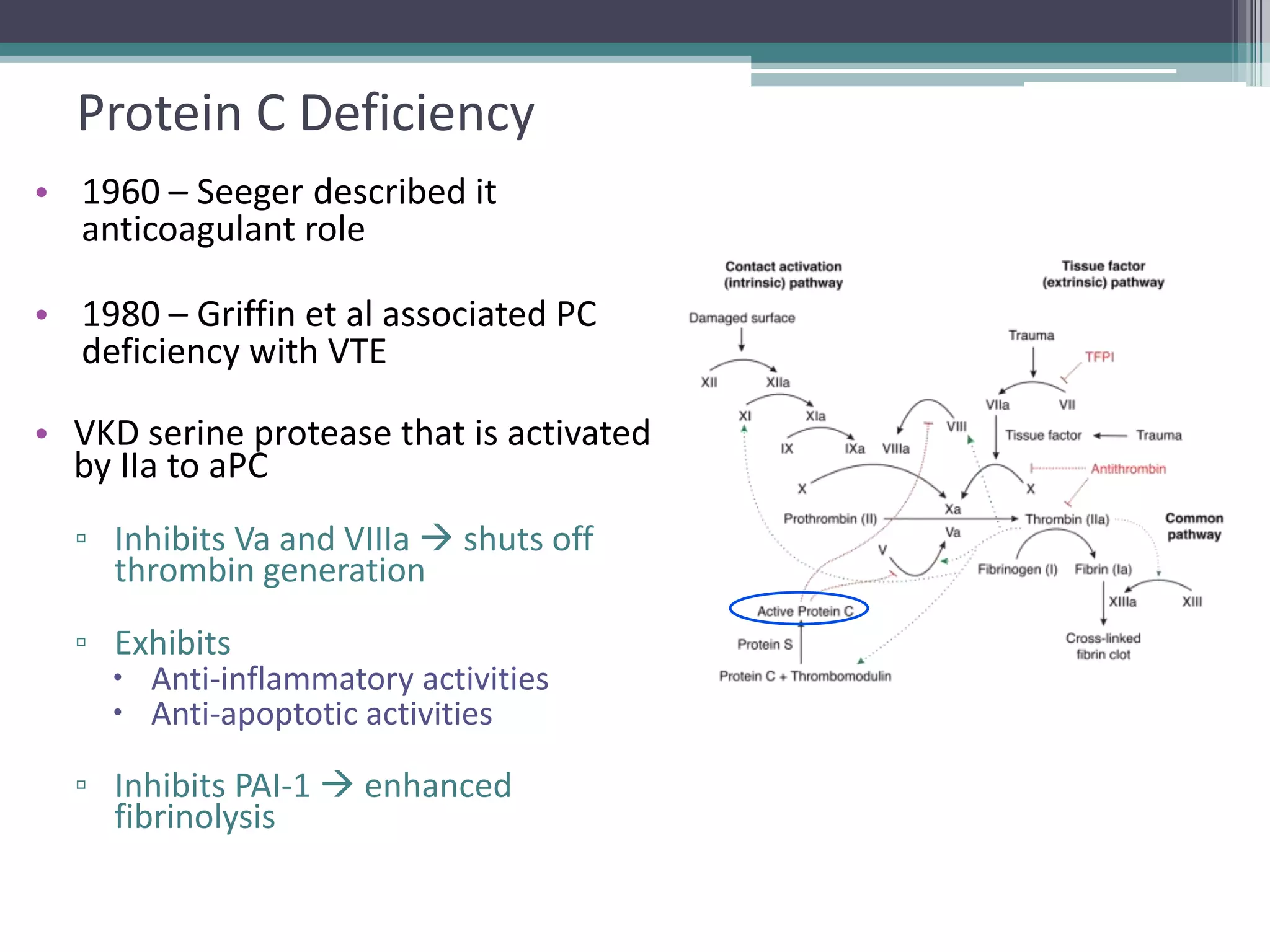
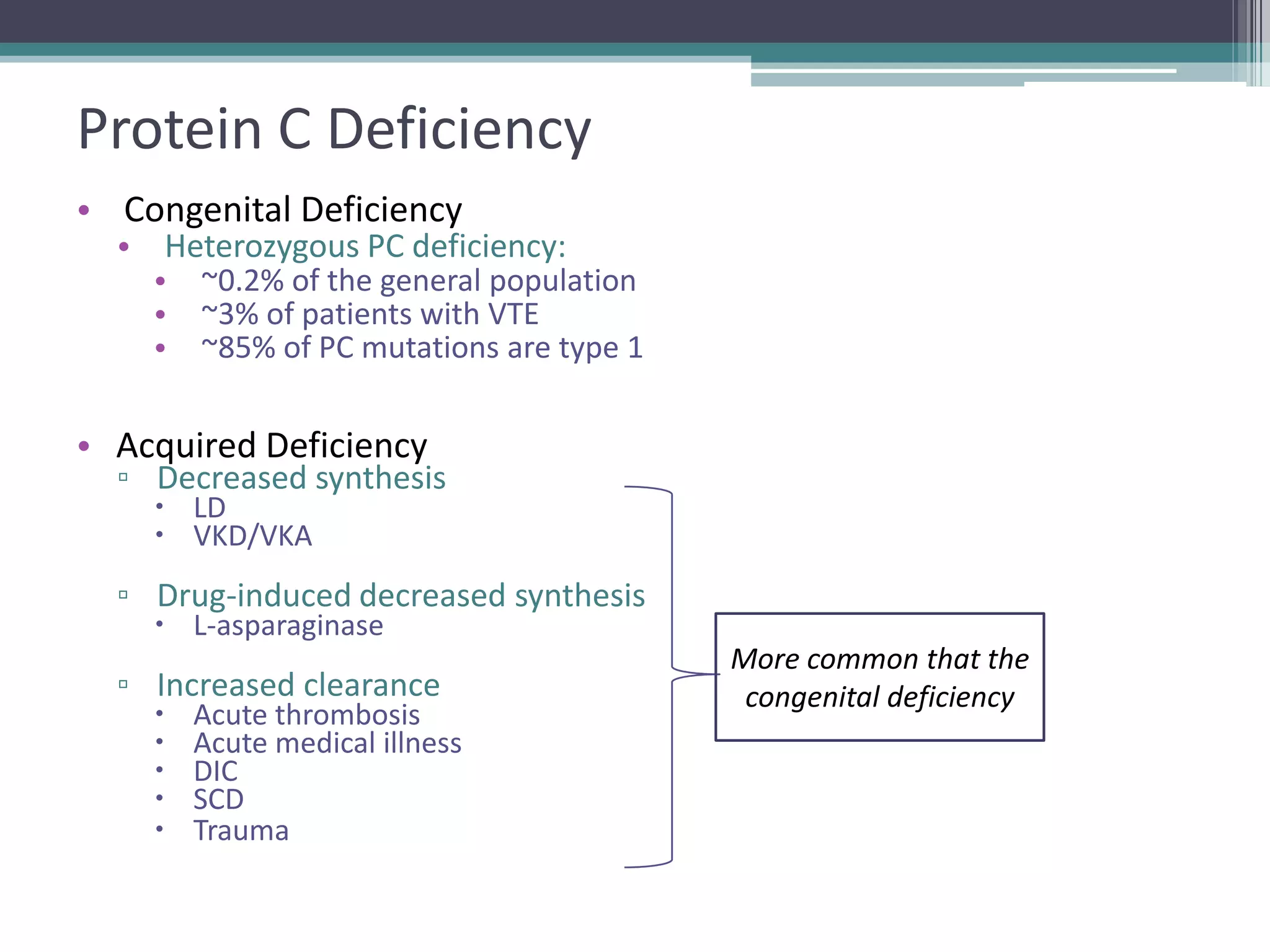
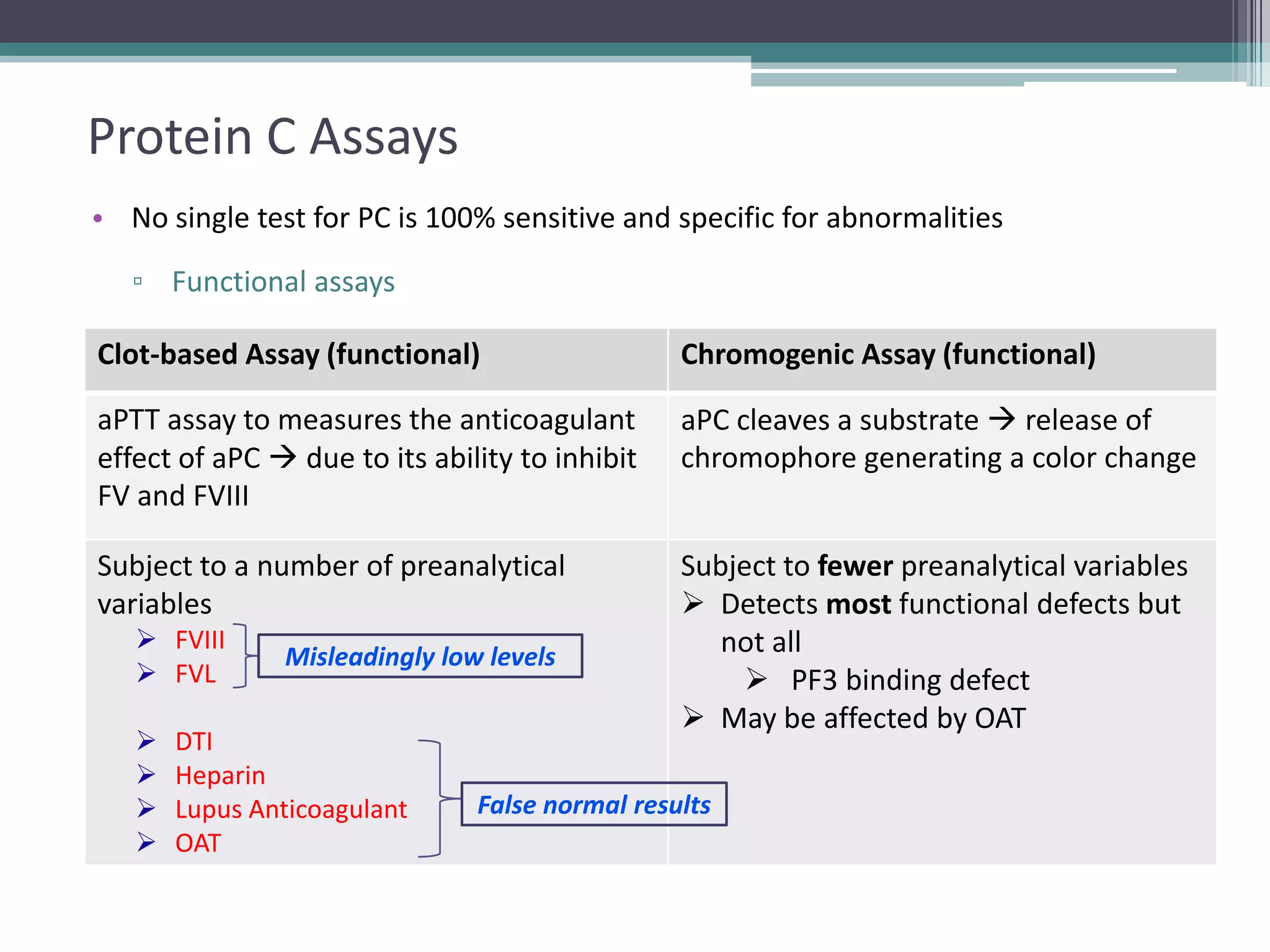
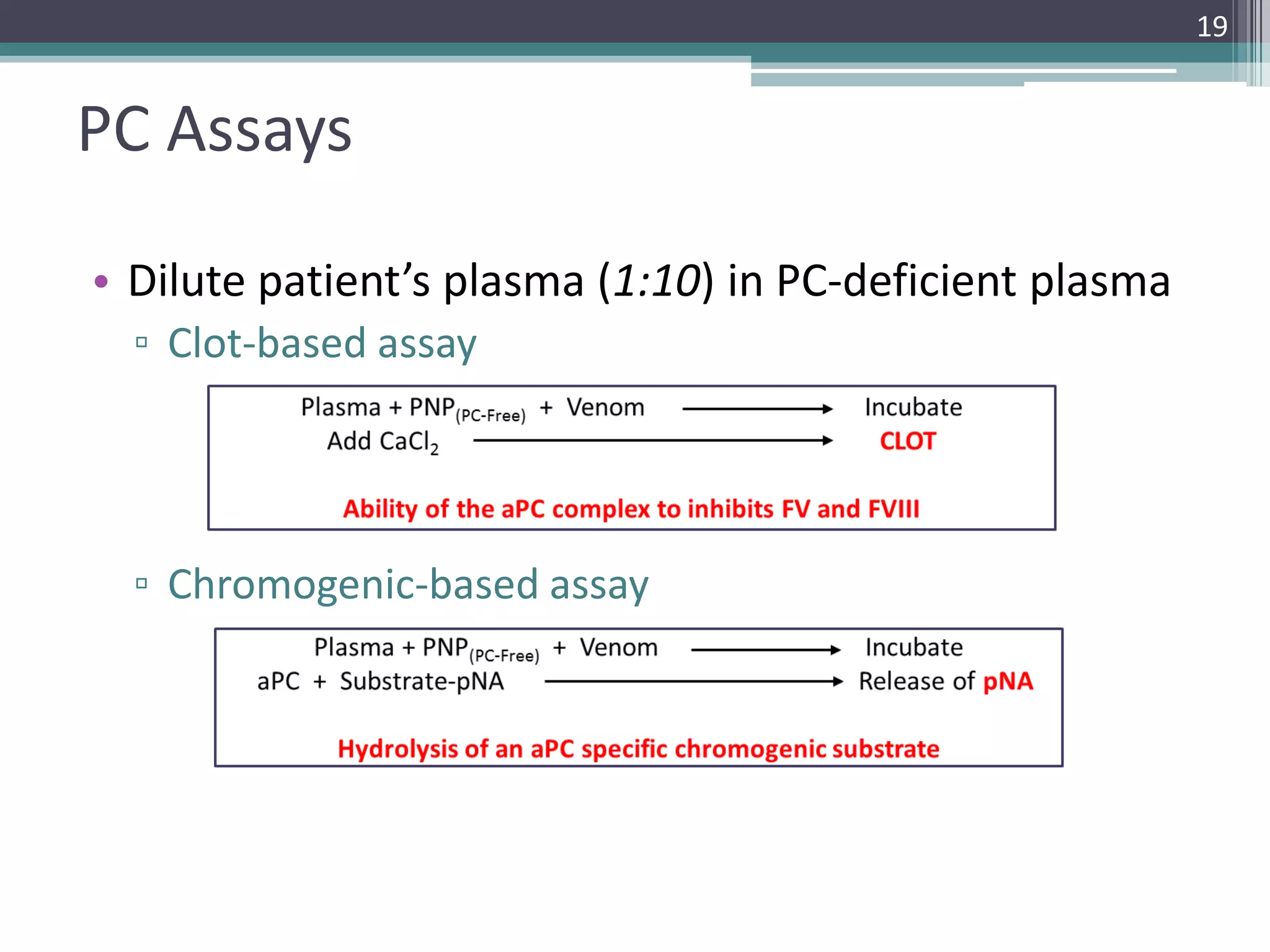
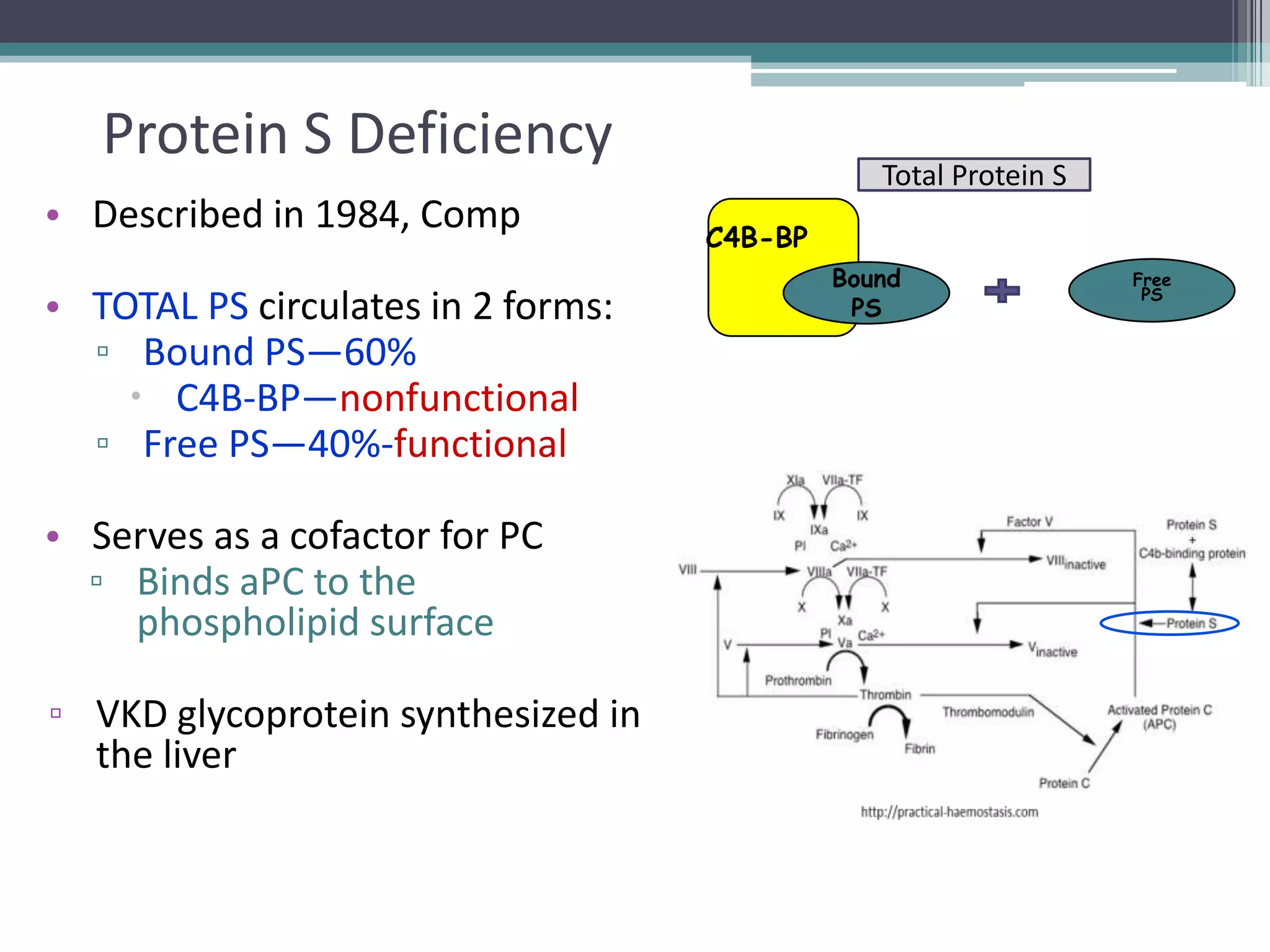
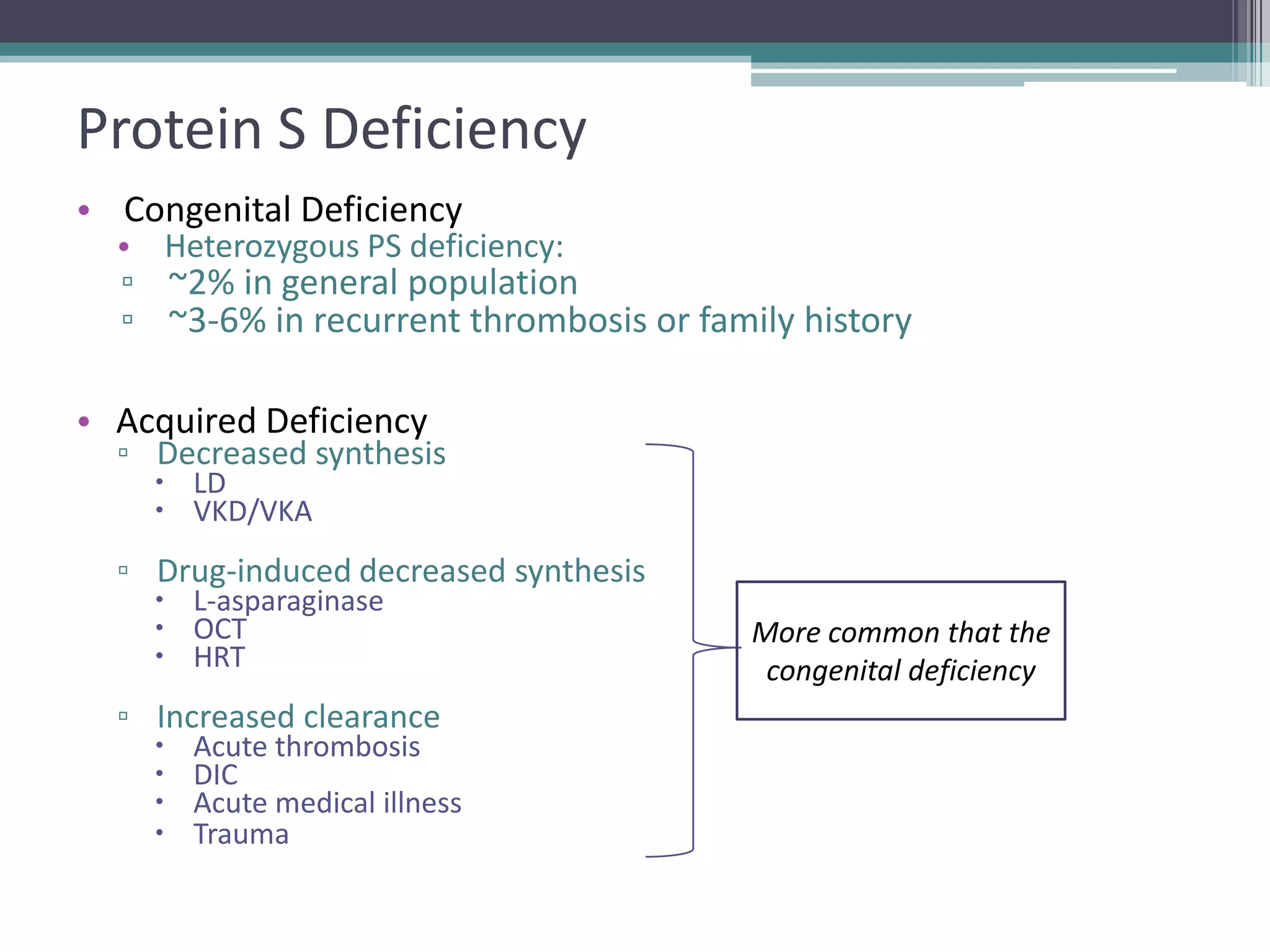
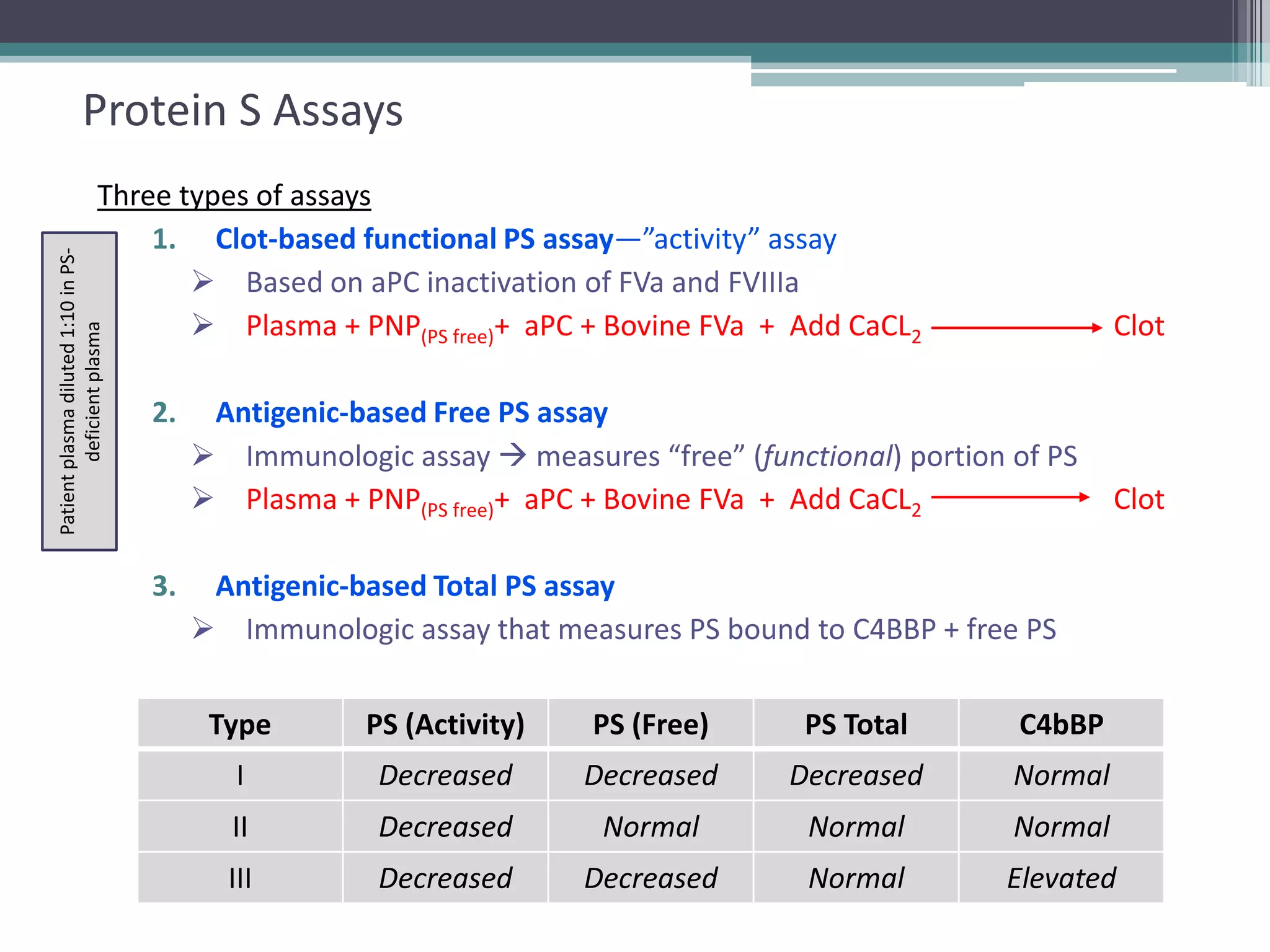
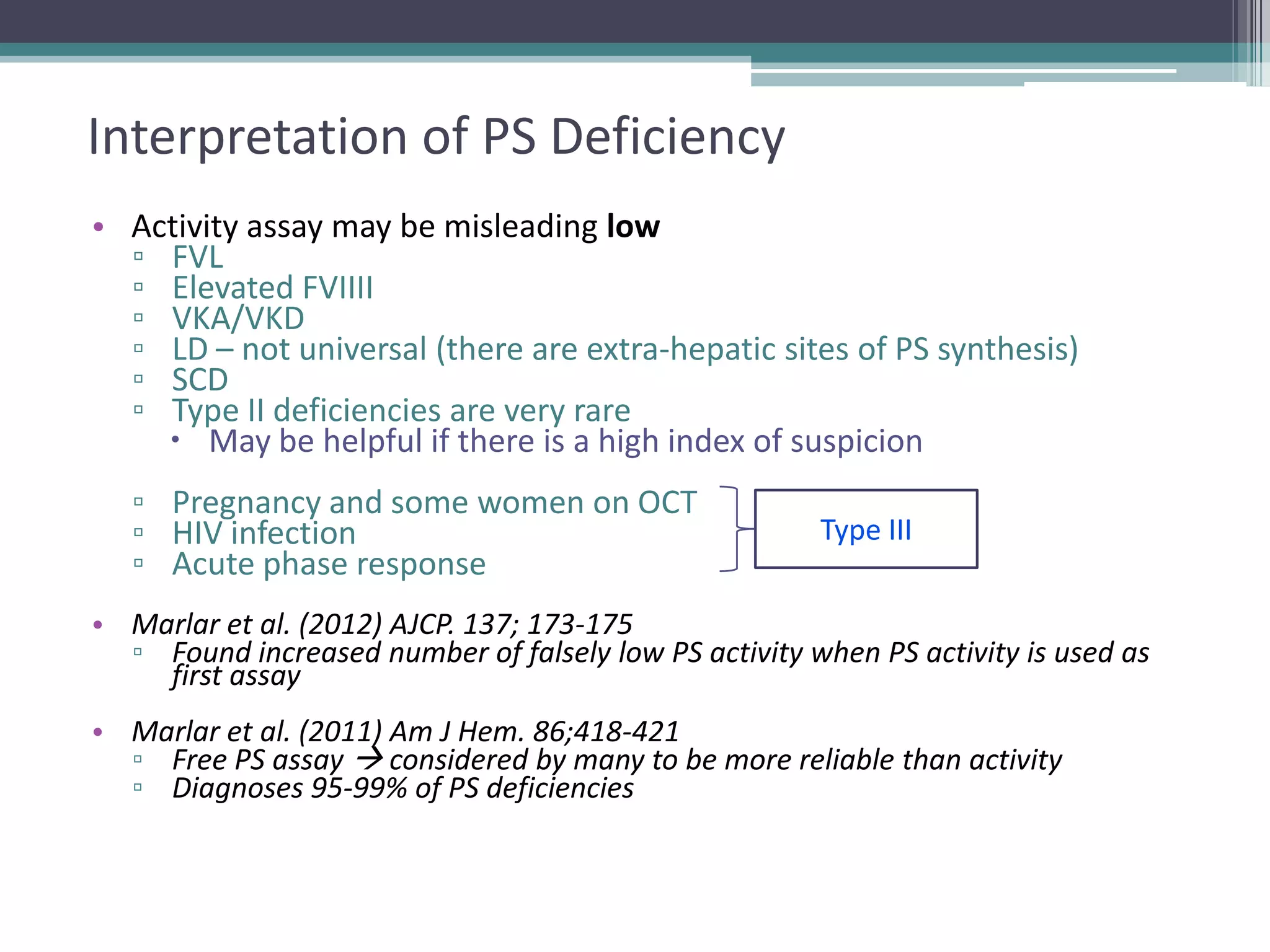
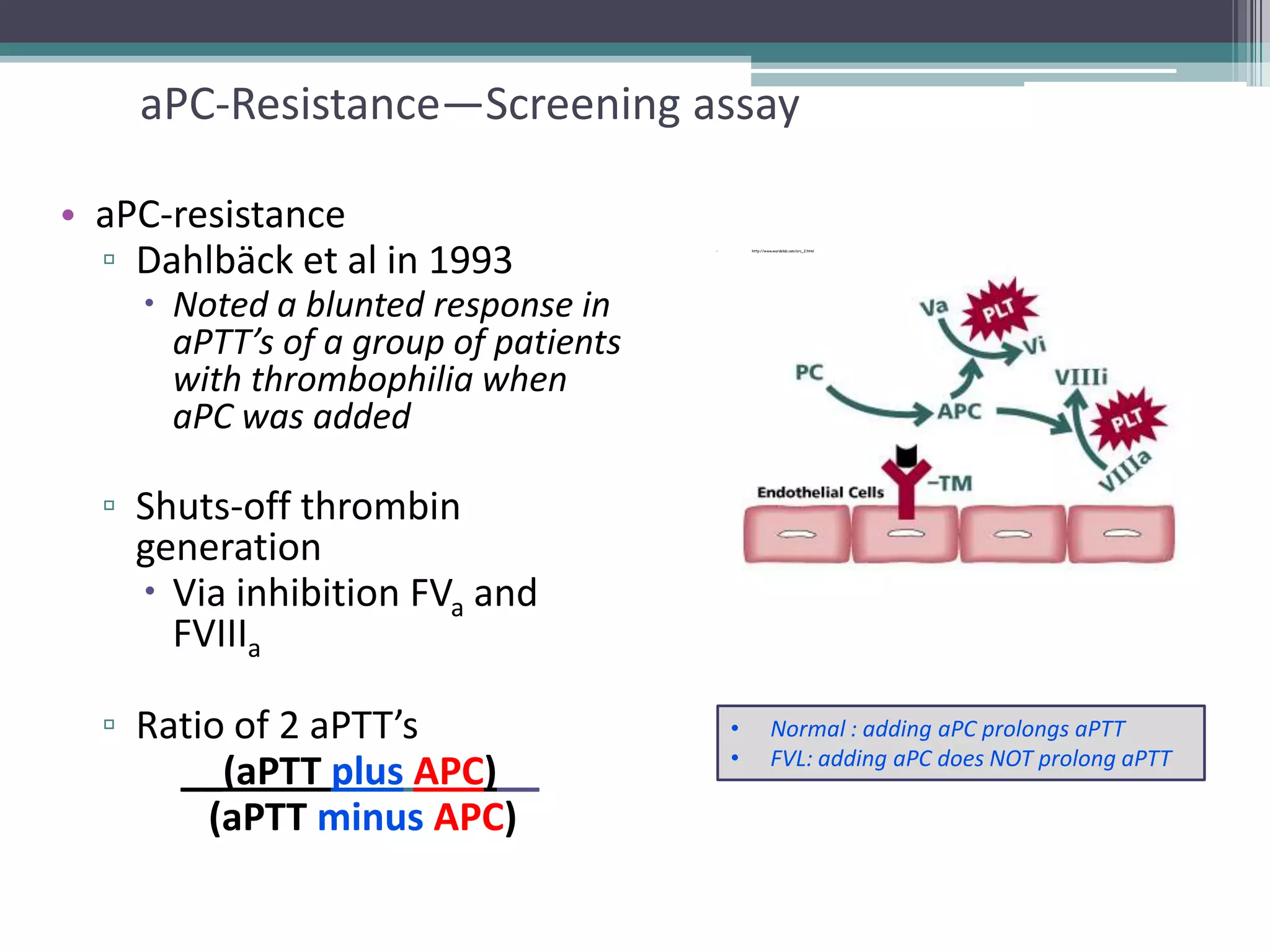
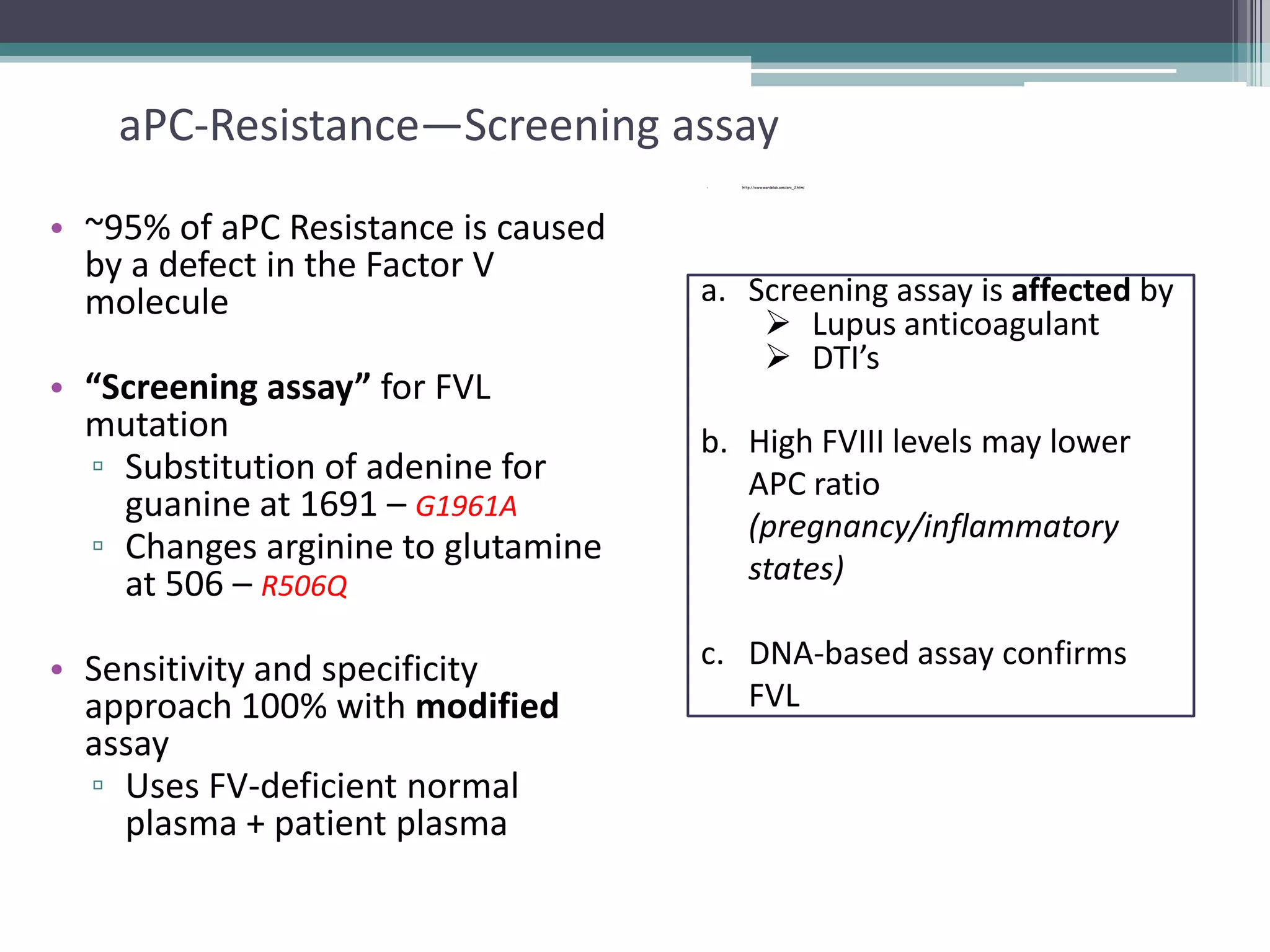
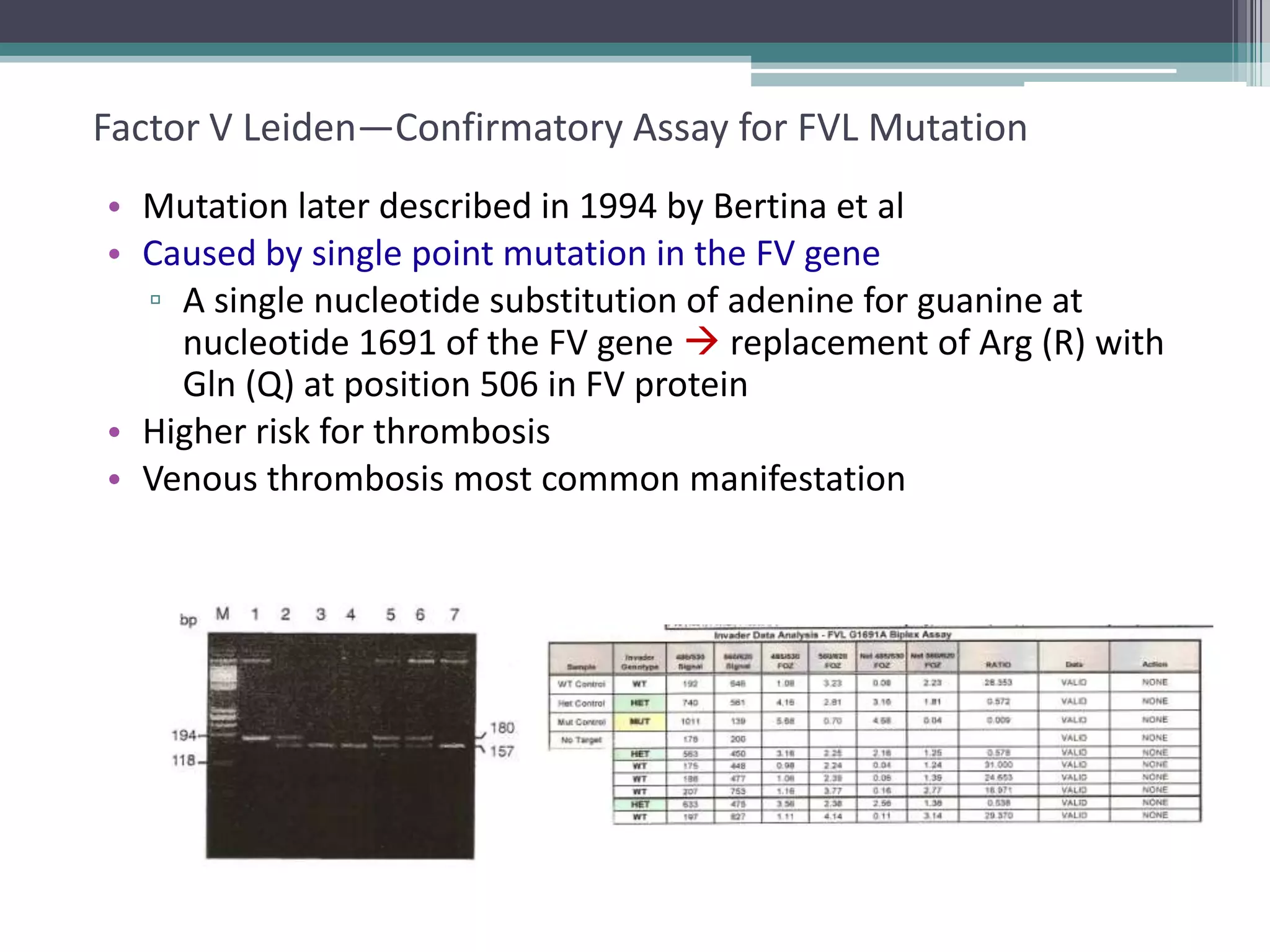
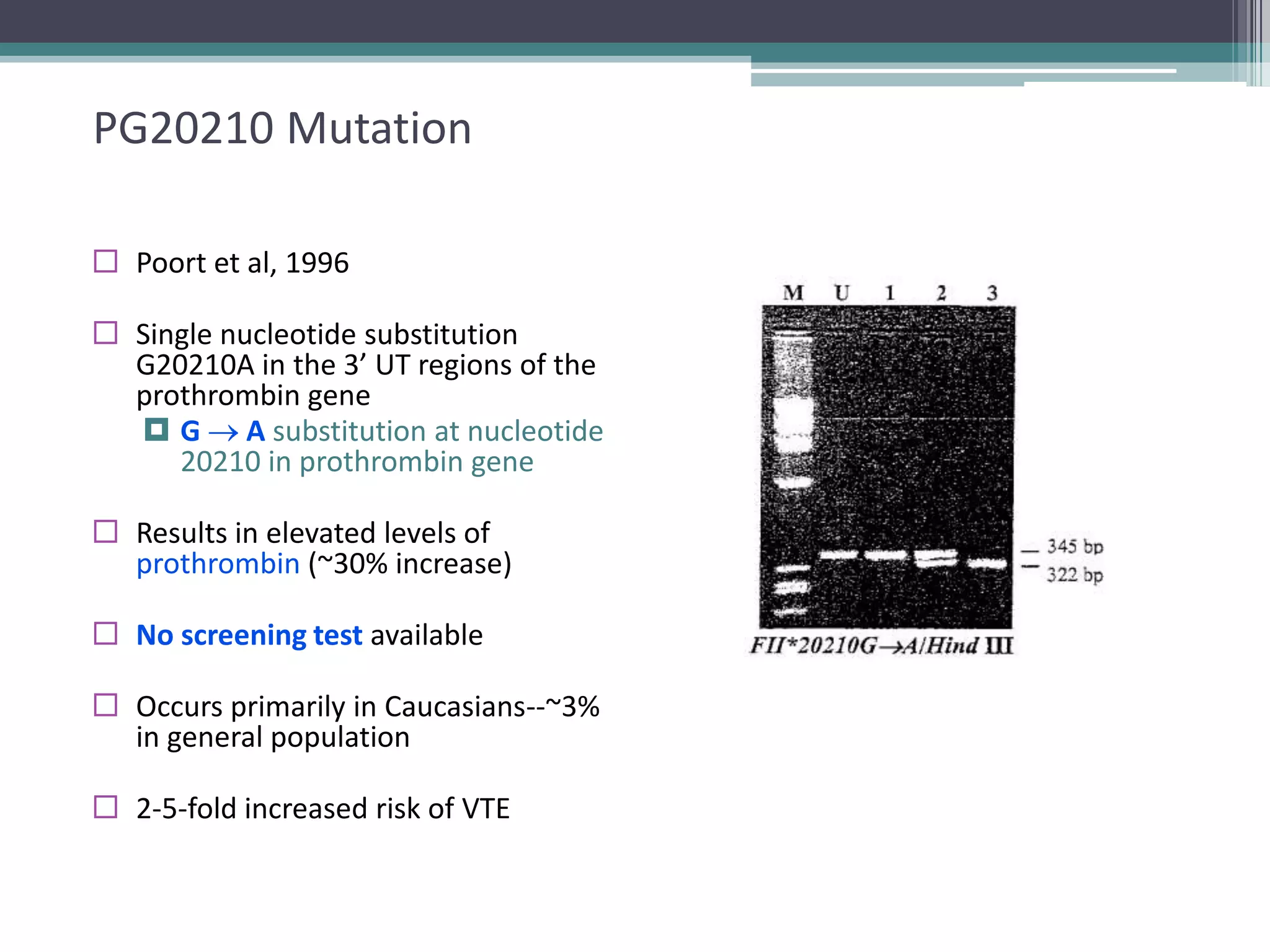
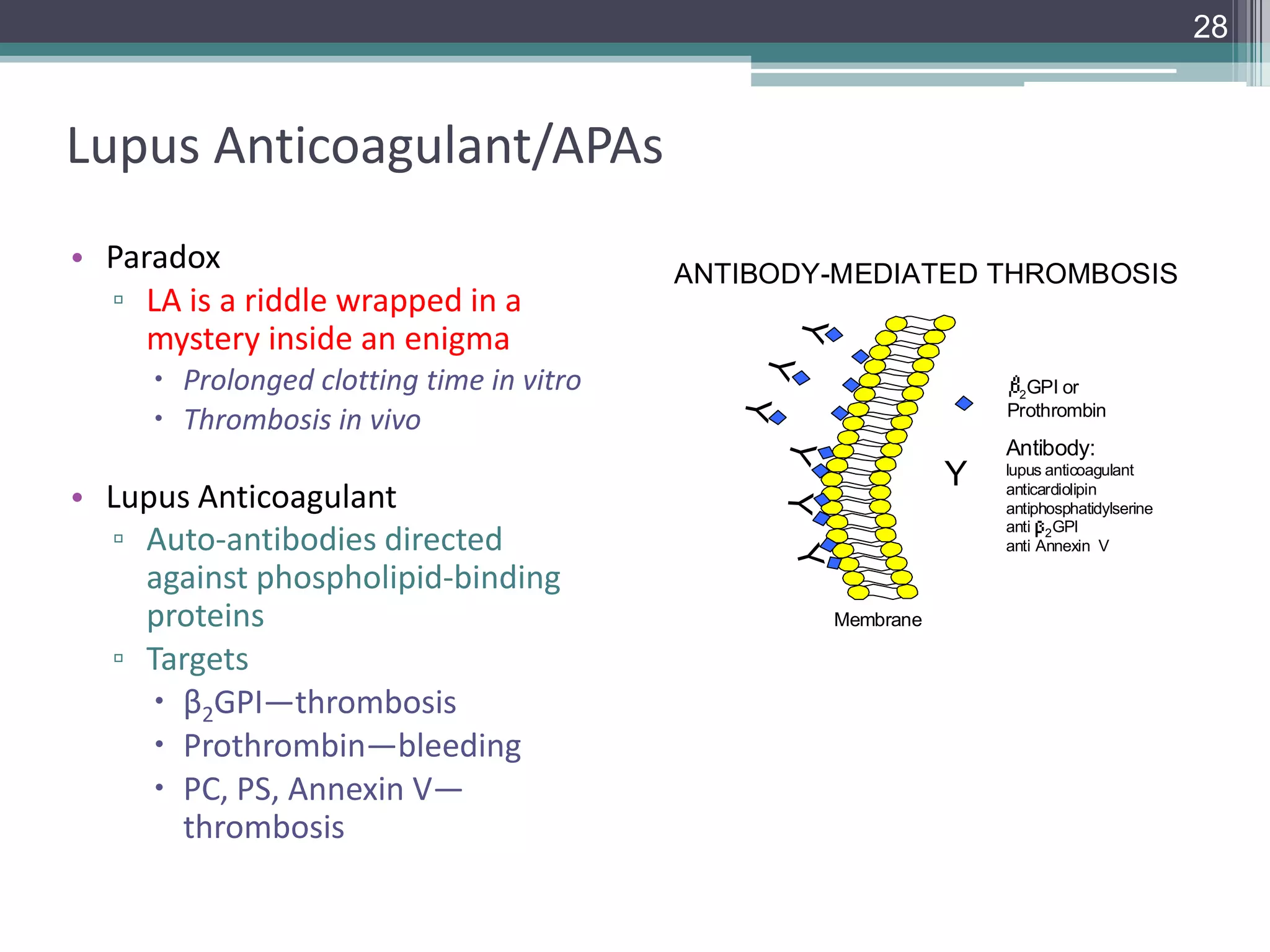
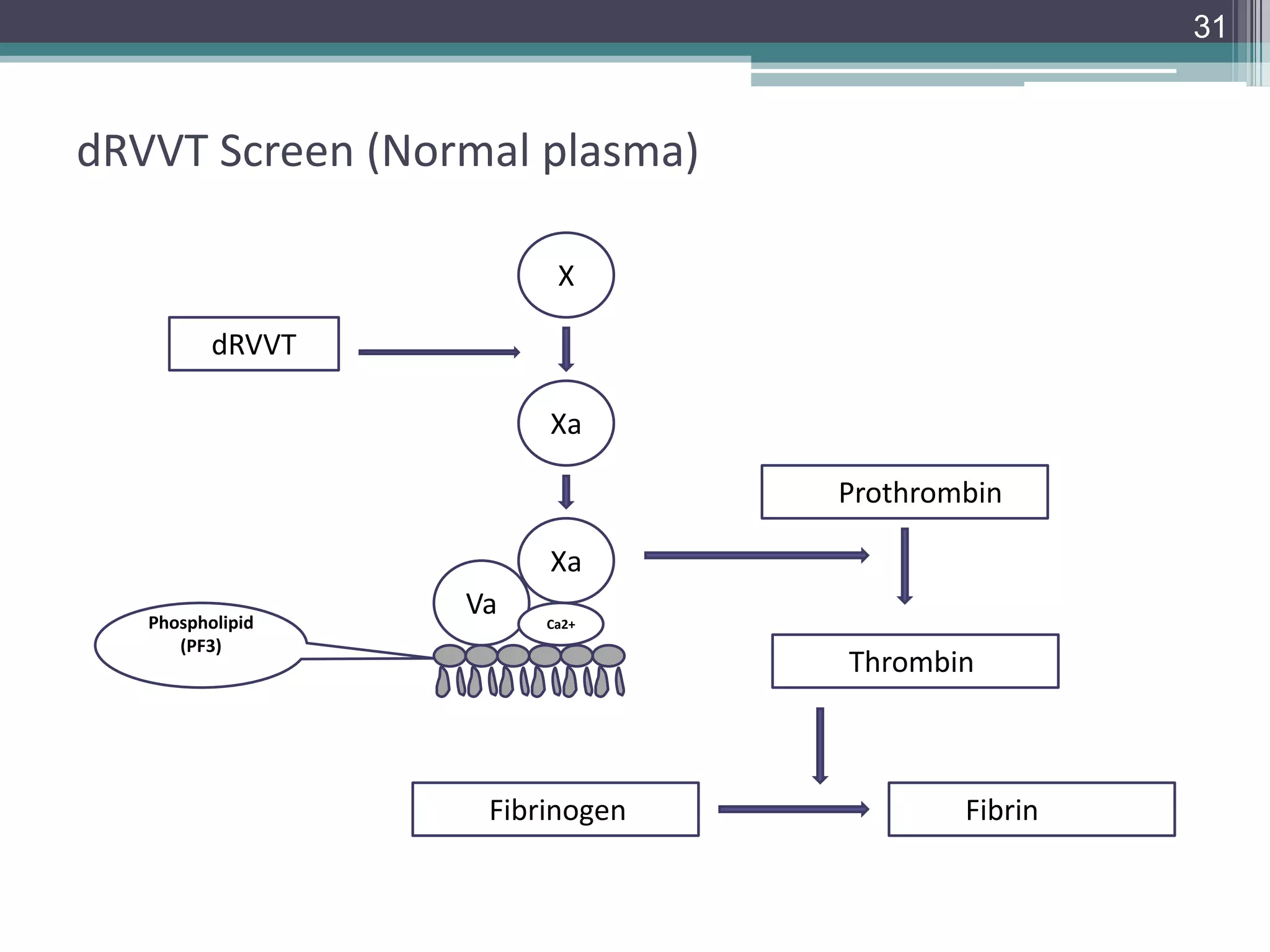
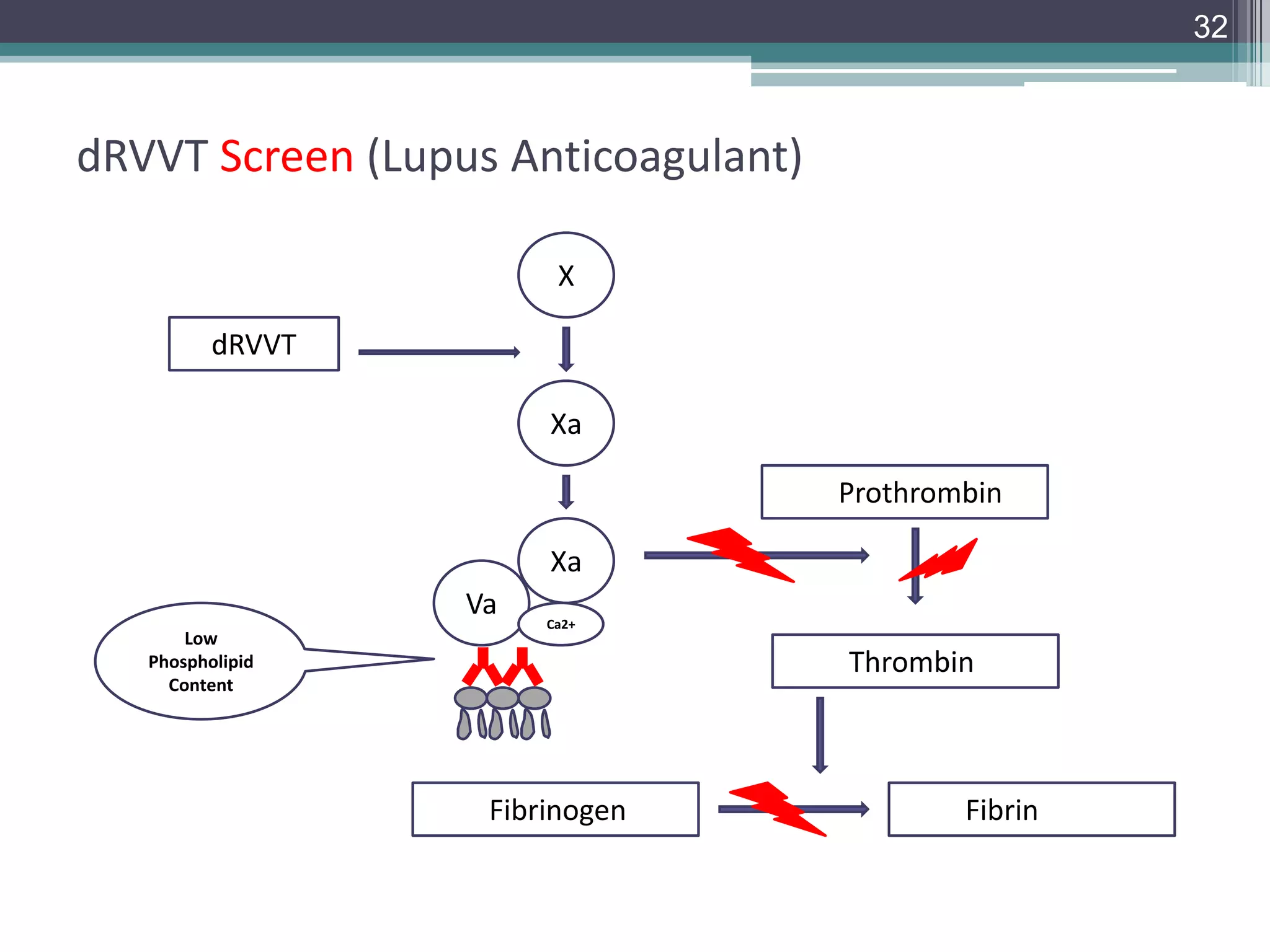
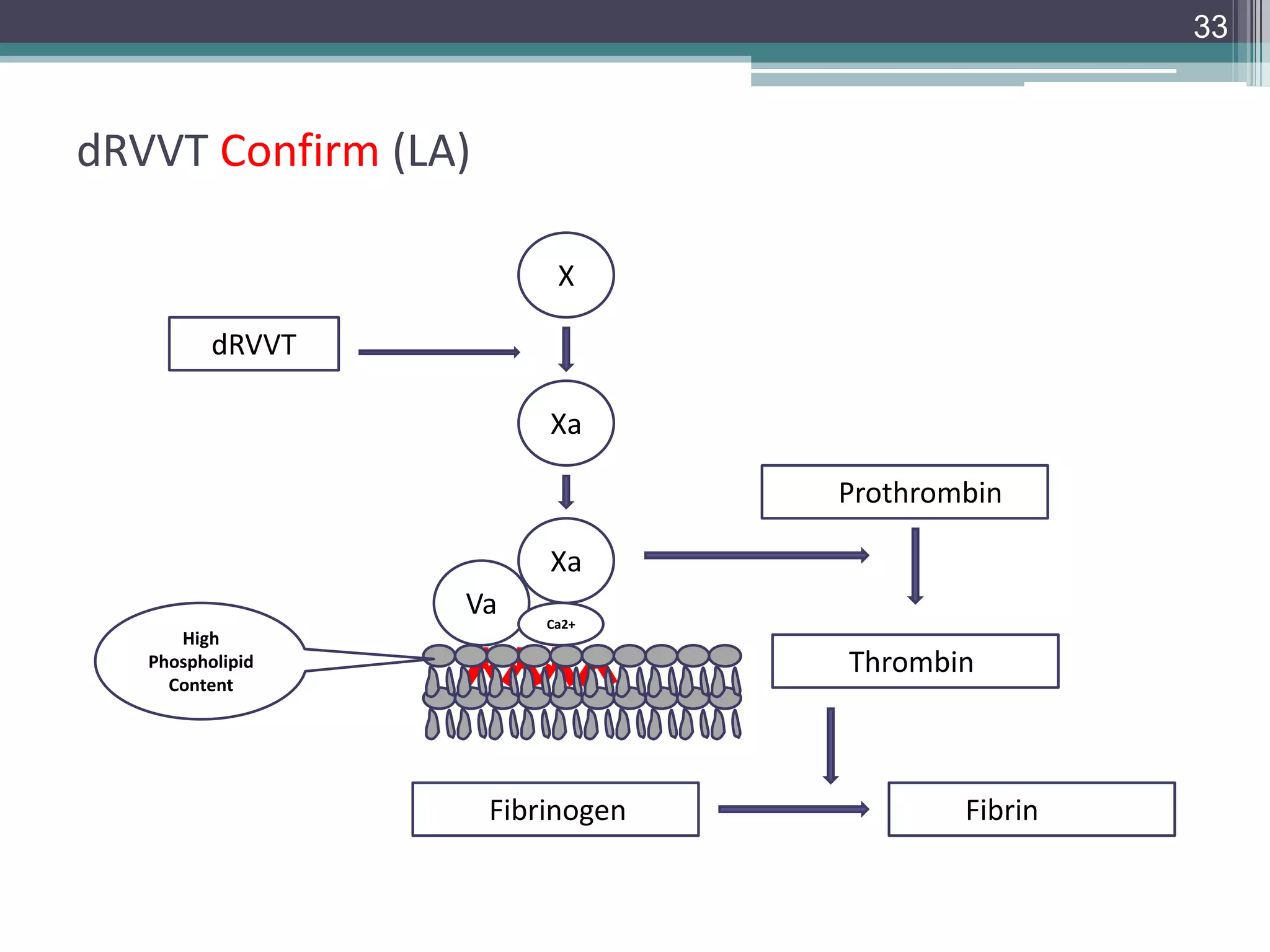
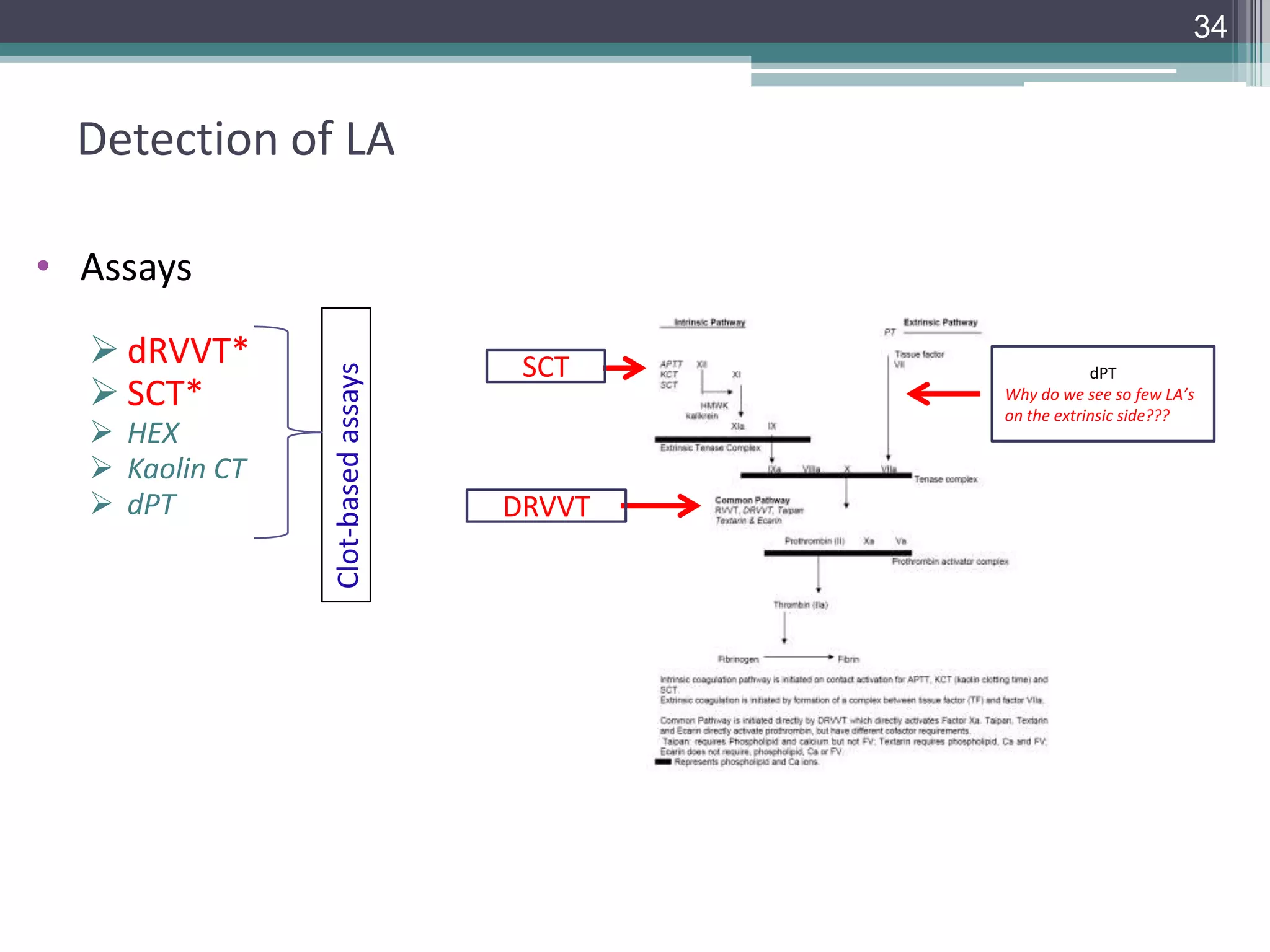
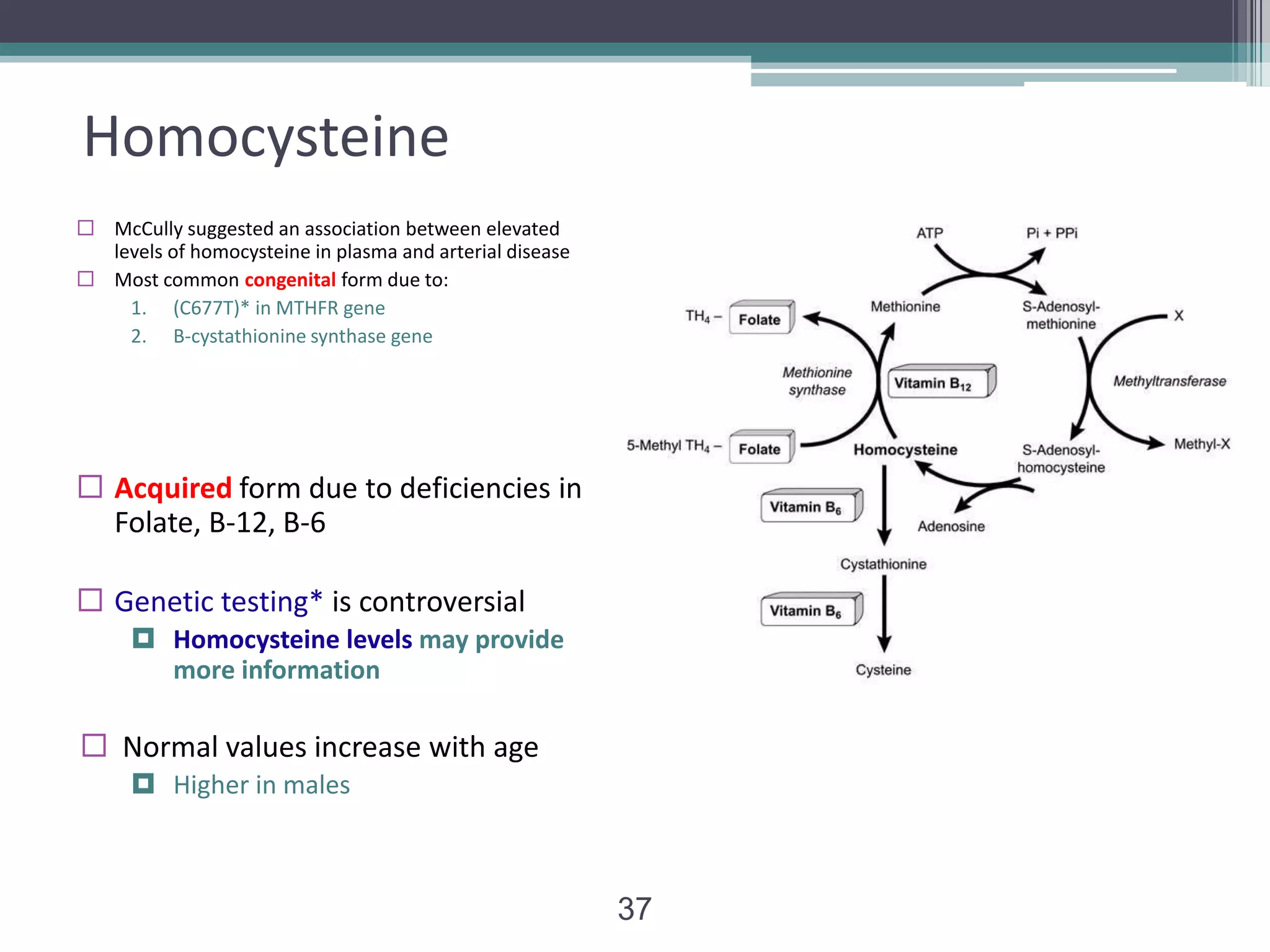
This document discusses thrombophilia testing and risk factors for thrombosis. It describes Virchow's triad of factors that can lead to thrombosis, including changes in blood flow, endothelial injury, and hypercoagulability. Both congenital and acquired risk factors are discussed, including deficiencies in natural anticoagulants like protein C, protein S, and antithrombin. Assays used to test for these deficiencies, like functional, antigenic, and DNA-based assays, are outlined. The roles of the laboratory and physician in thrombophilia testing are also summarized.