Embed presentation
Downloaded 135 times



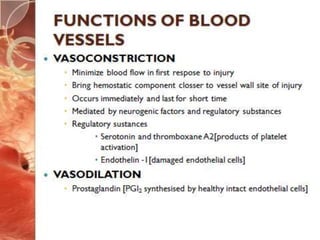
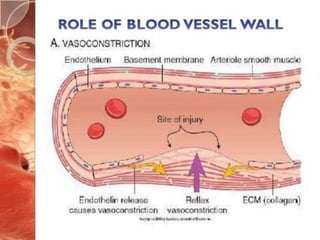






![PLATELET ROLE IN HEMOSTASIS
Perform surveillance of blood vessel continuity
Platelet-platelet interactions[primary hemostatic plug]
Platelet – coagulation protein interactions[secondary
hemostatic plug]
Aid in healing injured tissue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primaryhemostasis-180530043622/85/Primary-hemostasis-22-320.jpg)
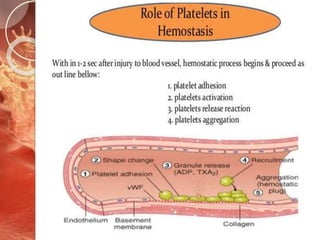


![Platelet aggregation
Newly arriving platelets flowing into the area become
activated by contact with agonists
such as ADP and thromboxane A2[released
by the initial adherent and activated platelets]
Products from the damaged tissue and
endothelial cells.
Thrombin[a procoagulant enzyme generated
by tissue factor /F-VIIa]
Mediated by fibrinogen which forms bridge between
platelets via Gp IIb Gp IIIa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primaryhemostasis-180530043622/85/Primary-hemostasis-30-320.jpg)
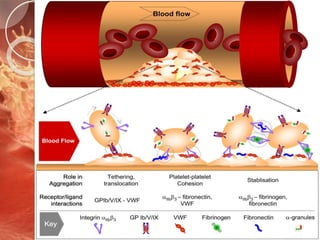
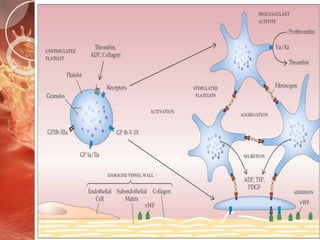





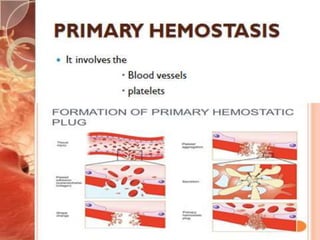
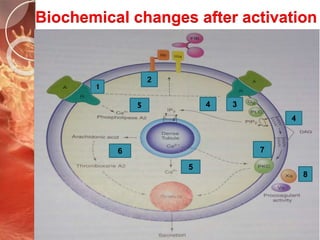
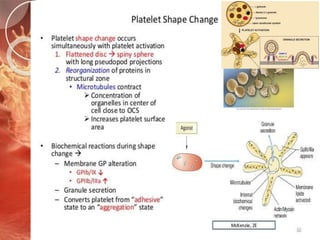
The document outlines the role of platelets in hemostasis, emphasizing their structure and functions, including adhesion, activation, and aggregation. Key processes involve the interaction of platelets with collagen, von Willebrand factor, and various agonists, which lead to the formation of a hemostatic plug. It highlights the biochemical changes during platelet activation and the formation of bridges between platelets mediated by fibrinogen.





















![PLATELET ROLE IN HEMOSTASIS
Perform surveillance of blood vessel continuity
Platelet-platelet interactions[primary hemostatic plug]
Platelet – coagulation protein interactions[secondary
hemostatic plug]
Aid in healing injured tissue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primaryhemostasis-180530043622/85/Primary-hemostasis-22-320.jpg)







![Platelet aggregation
Newly arriving platelets flowing into the area become
activated by contact with agonists
such as ADP and thromboxane A2[released
by the initial adherent and activated platelets]
Products from the damaged tissue and
endothelial cells.
Thrombin[a procoagulant enzyme generated
by tissue factor /F-VIIa]
Mediated by fibrinogen which forms bridge between
platelets via Gp IIb Gp IIIa](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primaryhemostasis-180530043622/85/Primary-hemostasis-30-320.jpg)





